Marek Wadinger
Deep Dictionary-Free Method for Identifying Linear Model of Nonlinear System with Input Delay
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Nonlinear dynamical systems with input delays pose significant challenges for prediction, estimation, and control due to their inherent complexity and the impact of delays on system behavior. Traditional linear control techniques often fail in these contexts, necessitating innovative approaches. This paper introduces a novel approach to approximate the Koopman operator using an LSTM-enhanced Deep Koopman model, enabling linear representations of nonlinear systems with time delays. By incorporating Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) layers, the proposed framework captures historical dependencies and efficiently encodes time-delayed system dynamics into a latent space. Unlike traditional extended Dynamic Mode Decomposition (eDMD) approaches that rely on predefined dictionaries, the LSTM-enhanced Deep Koopman model is dictionary-free, which mitigates the problems with the underlying dynamics being known and incorporated into the dictionary. Quantitative comparisons with extended eDMD on a simulated system demonstrate highly significant performance gains in prediction accuracy in cases where the true nonlinear dynamics are unknown and achieve comparable results to eDMD with known dynamics of a system.
Change-Point Detection in Industrial Data Streams based on Online Dynamic Mode Decomposition with Control
Jul 08, 2024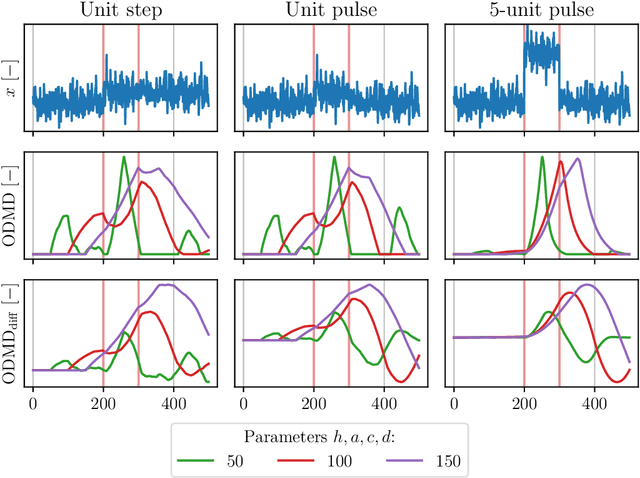
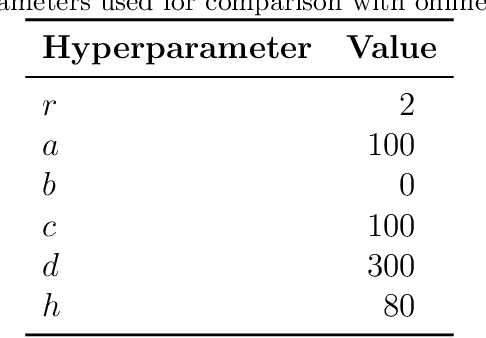
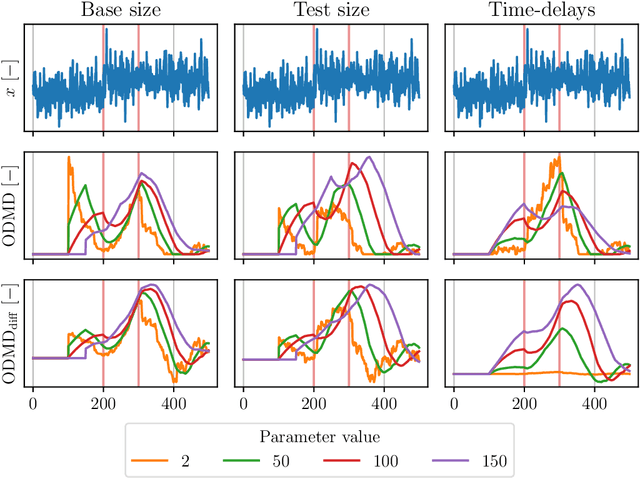
Abstract:We propose a novel change-point detection method based on online Dynamic Mode Decomposition with control (ODMDwC). Leveraging ODMDwC's ability to find and track linear approximation of a non-linear system while incorporating control effects, the proposed method dynamically adapts to its changing behavior due to aging and seasonality. This approach enables the detection of changes in spatial, temporal, and spectral patterns, providing a robust solution that preserves correspondence between the score and the extent of change in the system dynamics. We formulate a truncated version of ODMDwC and utilize higher-order time-delay embeddings to mitigate noise and extract broad-band features. Our method addresses the challenges faced in industrial settings where safety-critical systems generate non-uniform data streams while requiring timely and accurate change-point detection to protect profit and life. Our results demonstrate that this method yields intuitive and improved detection results compared to the Singular-Value-Decomposition-based method. We validate our approach using synthetic and real-world data, showing its competitiveness to other approaches on complex systems' benchmark datasets. Provided guidelines for hyperparameters selection enhance our method's practical applicability.
Adaptable and Interpretable Framework for Novelty Detection in Real-Time IoT Systems
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:This paper presents the Real-time Adaptive and Interpretable Detection (RAID) algorithm. The novel approach addresses the limitations of state-of-the-art anomaly detection methods for multivariate dynamic processes, which are restricted to detecting anomalies within the scope of the model training conditions. The RAID algorithm adapts to non-stationary effects such as data drift and change points that may not be accounted for during model development, resulting in prolonged service life. A dynamic model based on joint probability distribution handles anomalous behavior detection in a system and the root cause isolation based on adaptive process limits. RAID algorithm does not require changes to existing process automation infrastructures, making it highly deployable across different domains. Two case studies involving real dynamic system data demonstrate the benefits of the RAID algorithm, including change point adaptation, root cause isolation, and improved detection accuracy.
Real-Time Outlier Detection with Dynamic Process Limits
Jan 31, 2023



Abstract:Anomaly detection methods are part of the systems where rare events may endanger an operation's profitability, safety, and environmental aspects. Although many state-of-the-art anomaly detection methods were developed to date, their deployment is limited to the operation conditions present during the model training. Online anomaly detection brings the capability to adapt to data drifts and change points that may not be represented during model development resulting in prolonged service life. This paper proposes an online anomaly detection algorithm for existing real-time infrastructures where low-latency detection is required and novel patterns in data occur unpredictably. The online inverse cumulative distribution-based approach is introduced to eliminate common problems of offline anomaly detectors, meanwhile providing dynamic process limits to normal operation. The benefit of the proposed method is the ease of use, fast computation, and deployability as shown in two case studies of real microgrid operation data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge