Manuel García-Domínguez
Neural Style Transfer and Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation to deal with the Domain Shift Problem on Spheroid Segmentation
Dec 16, 2021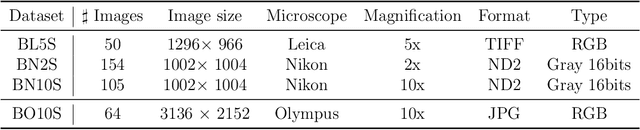
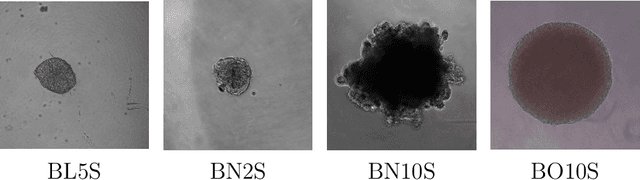
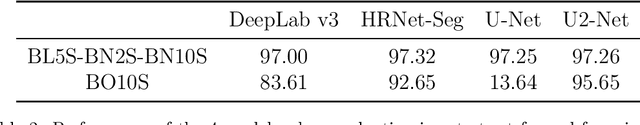
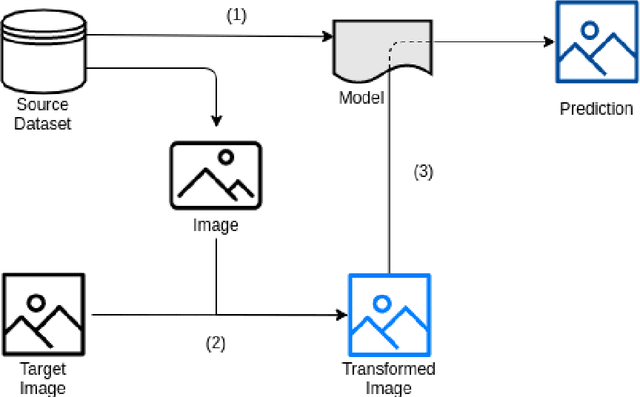
Abstract:Background and objectives. Domain shift is a generalisation problem of machine learning models that occurs when the data distribution of the training set is different to the data distribution encountered by the model when it is deployed. This is common in the context of biomedical image segmentation due to the variance of experimental conditions, equipment, and capturing settings. In this work, we address this challenge by studying both neural style transfer algorithms and unpaired image-to-image translation methods in the context of the segmentation of tumour spheroids. Methods. We have illustrated the domain shift problem in the context of spheroid segmentation with 4 deep learning segmentation models that achieved an IoU over 97% when tested with images following the training distribution, but whose performance decreased up to an 84\% when applied to images captured under different conditions. In order to deal with this problem, we have explored 3 style transfer algorithms (NST, deep image analogy, and STROTSS), and 6 unpaired image-to-image translations algorithms (CycleGAN, DualGAN, ForkGAN, GANILLA, CUT, and FastCUT). These algorithms have been integrated into a high-level API that facilitates their application to other contexts where the domain-shift problem occurs. Results. We have considerably improved the performance of the 4 segmentation models when applied to images captured under different conditions by using both style transfer and image-to-image translation algorithms. In particular, there are 2 style transfer algorithms (NST and deep image analogy) and 1 unpaired image-to-image translations algorithm (CycleGAN) that improve the IoU of the models in a range from 0.24 to 76.07. Therefore, reaching a similar performance to the one obtained with the models are applied to images following the training distribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge