Mani Amani
Bootstrapped LLM Semantics for Context-Aware Path Planning
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Prompting robots with natural language (NL) has largely been studied as what task to execute (goal selection, skill sequencing) rather than how to execute that task safely and efficiently in semantically rich, human-centric spaces. We address this gap with a framework that turns a large language model (LLM) into a stochastic semantic sensor whose outputs modulate a classical planner. Given a prompt and a semantic map, we draw multiple LLM "danger" judgments and apply a Bayesian bootstrap to approximate a posterior over per-class risk. Using statistics from the posterior, we create a potential cost to formulate a path planning problem. Across simulated environments and a BIM-backed digital twin, our method adapts how the robot moves in response to explicit prompts and implicit contextual information. We present qualitative and quantitative results.
Bayesian BIM-Guided Construction Robot Navigation with NLP Safety Prompts in Dynamic Environments
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Construction robotics increasingly relies on natural language processing for task execution, creating a need for robust methods to interpret commands in complex, dynamic environments. While existing research primarily focuses on what tasks robots should perform, less attention has been paid to how these tasks should be executed safely and efficiently. This paper presents a novel probabilistic framework that uses sentiment analysis from natural language commands to dynamically adjust robot navigation policies in construction environments. The framework leverages Building Information Modeling (BIM) data and natural language prompts to create adaptive navigation strategies that account for varying levels of environmental risk and uncertainty. We introduce an object-aware path planning approach that combines exponential potential fields with a grid-based representation of the environment, where the potential fields are dynamically adjusted based on the semantic analysis of user prompts. The framework employs Bayesian inference to consolidate multiple information sources: the static data from BIM, the semantic content of natural language commands, and the implied safety constraints from user prompts. We demonstrate our approach through experiments comparing three scenarios: baseline shortest-path planning, safety-oriented navigation, and risk-aware routing. Results show that our method successfully adapts path planning based on natural language sentiment, achieving a 50\% improvement in minimum distance to obstacles when safety is prioritized, while maintaining reasonable path lengths. Scenarios with contrasting prompts, such as "dangerous" and "safe", demonstrate the framework's ability to modify paths. This approach provides a flexible foundation for integrating human knowledge and safety considerations into construction robot navigation.
BIM-based Safe and Trustworthy Robot Pathfinding using Scalable MHA* Algorithms and Natural Language Processing
Nov 22, 2024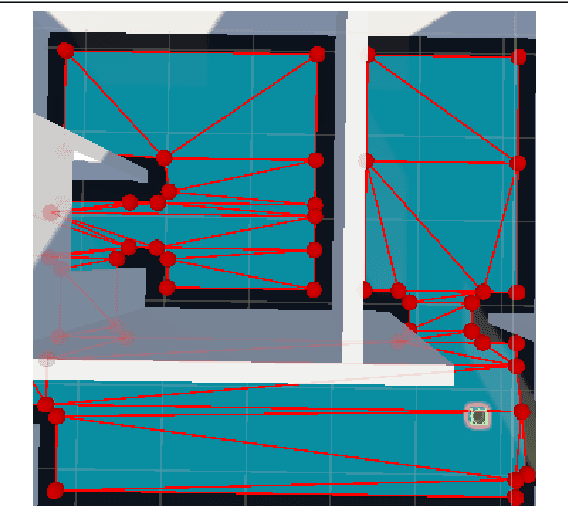


Abstract:Construction robots have gained significant traction in recent years in research and development. However, the application of industrial robots has unique challenges. Dynamic environments, domain-specific tasks, and complex localization and mapping are significant obstacles in their development. In construction job sites, moving objects and complex machinery can make pathfinding a difficult task due to the possibility of object collisions. Existing methods such as simultaneous localization and mapping are viable solutions to this problem, however, due to the precision and data quality required by the sensors and the processing of the information, they can be very computationally expensive. We propose using spatial and semantic information in building information modeling (BIM) to develop domain-specific pathfinding strategies. In this work, we integrate a multi-heuristic A* (MHA*) algorithm using APFs from the BIM spatial information and process textual information from the BIM using large language models (LLMs) to adjust the algorithm for dynamic object avoidance. We show increased robot object proximity by 80% while maintaining similar path lengths.
Adaptive Robot Perception in Construction Environments using 4D BIM
Sep 20, 2024Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is a pivotal component of robot perception for physical Human Robot Interaction (pHRI) tasks. In construction robotics, it is vital that robots have an accurate and robust perception of worker activities. This enhanced perception is the foundation of trustworthy and safe Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) in an industrial setting. Many developed HAR algorithms lack the robustness and adaptability to ensure seamless HRC. Recent works have employed multi-modal approaches to increase feature considerations. This paper further expands previous research to include 4D building information modeling (BIM) schedule data. We created a pipeline that transforms high-level BIM schedule activities into a set of low-level tasks in real-time. The framework then utilizes this subset as a tool to restrict the solution space that the HAR algorithm can predict activities from. By limiting this subspace through 4D BIM schedule data, the algorithm has a higher chance of predicting the true possible activities from a smaller pool of possibilities in a localized setting as compared to calculating all global possibilities at every point. Results indicate that the proposed approach achieves higher confidence predictions over the base model without leveraging the BIM data.
Ergonomic Optimization in Worker-Robot Bimanual Object Handover: Implementing REBA Using Reinforcement Learning in Virtual Reality
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Robots can serve as safety catalysts on construction job sites by taking over hazardous and repetitive tasks while alleviating the risks associated with existing manual workflows. Research on the safety of physical human-robot interaction (pHRI) is traditionally focused on addressing the risks associated with potential collisions. However, it is equally important to ensure that the workflows involving a collaborative robot are inherently safe, even though they may not result in an accident. For example, pHRI may require the human counterpart to use non-ergonomic body postures to conform to the robot hardware and physical configurations. Frequent and long-term exposure to such situations may result in chronic health issues. Safety and ergonomics assessment measures can be understood by robots if they are presented in algorithmic fashions so optimization for body postures is attainable. While frameworks such as Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA) have been an industry standard for many decades, they lack a rigorous mathematical structure which poses challenges in using them immediately for pHRI safety optimization purposes. Furthermore, learnable approaches have limited robustness outside of their training data, reducing generalizability. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that approaches optimization through Reinforcement Learning, ensuring precise, online ergonomic scores as compared to approximations, while being able to generalize and tune the regiment to any human and any task. To ensure practicality, the training is done in virtual reality utilizing Inverse Kinematics to simulate human movement mechanics. Experimental findings are compared to ergonomically naive object handover heuristics and indicate promising results where the developed framework can find the optimal object handover coordinates in pHRI contexts for manual material handling exemplary situations.
Expanding Frozen Vision-Language Models without Retraining: Towards Improved Robot Perception
Aug 31, 2023



Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown powerful capabilities in visual question answering and reasoning tasks by combining visual representations with the abstract skill set large language models (LLMs) learn during pretraining. Vision, while the most popular modality to augment LLMs with, is only one representation of a scene. In human-robot interaction scenarios, robot perception requires accurate scene understanding by the robot. In this paper, we define and demonstrate a method of aligning the embedding spaces of different modalities (in this case, inertial measurement unit (IMU) data) to the vision embedding space through a combination of supervised and contrastive training, enabling the VLM to understand and reason about these additional modalities without retraining. We opt to give the model IMU embeddings directly over using a separate human activity recognition model that feeds directly into the prompt to allow for any nonlinear interactions between the query, image, and IMU signal that would be lost by mapping the IMU data to a discrete activity label. Further, we demonstrate our methodology's efficacy through experiments involving human activity recognition using IMU data and visual inputs. Our results show that using multiple modalities as input improves the VLM's scene understanding and enhances its overall performance in various tasks, thus paving the way for more versatile and capable language models in multi-modal contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge