Maksim Dzhigil
Benefits of mirror weight symmetry for 3D mesh segmentation in biomedical applications
Sep 29, 2023
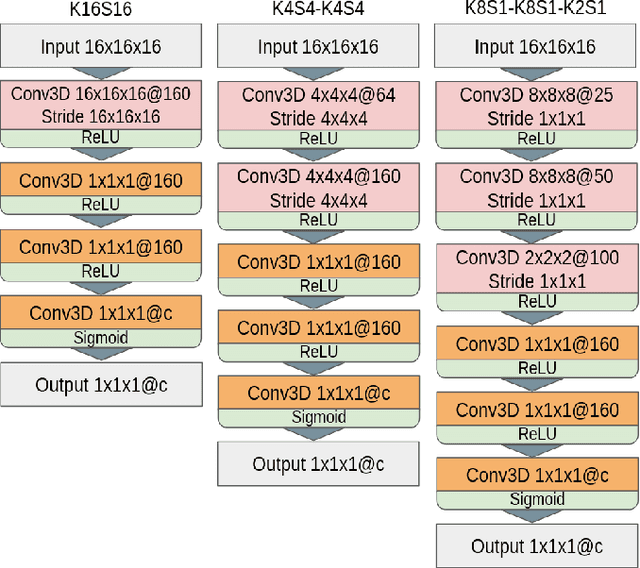
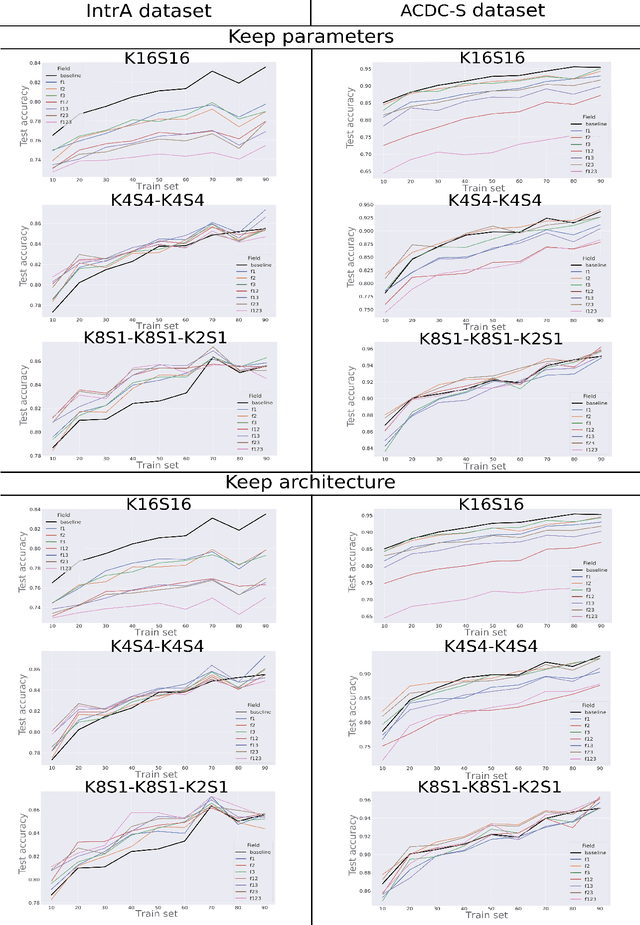
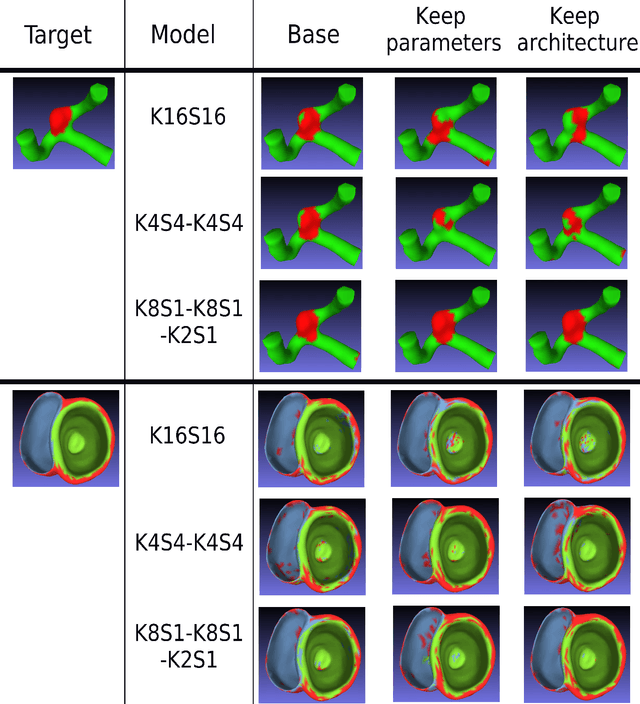
Abstract:3D mesh segmentation is an important task with many biomedical applications. The human body has bilateral symmetry and some variations in organ positions. It allows us to expect a positive effect of rotation and inversion invariant layers in convolutional neural networks that perform biomedical segmentations. In this study, we show the impact of weight symmetry in neural networks that perform 3D mesh segmentation. We analyze the problem of 3D mesh segmentation for pathological vessel structures (aneurysms) and conventional anatomical structures (endocardium and epicardium of ventricles). Local geometrical features are encoded as sampling from the signed distance function, and the neural network performs prediction for each mesh node. We show that weight symmetry gains from 1 to 3% of additional accuracy and allows decreasing the number of trainable parameters up to 8 times without suffering the performance loss if neural networks have at least three convolutional layers. This also works for very small training sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge