Mahsa Bazzaz
Analysis of Robustness of a Large Game Corpus
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Procedural content generation via machine learning (PCGML) in games involves using machine learning techniques to create game content such as maps and levels. 2D tile-based game levels have consistently served as a standard dataset for PCGML because they are a simplified version of game levels while maintaining the specific constraints typical of games, such as being solvable. In this work, we highlight the unique characteristics of game levels, including their structured discrete data nature, the local and global constraints inherent in the games, and the sensitivity of the game levels to small changes in input. We define the robustness of data as a measure of sensitivity to small changes in input that cause a change in output, and we use this measure to analyze and compare these levels to state-of-the-art machine learning datasets, showcasing the subtle differences in their nature. We also constructed a large dataset from four games inspired by popular classic tile-based games that showcase these characteristics and address the challenge of sparse data in PCGML by providing a significantly larger dataset than those currently available.
Level Generation with Constrained Expressive Range
Apr 04, 2025



Abstract:Expressive range analysis is a visualization-based technique used to evaluate the performance of generative models, particularly in game level generation. It typically employs two quantifiable metrics to position generated artifacts on a 2D plot, offering insight into how content is distributed within a defined metric space. In this work, we use the expressive range of a generator as the conceptual space of possible creations. Inspired by the quality diversity paradigm, we explore this space to generate levels. To do so, we use a constraint-based generator that systematically traverses and generates levels in this space. To train the constraint-based generator we use different tile patterns to learn from the initial example levels. We analyze how different patterns influence the exploration of the expressive range. Specifically, we compare the exploration process based on time, the number of successful and failed sample generations, and the overall interestingness of the generated levels. Unlike typical quality diversity approaches that rely on random generation and hope to get good coverage of the expressive range, this approach systematically traverses the grid ensuring more coverage. This helps create unique and interesting game levels while also improving our understanding of the generator's strengths and limitations.
Guided Game Level Repair via Explainable AI
Oct 30, 2024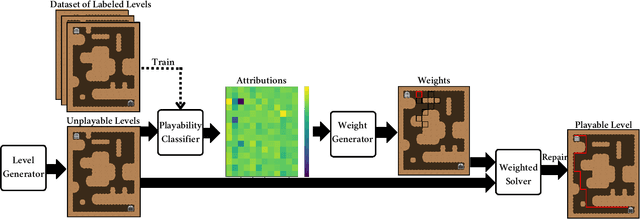
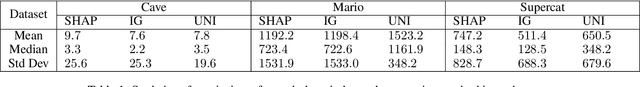
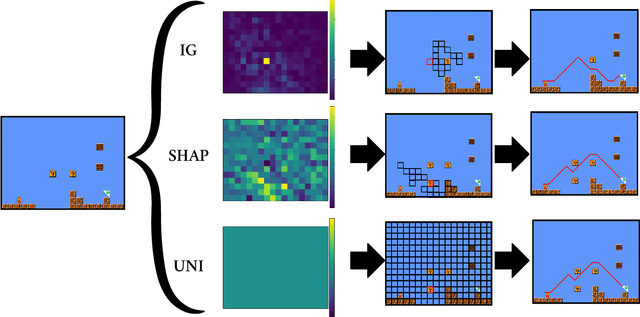
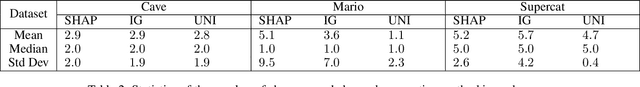
Abstract:Procedurally generated levels created by machine learning models can be unsolvable without further editing. Various methods have been developed to automatically repair these levels by enforcing hard constraints during the post-processing step. However, as levels increase in size, these constraint-based repairs become increasingly slow. This paper proposes using explainability methods to identify specific regions of a level that contribute to its unsolvability. By assigning higher weights to these regions, constraint-based solvers can prioritize these problematic areas, enabling more efficient repairs. Our results, tested across three games, demonstrate that this approach can help to repair procedurally generated levels faster.
Controllable Game Level Generation: Assessing the Effect of Negative Examples in GAN Models
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are unsupervised models designed to learn and replicate a target distribution. The vanilla versions of these models can be extended to more controllable models. Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (CGANs) extend vanilla GANs by conditioning both the generator and discriminator on some additional information (labels). Controllable models based on complementary learning, such as Rumi-GAN, have been introduced. Rumi-GANs leverage negative examples to enhance the generator's ability to learn positive examples. We evaluate the performance of two controllable GAN variants, CGAN and Rumi-GAN, in generating game levels targeting specific constraints of interest: playability and controllability. This evaluation is conducted under two scenarios: with and without the inclusion of negative examples. The goal is to determine whether incorporating negative examples helps the GAN models avoid generating undesirable outputs. Our findings highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each method in enforcing the generation of specific conditions when generating outputs based on given positive and negative examples.
Active Learning for Classifying 2D Grid-Based Level Completability
Sep 08, 2023



Abstract:Determining the completability of levels generated by procedural generators such as machine learning models can be challenging, as it can involve the use of solver agents that often require a significant amount of time to analyze and solve levels. Active learning is not yet widely adopted in game evaluations, although it has been used successfully in natural language processing, image and speech recognition, and computer vision, where the availability of labeled data is limited or expensive. In this paper, we propose the use of active learning for learning level completability classification. Through an active learning approach, we train deep-learning models to classify the completability of generated levels for Super Mario Bros., Kid Icarus, and a Zelda-like game. We compare active learning for querying levels to label with completability against random queries. Our results show using an active learning approach to label levels results in better classifier performance with the same amount of labeled data.
* 4 pages, 3 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge