Mahek Vora
Unsupervised SE(3) Disentanglement for in situ Macromolecular Morphology Identification from Cryo-Electron Tomography
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) provides direct 3D visualization of macromolecules inside the cell, enabling analysis of their in situ morphology. This morphology can be regarded as an SE(3)-invariant, denoised volumetric representation of subvolumes extracted from tomograms. Inferring morphology is therefore an inverse problem of estimating both a template morphology and its SE(3) transformation. Existing expectation-maximization based solution to this problem often misses rare but important morphologies and requires extensive manual hyperparameter tuning. Addressing this issue, we present a disentangled deep representation learning framework that separates SE(3) transformations from morphological content in the representation space. The framework includes a novel multi-choice learning module that enables this disentanglement for highly noisy cryo-ET data, and the learned morphological content is used to generate template morphologies. Experiments on simulated and real cryo-ET datasets demonstrate clear improvements over prior methods, including the discovery of previously unidentified macromolecular morphologies.
Large language model for Bible sentiment analysis: Sermon on the Mount
Jan 01, 2024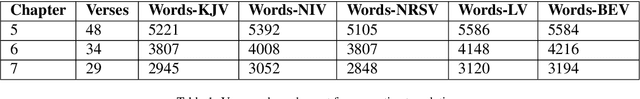
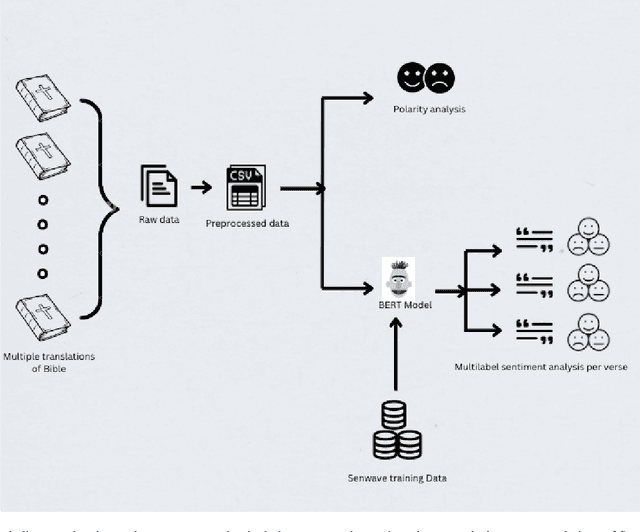
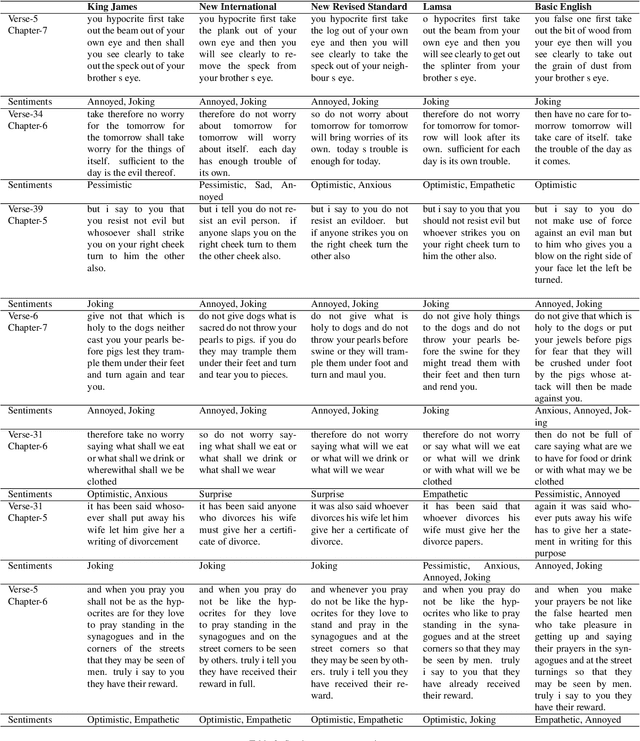
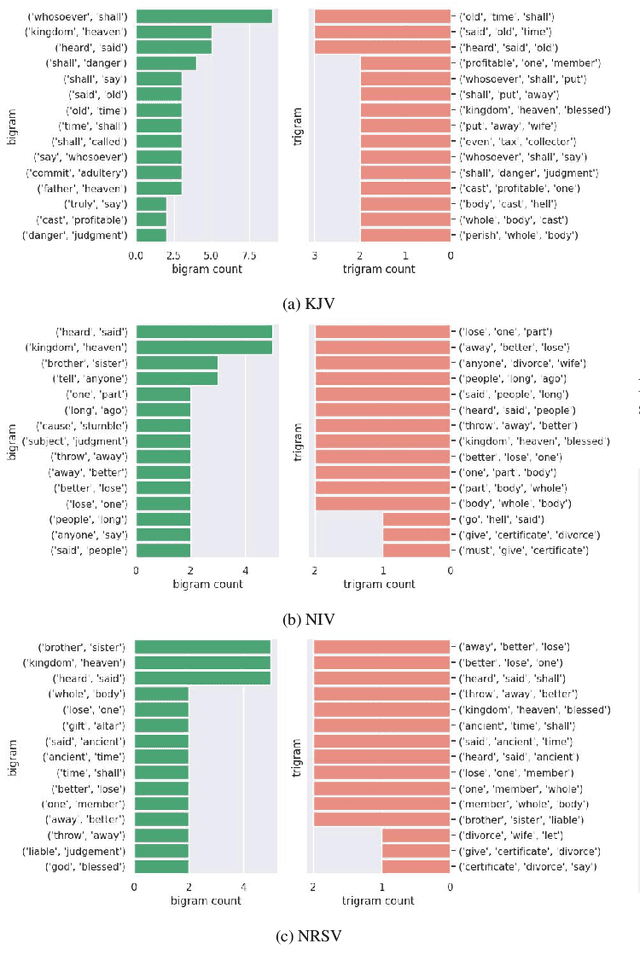
Abstract:The revolution of natural language processing via large language models has motivated its use in multidisciplinary areas that include social sciences and humanities and more specifically, comparative religion. Sentiment analysis provides a mechanism to study the emotions expressed in text. Recently, sentiment analysis has been used to study and compare translations of the Bhagavad Gita, which is a fundamental and sacred Hindu text. In this study, we use sentiment analysis for studying selected chapters of the Bible. These chapters are known as the Sermon on the Mount. We utilize a pre-trained language model for sentiment analysis by reviewing five translations of the Sermon on the Mount, which include the King James version, the New International Version, the New Revised Standard Version, the Lamsa Version, and the Basic English Version. We provide a chapter-by-chapter and verse-by-verse comparison using sentiment and semantic analysis and review the major sentiments expressed. Our results highlight the varying sentiments across the chapters and verses. We found that the vocabulary of the respective translations is significantly different. We detected different levels of humour, optimism, and empathy in the respective chapters that were used by Jesus to deliver his message.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge