Maaike H. T. de Boer
Modular Design Patterns for Hybrid Actors
Sep 20, 2021



Abstract:Recently, a boxology (graphical language) with design patterns for hybrid AI was proposed, combining symbolic and sub-symbolic learning and reasoning. In this paper, we extend this boxology with actors and their interactions. The main contributions of this paper are: 1) an extension of the taxonomy to describe distributed hybrid AI systems with actors and interactions; and 2) showing examples using a few design patterns relevant in multi-agent systems and human-agent interaction in general and, specifically, in the manufacturing domain.
Gender prediction using limited Twitter Data
Sep 29, 2020
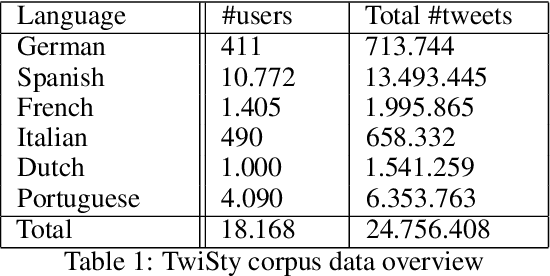
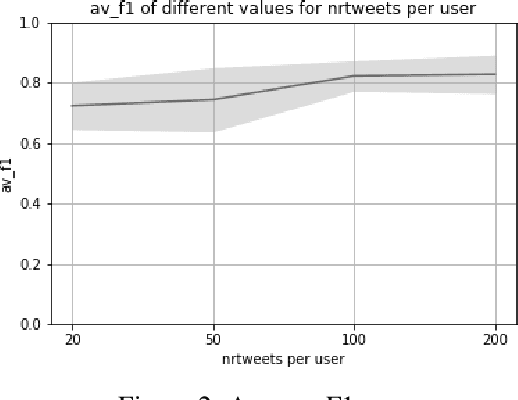
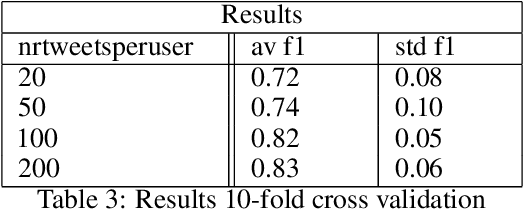
Abstract:Transformer models have shown impressive performance on a variety of NLP tasks. Off-the-shelf, pre-trained models can be fine-tuned for specific NLP classification tasks, reducing the need for large amounts of additional training data. However, little research has addressed how much data is required to accurately fine-tune such pre-trained transformer models, and how much data is needed for accurate prediction. This paper explores the usability of BERT (a Transformer model for word embedding) for gender prediction on social media. Forensic applications include detecting gender obfuscation, e.g. males posing as females in chat rooms. A Dutch BERT model is fine-tuned on different samples of a Dutch Twitter dataset labeled for gender, varying in the number of tweets used per person. The results show that finetuning BERT contributes to good gender classification performance (80% F1) when finetuned on only 200 tweets per person. But when using just 20 tweets per person, the performance of our classifier deteriorates non-steeply (to 70% F1). These results show that even with relatively small amounts of data, BERT can be fine-tuned to accurately help predict the gender of Twitter users, and, consequently, that it is possible to determine gender on the basis of just a low volume of tweets. This opens up an operational perspective on the swift detection of gender.
Opinion aspect extraction in Dutch childrens diary entries
Oct 21, 2019



Abstract:Aspect extraction can be used in dialogue systems to understand the topic of opinionated text. Expressing an empathetic reaction to an opinion can strengthen the bond between a human and, for example, a robot. The aim of this study is three-fold: 1. create a new annotated dataset for both aspect extraction and opinion words for Dutch childrens language, 2. acquire aspect extraction results for this task and 3. improve current results for aspect extraction in Dutch reviews. This was done by training a deep learning Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) model, originally developed for an English review dataset, on Dutch restaurant review data to classify both opinion words and their respective aspects. We obtained state-of-the-art performance on the Dutch restaurant review dataset. Additionally, we acquired aspect extraction results for the Dutch childrens dataset. Since the model was trained on standardised language, these results are quite promising.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge