M. Abdullah-Al-Wadud
Clustering Algorithms to Analyze the Road Traffic Crashes
Aug 07, 2021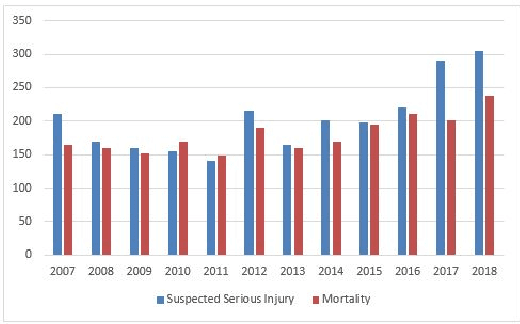
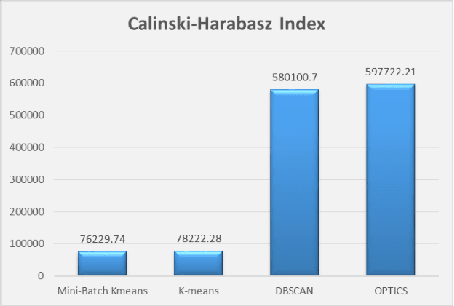
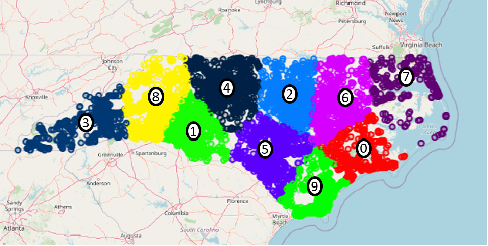
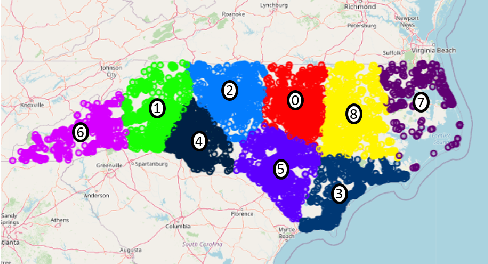
Abstract:Selecting an appropriate clustering method as well as an optimal number of clusters in road accident data is at times confusing and difficult. This paper analyzes shortcomings of different existing techniques applied to cluster accident-prone areas and recommends using Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) and Ordering Points To Identify the Clustering Structure (OPTICS) to overcome them. Comparative performance analysis based on real-life data on the recorded cases of road accidents in North Carolina also show more effectiveness and efficiency achieved by these algorithms.
* 6 pages, 10 figures, 2 tables
A Genetic Algorithm for Software Design Migration from Structured to Object Oriented Paradigm
Jul 23, 2014



Abstract:The potential benefit of migrating software design from Structured to Object Oriented Paradigm is manifolded including modularity, manageability and extendability. This design migration should be automated as it will reduce the time required in manual process. Our previous work has addressed this issue in terms of optimal graph clustering problem formulated by a quadratic Integer Program (IP). However, it has been realized that solution to the IP is computationally hard and thus heuristic based methods are required to get a near optimal solution. This paper presents a Genetic Algorithm (GA) for optimal clustering with an objective of maximizing intra-cluster edges whereas minimizing the inter-cluster ones. The proposed algorithm relies on fitness based parent selection and cross-overing cluster elements to reach an optimal solution step by step. The scheme was implemented and tested against a set of real and synthetic data. The experimental results show that GA outperforms our previous works based on Greedy and Monte Carlo approaches by 40% and 49.5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge