Lydia Morawiec
Kernel Ridge Regression Using Importance Sampling with Application to Seismic Response Prediction
Sep 19, 2020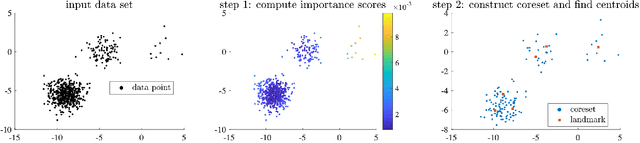
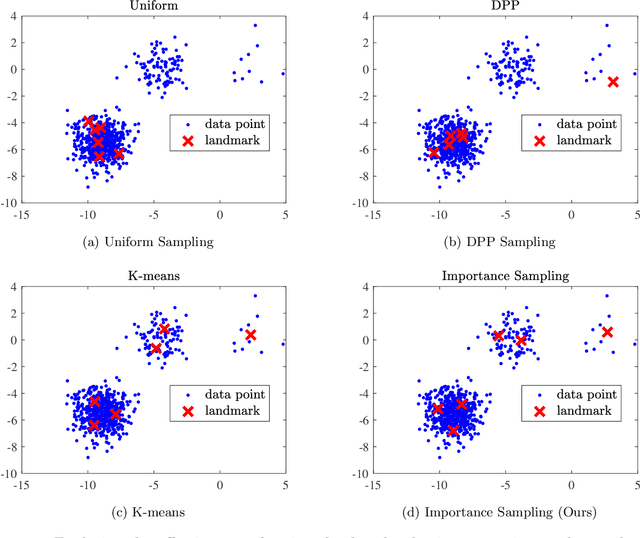
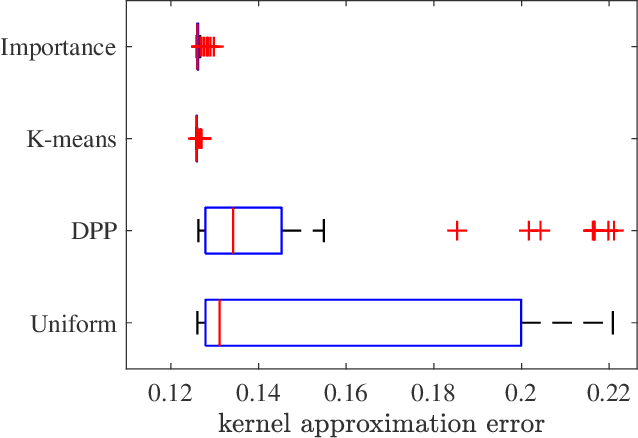
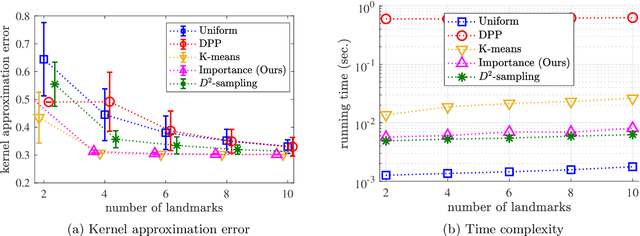
Abstract:Scalable kernel methods, including kernel ridge regression, often rely on low-rank matrix approximations using the Nystrom method, which involves selecting landmark points from large data sets. The existing approaches to selecting landmarks are typically computationally demanding as they require manipulating and performing computations with large matrices in the input or feature space. In this paper, our contribution is twofold. The first contribution is to propose a novel landmark selection method that promotes diversity using an efficient two-step approach. Our landmark selection technique follows a coarse to fine strategy, where the first step computes importance scores with a single pass over the whole data. The second step performs K-means clustering on the constructed coreset to use the obtained centroids as landmarks. Hence, the introduced method provides tunable trade-offs between accuracy and efficiency. Our second contribution is to investigate the performance of several landmark selection techniques using a novel application of kernel methods for predicting structural responses due to earthquake load and material uncertainties. Our experiments exhibit the merits of our proposed landmark selection scheme against baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge