Luis Nunes
Learning Rhetorical Structure Theory-based descriptions of observed behaviour
Jun 24, 2022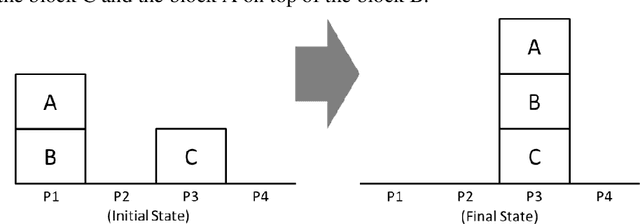
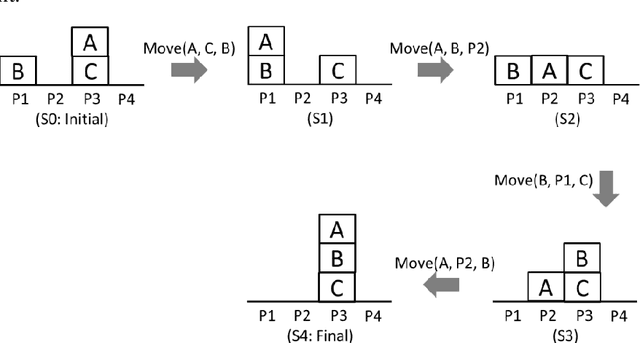
Abstract:In a previous paper, we have proposed a set of concepts, axiom schemata and algorithms that can be used by agents to learn to describe their behaviour, goals, capabilities, and environment. The current paper proposes a new set of concepts, axiom schemata and algorithms that allow the agent to learn new descriptions of an observed behaviour (e.g., perplexing actions), of its actor (e.g., undesired propositions or actions), and of its environment (e.g., incompatible propositions). Each learned description (e.g., a certain action prevents another action from being performed in the future) is represented by a relationship between entities (either propositions or actions) and is learned by the agent, just by observation, using domain-independent axiom schemata and or learning algorithms. The relations used by agents to represent the descriptions they learn were inspired on the Theory of Rhetorical Structure (RST). The main contribution of the paper is the relation family Although, inspired on the RST relation Concession. The accurate definition of the relations of the family Although involves a set of deontic concepts whose definition and corresponding algorithms are presented. The relations of the family Although, once extracted from the agent's observations, express surprise at the observed behaviour and, in certain circumstances, present a justification for it. The paper shows results of the presented proposals in a demonstration scenario, using implemented software.
Software Agents with Concerns of their Own
Nov 12, 2015Abstract:We claim that it is possible to have artificial software agents for which their actions and the world they inhabit have first-person or intrinsic meanings. The first-person or intrinsic meaning of an entity to a system is defined as its relation with the system's goals and capabilities, given the properties of the environment in which it operates. Therefore, for a system to develop first-person meanings, it must see itself as a goal-directed actor, facing limitations and opportunities dictated by its own capabilities, and by the properties of the environment. The first part of the paper discusses this claim in the context of arguments against and proposals addressing the development of computer programs with first-person meanings. A set of definitions is also presented, most importantly the concepts of cold and phenomenal first-person meanings. The second part of the paper presents preliminary proposals and achievements, resulting of actual software implementations, within a research approach that aims to develop software agents that intrinsically understand their actions and what happens to them. As a result, an agent with no a priori notion of its goals and capabilities, and of the properties of its environment acquires all these notions by observing itself in action. The cold first-person meanings of the agent's actions and of what happens to it are defined using these acquired notions. Although not solving the full problem of first-person meanings, the proposed approach and preliminary results allow us some confidence to address the problems yet to be considered, in particular the phenomenal aspect of first-person meanings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge