Lucio La Cava
Culturally Grounded Personas in Large Language Models: Characterization and Alignment with Socio-Psychological Value Frameworks
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Despite the growing utility of Large Language Models (LLMs) for simulating human behavior, the extent to which these synthetic personas accurately reflect world and moral value systems across different cultural conditionings remains uncertain. This paper investigates the alignment of synthetic, culturally-grounded personas with established frameworks, specifically the World Values Survey (WVS), the Inglehart-Welzel Cultural Map, and Moral Foundations Theory. We conceptualize and produce LLM-generated personas based on a set of interpretable WVS-derived variables, and we examine the generated personas through three complementary lenses: positioning on the Inglehart-Welzel map, which unveils their interpretation reflecting stable differences across cultural conditionings; demographic-level consistency with the World Values Survey, where response distributions broadly track human group patterns; and moral profiles derived from a Moral Foundations questionnaire, which we analyze through a culture-to-morality mapping to characterize how moral responses vary across different cultural configurations. Our approach of culturally-grounded persona generation and analysis enables evaluation of cross-cultural structure and moral variation.
Machines in the Crowd? Measuring the Footprint of Machine-Generated Text on Reddit
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence is reshaping online communication by enabling large-scale production of Machine-Generated Text (MGT) at low cost. While its presence is rapidly growing across the Web, little is known about how MGT integrates into social media environments. In this paper, we present the first large-scale characterization of MGT on Reddit. Using a state-of-the-art statistical method for detection of MGT, we analyze over two years of activity (2022-2024) across 51 subreddits representative of Reddit's main community types such as information seeking, social support, and discussion. We study the concentration of MGT across communities and over time, and compared MGT to human-authored text in terms of social signals it expresses and engagement it receives. Our very conservative estimate of MGT prevalence indicates that synthetic text is marginally present on Reddit, but it can reach peaks of up to 9% in some communities in some months. MGT is unevenly distributed across communities, more prevalent in subreddits focused on technical knowledge and social support, and often concentrated in the activity of a small fraction of users. MGT also conveys distinct social signals of warmth and status giving typical of language of AI assistants. Despite these stylistic differences, MGT achieves engagement levels comparable than human-authored content and in a few cases even higher, suggesting that AI-generated text is becoming an organic component of online social discourse. This work offers the first perspective on the MGT footprint on Reddit, paving the way for new investigations involving platform governance, detection strategies, and community dynamics.
OpenTuringBench: An Open-Model-based Benchmark and Framework for Machine-Generated Text Detection and Attribution
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Open Large Language Models (OLLMs) are increasingly leveraged in generative AI applications, posing new challenges for detecting their outputs. We propose OpenTuringBench, a new benchmark based on OLLMs, designed to train and evaluate machine-generated text detectors on the Turing Test and Authorship Attribution problems. OpenTuringBench focuses on a representative set of OLLMs, and features a number of challenging evaluation tasks, including human/machine-manipulated texts, out-of-domain texts, and texts from previously unseen models. We also provide OTBDetector, a contrastive learning framework to detect and attribute OLLM-based machine-generated texts. Results highlight the relevance and varying degrees of difficulty of the OpenTuringBench tasks, with our detector achieving remarkable capabilities across the various tasks and outperforming most existing detectors. Resources are available on the OpenTuringBench Hugging Face repository at https://huggingface.co/datasets/MLNTeam-Unical/OpenTuringBench
Heuristic-Informed Mixture of Experts for Link Prediction in Multilayer Networks
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Link prediction algorithms for multilayer networks are in principle required to effectively account for the entire layered structure while capturing the unique contexts offered by each layer. However, many existing approaches excel at predicting specific links in certain layers but struggle with others, as they fail to effectively leverage the diverse information encoded across different network layers. In this paper, we present MoE-ML-LP, the first Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) framework specifically designed for multilayer link prediction. Building on top of multilayer heuristics for link prediction, MoE-ML-LP synthesizes the decisions taken by diverse experts, resulting in significantly enhanced predictive capabilities. Our extensive experimental evaluation on real-world and synthetic networks demonstrates that MoE-ML-LP consistently outperforms several baselines and competing methods, achieving remarkable improvements of +60% in Mean Reciprocal Rank, +82% in Hits@1, +55% in Hits@5, and +41% in Hits@10. Furthermore, MoE-ML-LP features a modular architecture that enables the seamless integration of newly developed experts without necessitating the re-training of the entire framework, fostering efficiency and scalability to new experts, paving the way for future advancements in link prediction.
Safeguarding Decentralized Social Media: LLM Agents for Automating Community Rule Compliance
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Ensuring content compliance with community guidelines is crucial for maintaining healthy online social environments. However, traditional human-based compliance checking struggles with scaling due to the increasing volume of user-generated content and a limited number of moderators. Recent advancements in Natural Language Understanding demonstrated by Large Language Models unlock new opportunities for automated content compliance verification. This work evaluates six AI-agents built on Open-LLMs for automated rule compliance checking in Decentralized Social Networks, a challenging environment due to heterogeneous community scopes and rules. Analyzing over 50,000 posts from hundreds of Mastodon servers, we find that AI-agents effectively detect non-compliant content, grasp linguistic subtleties, and adapt to diverse community contexts. Most agents also show high inter-rater reliability and consistency in score justification and suggestions for compliance. Human-based evaluation with domain experts confirmed the agents' reliability and usefulness, rendering them promising tools for semi-automated or human-in-the-loop content moderation systems.
Is Contrasting All You Need? Contrastive Learning for the Detection and Attribution of AI-generated Text
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:The significant progress in the development of Large Language Models has contributed to blurring the distinction between human and AI-generated text. The increasing pervasiveness of AI-generated text and the difficulty in detecting it poses new challenges for our society. In this paper, we tackle the problem of detecting and attributing AI-generated text by proposing WhosAI, a triplet-network contrastive learning framework designed to predict whether a given input text has been generated by humans or AI and to unveil the authorship of the text. Unlike most existing approaches, our proposed framework is conceived to learn semantic similarity representations from multiple generators at once, thus equally handling both detection and attribution tasks. Furthermore, WhosAI is model-agnostic and scalable to the release of new AI text-generation models by incorporating their generated instances into the embedding space learned by our framework. Experimental results on the TuringBench benchmark of 200K news articles show that our proposed framework achieves outstanding results in both the Turing Test and Authorship Attribution tasks, outperforming all the methods listed in the TuringBench benchmark leaderboards.
Talking the Talk Does Not Entail Walking the Walk: On the Limits of Large Language Models in Lexical Entailment Recognition
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:Verbs form the backbone of language, providing the structure and meaning to sentences. Yet, their intricate semantic nuances pose a longstanding challenge. Understanding verb relations through the concept of lexical entailment is crucial for comprehending sentence meanings and grasping verb dynamics. This work investigates the capabilities of eight Large Language Models in recognizing lexical entailment relations among verbs through differently devised prompting strategies and zero-/few-shot settings over verb pairs from two lexical databases, namely WordNet and HyperLex. Our findings unveil that the models can tackle the lexical entailment recognition task with moderately good performance, although at varying degree of effectiveness and under different conditions. Also, utilizing few-shot prompting can enhance the models' performance. However, perfectly solving the task arises as an unmet challenge for all examined LLMs, which raises an emergence for further research developments on this topic.
Open Models, Closed Minds? On Agents Capabilities in Mimicking Human Personalities through Open Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2024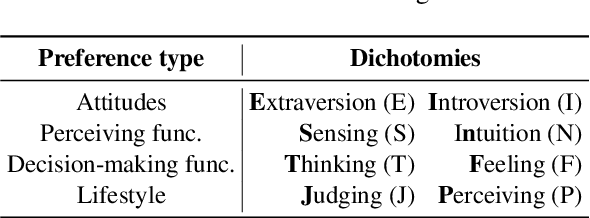
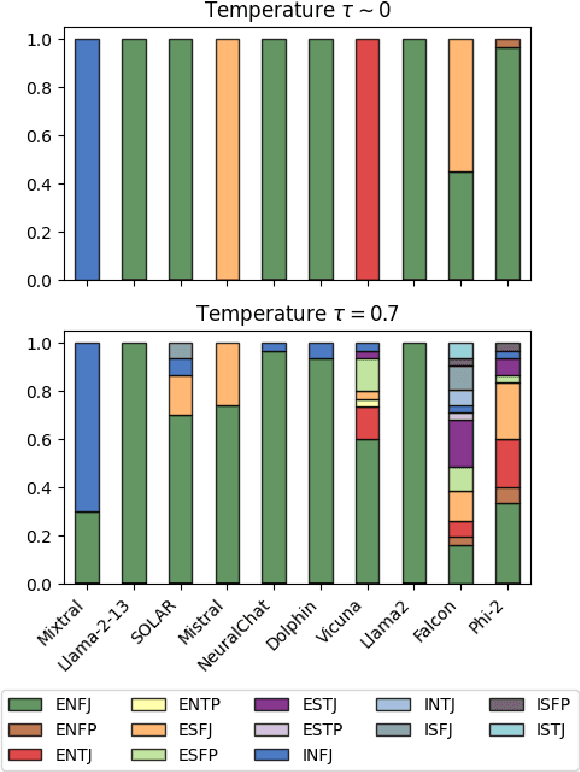
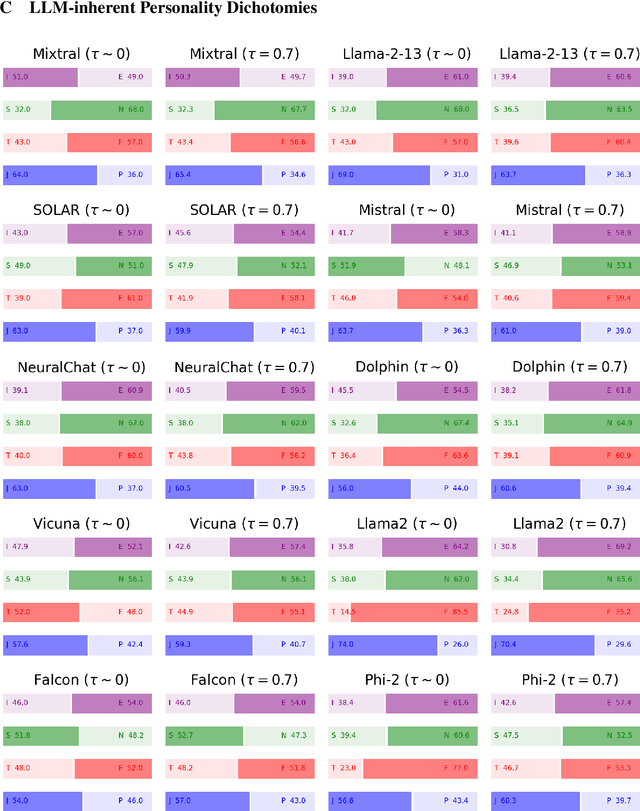
Abstract:The emergence of unveiling human-like behaviors in Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to a closer connection between NLP and human psychology, leading to a proliferation of computational agents. Scholars have been studying the inherent personalities displayed by LLM agents and attempting to incorporate human traits and behaviors into them. However, these efforts have primarily focused on commercially-licensed LLMs, neglecting the widespread use and notable advancements seen in Open LLMs. This work aims to address this gap by conducting a comprehensive examination of the ability of agents to emulate human personalities using Open LLMs. To achieve this, we generate a set of ten LLM Agents based on the most representative Open models and subject them to a series of assessments concerning the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) test. Our approach involves evaluating the intrinsic personality traits of Open LLM agents and determining the extent to which these agents can mimic human personalities when conditioned by specific personalities and roles. Our findings unveil that: $(i)$ each Open LLM agent showcases distinct human personalities; $(ii)$ personality-conditioned prompting produces varying effects on the agents, with only few successfully mirroring the imposed personality, while most of them being ``closed-minded'' (i.e., they retain their intrinsic traits); $(iii)$ combining role and personality conditioning can enhance the agents' ability to mimic human personalities; and $(iv)$ personalities typically associated with the role of teacher tend to be emulated with greater accuracy. Our work represents a step up in understanding the dense relationship between NLP and human psychology through the lens of Open LLMs.
Visually Wired NFTs: Exploring the Role of Inspiration in Non-Fungible Tokens
Apr 16, 2023Abstract:The fervor for Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) attracted countless creators, leading to a Big Bang of digital assets driven by latent or explicit forms of inspiration, as in many creative processes. This work exploits Vision Transformers and graph-based modeling to delve into visual inspiration phenomena between NFTs over the years. Our goals include unveiling the main structural traits that shape visual inspiration networks, exploring the interrelation between visual inspiration and asset performances, investigating crypto influence on inspiration processes, and explaining the inspiration relationships among NFTs. Our findings unveil how the pervasiveness of inspiration led to a temporary saturation of the visual feature space, the impact of the dichotomy between inspiring and inspired NFTs on their financial performance, and an intrinsic self-regulatory mechanism between markets and inspiration waves. Our work can serve as a starting point for gaining a broader view of the evolution of Web3.
Show me your NFT and I tell you how it will perform: Multimodal representation learning for NFT selling price prediction
Feb 06, 2023Abstract:Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) represent deeds of ownership, based on blockchain technologies and smart contracts, of unique crypto assets on digital art forms (e.g., artworks or collectibles). In the spotlight after skyrocketing in 2021, NFTs have attracted the attention of crypto enthusiasts and investors intent on placing promising investments in this profitable market. However, the NFT financial performance prediction has not been widely explored to date. In this work, we address the above problem based on the hypothesis that NFT images and their textual descriptions are essential proxies to predict the NFT selling prices. To this purpose, we propose MERLIN, a novel multimodal deep learning framework designed to train Transformer-based language and visual models, along with graph neural network models, on collections of NFTs' images and texts. A key aspect in MERLIN is its independence on financial features, as it exploits only the primary data a user interested in NFT trading would like to deal with, i.e., NFT images and textual descriptions. By learning dense representations of such data, a price-category classification task is performed by MERLIN models, which can also be tuned according to user preferences in the inference phase to mimic different risk-return investment profiles. Experimental evaluation on a publicly available dataset has shown that MERLIN models achieve significant performances according to several financial assessment criteria, fostering profitable investments, and also beating baseline machine-learning classifiers based on financial features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge