Louis Grandjean
Rapid Lung Ultrasound COVID-19 Severity Scoring with Resource-Efficient Deep Feature Extraction
Jul 22, 2022
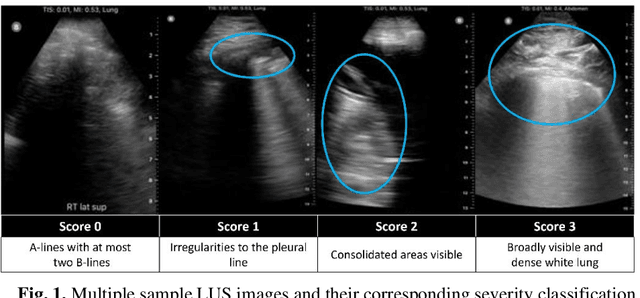
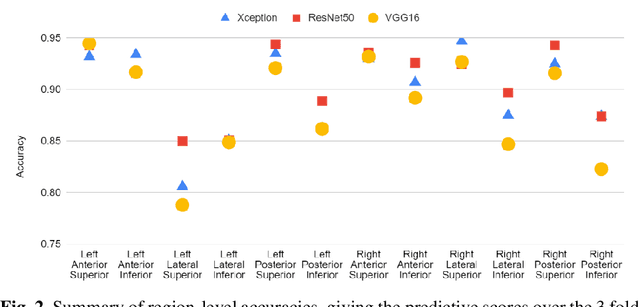
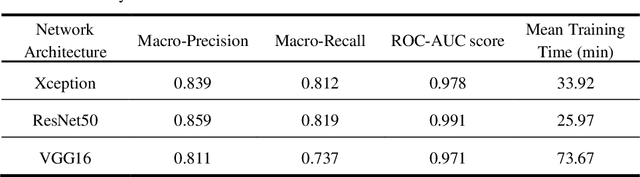
Abstract:Artificial intelligence-based analysis of lung ultrasound imaging has been demonstrated as an effective technique for rapid diagnostic decision support throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. However, such techniques can require days- or weeks-long training processes and hyper-parameter tuning to develop intelligent deep learning image analysis models. This work focuses on leveraging 'off-the-shelf' pre-trained models as deep feature extractors for scoring disease severity with minimal training time. We propose using pre-trained initializations of existing methods ahead of simple and compact neural networks to reduce reliance on computational capacity. This reduction of computational capacity is of critical importance in time-limited or resource-constrained circumstances, such as the early stages of a pandemic. On a dataset of 49 patients, comprising over 20,000 images, we demonstrate that the use of existing methods as feature extractors results in the effective classification of COVID-19-related pneumonia severity while requiring only minutes of training time. Our methods can achieve an accuracy of over 0.93 on a 4-level severity score scale and provides comparable per-patient region and global scores compared to expert annotated ground truths. These results demonstrate the capability for rapid deployment and use of such minimally-adapted methods for progress monitoring, patient stratification and management in clinical practice for COVID-19 patients, and potentially in other respiratory diseases.
Lung Ultrasound Segmentation and Adaptation between COVID-19 and Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Aug 06, 2021
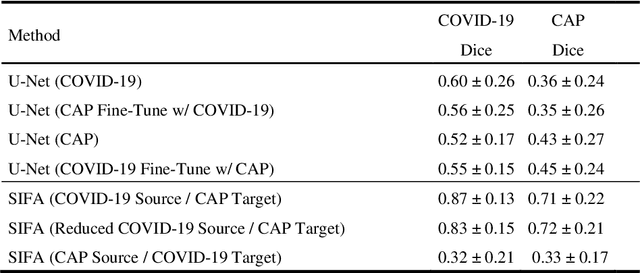
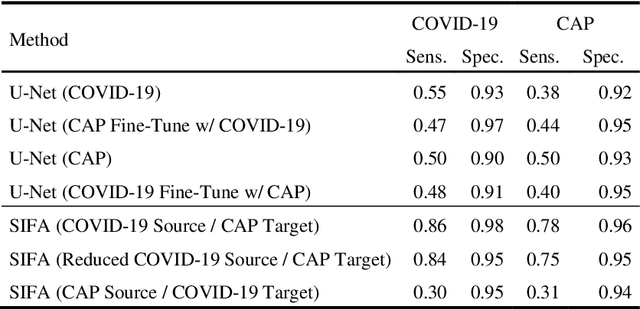
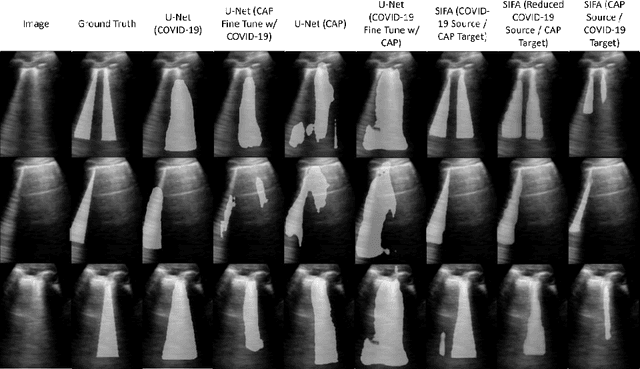
Abstract:Lung ultrasound imaging has been shown effective in detecting typical patterns for interstitial pneumonia, as a point-of-care tool for both patients with COVID-19 and other community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). In this work, we focus on the hyperechoic B-line segmentation task. Using deep neural networks, we automatically outline the regions that are indicative of pathology-sensitive artifacts and their associated sonographic patterns. With a real-world data-scarce scenario, we investigate approaches to utilize both COVID-19 and CAP lung ultrasound data to train the networks; comparing fine-tuning and unsupervised domain adaptation. Segmenting either type of lung condition at inference may support a range of clinical applications during evolving epidemic stages, but also demonstrates value in resource-constrained clinical scenarios. Adapting real clinical data acquired from COVID-19 patients to those from CAP patients significantly improved Dice scores from 0.60 to 0.87 (p < 0.001) and from 0.43 to 0.71 (p < 0.001), on independent COVID-19 and CAP test cases, respectively. It is of practical value that the improvement was demonstrated with only a small amount of data in both training and adaptation data sets, a common constraint for deploying machine learning models in clinical practice. Interestingly, we also report that the inverse adaptation, from labelled CAP data to unlabeled COVID-19 data, did not demonstrate an improvement when tested on either condition. Furthermore, we offer a possible explanation that correlates the segmentation performance to label consistency and data domain diversity in this point-of-care lung ultrasound application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge