Liran Oren
Acoustic to Articulatory Speech Inversion for Children with Velopharyngeal Insufficiency
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Traditional clinical approaches for assessing nasality, such as nasopharyngoscopy and nasometry, involve unpleasant experiences and are problematic for children. Speech Inversion (SI), a noninvasive technique, offers a promising alternative for estimating articulatory movement without the need for physical instrumentation. In this study, an SI system trained on nasalance data from healthy adults is augmented with source information from electroglottography and acoustically derived F0, periodic and aperiodic energy estimates as proxies for glottal control. This model achieves 16.92% relative improvement in Pearson Product-Moment Correlation (PPMC) compared to a previous SI system for nasalance estimation. To adapt the SI system for nasalance estimation in children with Velopharyngeal Insufficiency (VPI), the model initially trained on adult speech was fine-tuned using children with VPI data, yielding an 7.90% relative improvement in PPMC compared to its performance before fine-tuning.
Enhancing Acoustic-to-Articulatory Speech Inversion by Incorporating Nasality
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Speech is produced through the coordination of vocal tract constricting organs: lips, tongue, velum, and glottis. Previous works developed Speech Inversion (SI) systems to recover acoustic-to-articulatory mappings for lip and tongue constrictions, called oral tract variables (TVs), which were later enhanced by including source information (periodic and aperiodic energies, and F0 frequency) as proxies for glottal control. Comparison of the nasometric measures with high-speed nasopharyngoscopy showed that nasalance can serve as ground truth, and that an SI system trained with it reliably recovers velum movement patterns for American English speakers. Here, two SI training approaches are compared: baseline models that estimate oral TVs and nasalance independently, and a synergistic model that combines oral TVs and source features with nasalance. The synergistic model shows relative improvements of 5% in oral TVs estimation and 9% in nasalance estimation compared to the baseline models.
Speaker-independent Speech Inversion for Estimation of Nasalance
May 31, 2023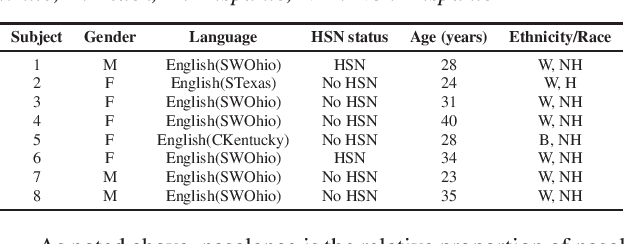
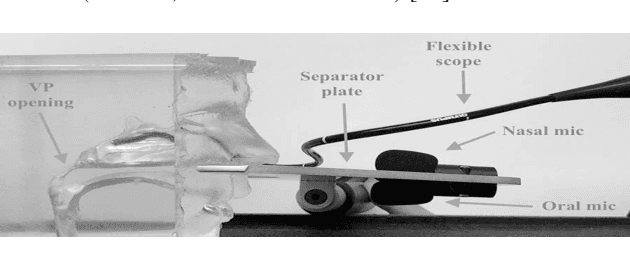
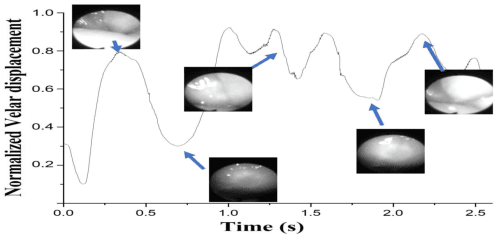

Abstract:The velopharyngeal (VP) valve regulates the opening between the nasal and oral cavities. This valve opens and closes through a coordinated motion of the velum and pharyngeal walls. Nasalance is an objective measure derived from the oral and nasal acoustic signals that correlate with nasality. In this work, we evaluate the degree to which the nasalance measure reflects fine-grained patterns of VP movement by comparison with simultaneously collected direct measures of VP opening using high-speed nasopharyngoscopy (HSN). We show that nasalance is significantly correlated with the HSN signal, and that both match expected patterns of nasality. We then train a temporal convolution-based speech inversion system in a speaker-independent fashion to estimate VP movement for nasality, using nasalance as the ground truth. In further experiments, we also show the importance of incorporating source features (from glottal activity) to improve nasality prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge