Liquan Chen
Tackling Resource-Constrained and Data-Heterogeneity in Federated Learning with Double-Weight Sparse Pack
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Federated learning has drawn widespread interest from researchers, yet the data heterogeneity across edge clients remains a key challenge, often degrading model performance. Existing methods enhance model compatibility with data heterogeneity by splitting models and knowledge distillation. However, they neglect the insufficient communication bandwidth and computing power on the client, failing to strike an effective balance between addressing data heterogeneity and accommodating limited client resources. To tackle this limitation, we propose a personalized federated learning method based on cosine sparsification parameter packing and dual-weighted aggregation (FedCSPACK), which effectively leverages the limited client resources and reduces the impact of data heterogeneity on model performance. In FedCSPACK, the client packages model parameters and selects the most contributing parameter packages for sharing based on cosine similarity, effectively reducing bandwidth requirements. The client then generates a mask matrix anchored to the shared parameter package to improve the alignment and aggregation efficiency of sparse updates on the server. Furthermore, directional and distribution distance weights are embedded in the mask to implement a weighted-guided aggregation mechanism, enhancing the robustness and generalization performance of the global model. Extensive experiments across four datasets using ten state-of-the-art methods demonstrate that FedCSPACK effectively improves communication and computational efficiency while maintaining high model accuracy.
Secret Key Generation for IRS-Assisted Multi-Antenna Systems: A Machine Learning-Based Approach
Apr 28, 2023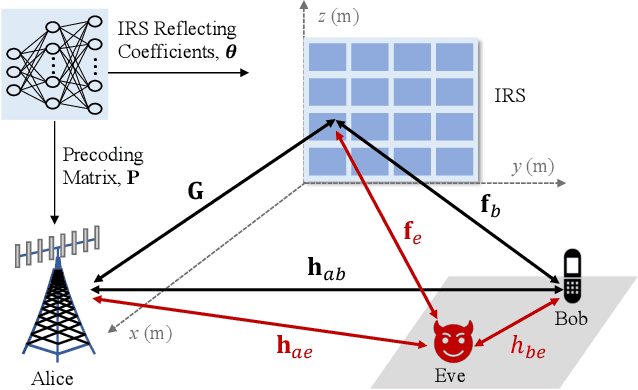
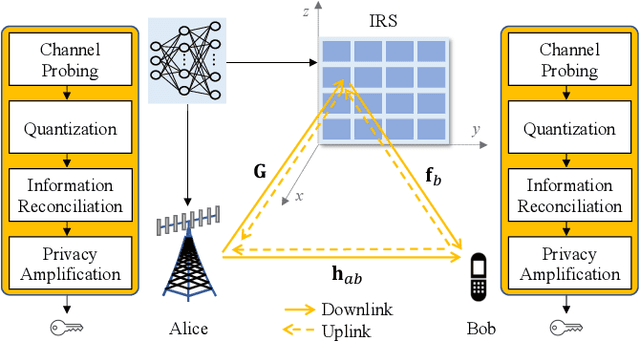
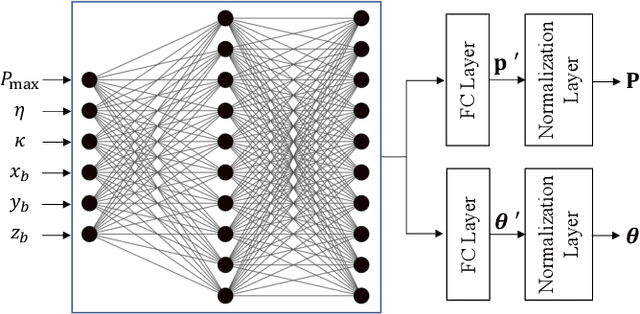
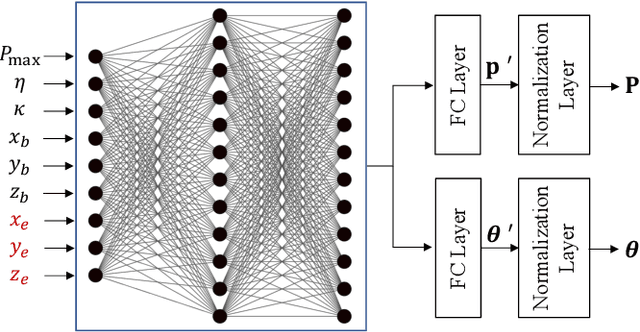
Abstract:Physical-layer key generation (PKG) based on wireless channels is a lightweight technique to establish secure keys between legitimate communication nodes. Recently, intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) have been leveraged to enhance the performance of PKG in terms of secret key rate (SKR), as it can reconfigure the wireless propagation environment and introduce more channel randomness. In this paper, we investigate an IRS-assisted PKG system, taking into account the channel spatial correlation at both the base station (BS) and the IRS. Based on the considered system model, the closed-form expression of SKR is derived analytically considering correlated eavesdropping channels. Aiming to maximise the SKR, a joint design problem of the BS precoding matrix and the IRS phase shift vector is formulated. To address this high-dimensional non-convex optimisation problem, we propose a novel unsupervised deep neural network (DNN)-based algorithm with a simple structure. Different from most previous works that adopt iterative optimisation to solve the problem, the proposed DNN-based algorithm directly obtains the BS precoding and IRS phase shifts as the output of the DNN. Simulation results reveal that the proposed DNN-based algorithm outperforms the benchmark methods with regard to SKR.
Machine Learning-Based Secret Key Generation for IRS-assisted Multi-antenna Systems
Jan 19, 2023Abstract:Physical-layer key generation (PKG) based on wireless channels is a lightweight technique to establish secure keys between legitimate communication nodes. Recently, intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) have been leveraged to enhance the performance of PKG in terms of secret key rate (SKR), as it can reconfigure the wireless propagation environment and introduce more channel randomness. In this paper, we investigate an IRS-assisted PKG system, taking into account the channel spatial correlation at both the base station (BS) and the IRS. Based on the considered system model, the closed form expression of SKR is derived analytically. Aiming to maximize the SKR, a joint design problem of the BS precoding matrix and the IRS reflecting coefficient vector is formulated. To address this high-dimensional non-convex optimization problem, we propose a novel unsupervised deep neural network (DNN) based algorithm with a simple structure. Different from most previous works that adopt the iterative optimization to solve the problem, the proposed DNN based algorithm directly obtains the BS precoding and IRS phase shifts as the output of the DNN. Simulation results reveal that the proposed DNN-based algorithm outperforms the benchmark methods with regard to SKR.
Towards Receiver-Agnostic and Collaborative Radio Frequency Fingerprint Identification
Jul 06, 2022



Abstract:Radio frequency fingerprint identification (RFFI) is an emerging device authentication technique, which exploits the hardware characteristics of the RF front-end as device identifiers. RFFI is implemented in the wireless receiver and acts to extract the transmitter impairments and then perform classification. The receiver hardware impairments will actually interfere with the feature extraction process, but its effect and mitigation have not been comprehensively studied. In this paper, we propose a receiver-agnostic RFFI system that is not sensitive to the changes in receiver characteristics; it is implemented by employing adversarial training to learn the receiver-independent features. Moreover, when there are multiple receivers, this functionality can perform collaborative inference to enhance classification accuracy. Finally, we show how it is possible to leverage fine-tuning for further improvement with fewer collected signals. To validate the approach, we have conducted extensive experimental evaluation by applying the approach to a LoRaWAN case study involving ten LoRa devices and 20 software-defined radio (SDR) receivers. The results show that receiver-agnostic training enables the trained neural network to become robust to changes in receiver characteristics. The collaborative inference improves classification accuracy by up to 20% beyond a single-receiver RFFI system and fine-tuning can bring a 40% improvement for under-performing receivers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge