Lilian Wanzare
Maseno University Kenya
Building low-resource African language corpora: A case study of Kidawida, Kalenjin and Dholuo
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:Natural Language Processing is a crucial frontier in artificial intelligence, with broad applications in many areas, including public health, agriculture, education, and commerce. However, due to the lack of substantial linguistic resources, many African languages remain underrepresented in this digital transformation. This paper presents a case study on the development of linguistic corpora for three under-resourced Kenyan languages, Kidaw'ida, Kalenjin, and Dholuo, with the aim of advancing natural language processing and linguistic research in African communities. Our project, which lasted one year, employed a selective crowd-sourcing methodology to collect text and speech data from native speakers of these languages. Data collection involved (1) recording conversations and translation of the resulting text into Kiswahili, thereby creating parallel corpora, and (2) reading and recording written texts to generate speech corpora. We made these resources freely accessible via open-research platforms, namely Zenodo for the parallel text corpora and Mozilla Common Voice for the speech datasets, thus facilitating ongoing contributions and access for developers to train models and develop Natural Language Processing applications. The project demonstrates how grassroots efforts in corpus building can support the inclusion of African languages in artificial intelligence innovations. In addition to filling resource gaps, these corpora are vital in promoting linguistic diversity and empowering local communities by enabling Natural Language Processing applications tailored to their needs. As African countries like Kenya increasingly embrace digital transformation, developing indigenous language resources becomes essential for inclusive growth. We encourage continued collaboration from native speakers and developers to expand and utilize these corpora.
Kenyan Sign Language (KSL) Dataset: Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Bridging Communication Barrier among the Deaf Learners
Oct 23, 2024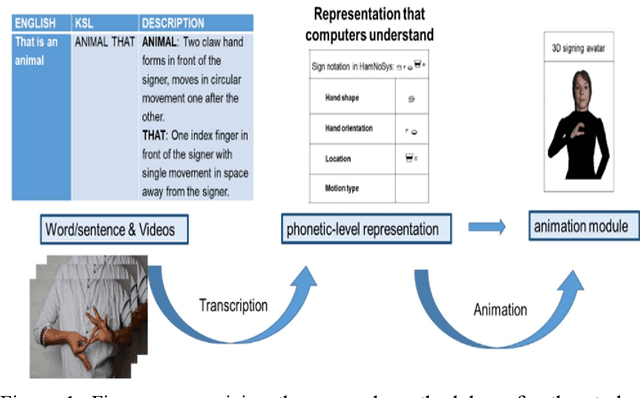
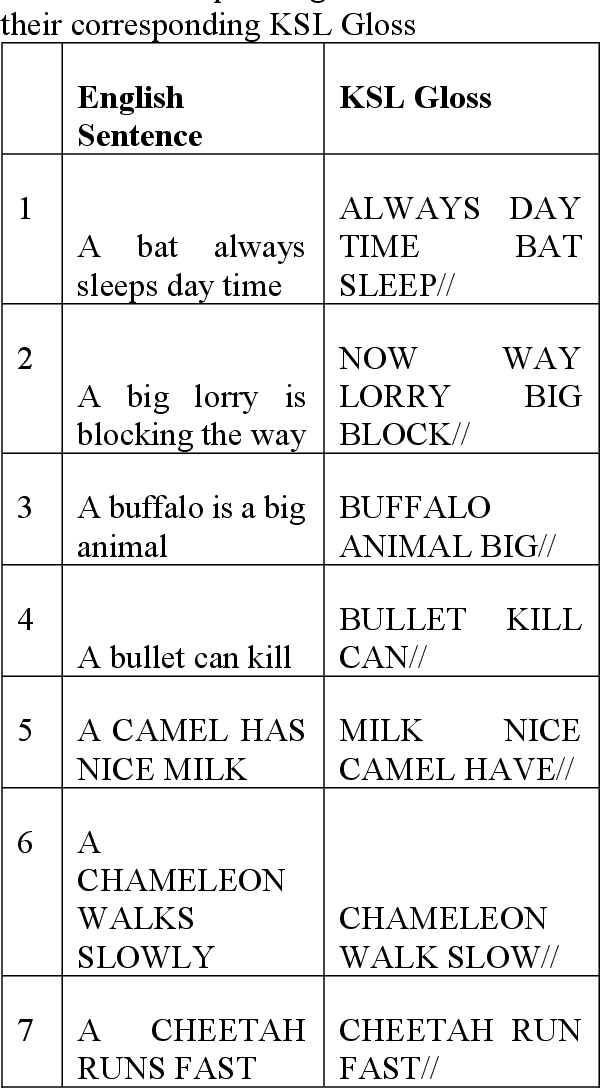

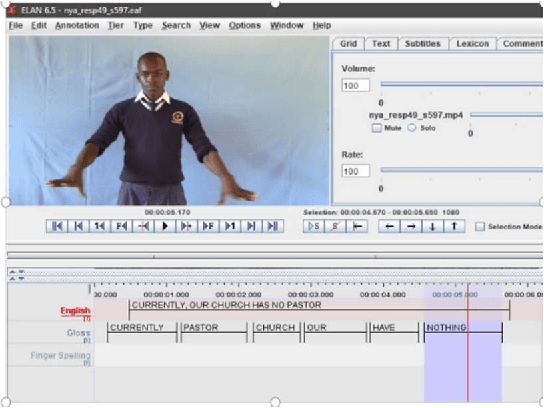
Abstract:Kenyan Sign Language (KSL) is the primary language used by the deaf community in Kenya. It is the medium of instruction from Pre-primary 1 to university among deaf learners, facilitating their education and academic achievement. Kenyan Sign Language is used for social interaction, expression of needs, making requests and general communication among persons who are deaf in Kenya. However, there exists a language barrier between the deaf and the hearing people in Kenya. Thus, the innovation on AI4KSL is key in eliminating the communication barrier. Artificial intelligence for KSL is a two-year research project (2023-2024) that aims to create a digital open-access AI of spontaneous and elicited data from a representative sample of the Kenyan deaf community. The purpose of this study is to develop AI assistive technology dataset that translates English to KSL as a way of fostering inclusion and bridging language barriers among deaf learners in Kenya. Specific objectives are: Build KSL dataset for spoken English and video recorded Kenyan Sign Language and to build transcriptions of the KSL signs to a phonetic-level interface of the sign language. In this paper, the methodology for building the dataset is described. Data was collected from 48 teachers and tutors of the deaf learners and 400 learners who are Deaf. Participants engaged mainly in sign language elicitation tasks through reading and singing. Findings of the dataset consisted of about 14,000 English sentences with corresponding KSL Gloss derived from a pool of about 4000 words and about 20,000 signed KSL videos that are either signed words or sentences. The second level of data outcomes consisted of 10,000 split and segmented KSL videos. The third outcome of the dataset consists of 4,000 transcribed words into five articulatory parameters according to HamNoSys system.
Phonemic Representation and Transcription for Speech to Text Applications for Under-resourced Indigenous African Languages: The Case of Kiswahili
Oct 29, 2022Abstract:Building automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems is a challenging task, especially for under-resourced languages that need to construct corpora nearly from scratch and lack sufficient training data. It has emerged that several African indigenous languages, including Kiswahili, are technologically under-resourced. ASR systems are crucial, particularly for the hearing-impaired persons who can benefit from having transcripts in their native languages. However, the absence of transcribed speech datasets has complicated efforts to develop ASR models for these indigenous languages. This paper explores the transcription process and the development of a Kiswahili speech corpus, which includes both read-out texts and spontaneous speech data from native Kiswahili speakers. The study also discusses the vowels and consonants in Kiswahili and provides an updated Kiswahili phoneme dictionary for the ASR model that was created using the CMU Sphinx speech recognition toolbox, an open-source speech recognition toolkit. The ASR model was trained using an extended phonetic set that yielded a WER and SER of 18.87% and 49.5%, respectively, an improved performance than previous similar research for under-resourced languages.
Kencorpus: A Kenyan Language Corpus of Swahili, Dholuo and Luhya for Natural Language Processing Tasks
Aug 25, 2022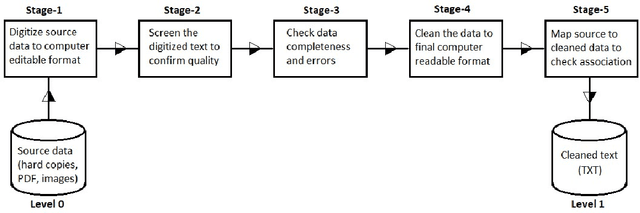
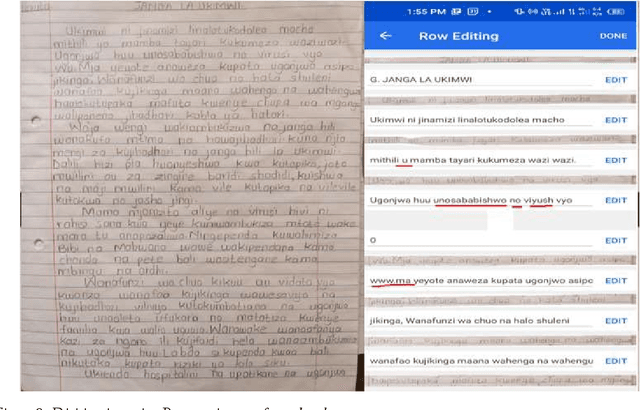

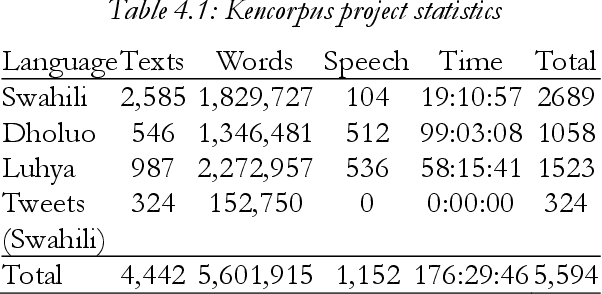
Abstract:Indigenous African languages are categorized as under-served in Artificial Intelligence and suffer poor digital inclusivity and information access. The challenge has been how to use machine learning and deep learning models without the requisite data. Kencorpus is a Kenyan Language corpus that intends to bridge the gap on how to collect, and store text and speech data that is good enough to enable data-driven solutions in applications such as machine translation, question answering and transcription in multilingual communities. Kencorpus is a corpus (text and speech) for three languages predominantly spoken in Kenya: Swahili, Dholuo and Luhya (dialects Lumarachi, Lulogooli and Lubukusu). This corpus intends to fill the gap of developing a dataset that can be used for Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning tasks for low-resource languages. Each of these languages contributed text and speech data for the language corpus. Data collection was done by researchers from communities, schools and collaborating partners (media, publishers). Kencorpus has a collection of 5,594 items, being 4,442 texts (5.6million words) and 1,152 speech files (177hrs). Based on this data, other datasets were also developed e.g POS tagging sets for Dholuo and Luhya (50,000 and 93,000 words tagged respectively), Question-Answer pairs from Swahili texts (7,537 QA pairs) and Translation of texts into Swahili (12,400 sentences). The datasets are useful for machine learning tasks such as text processing, annotation and translation. The project also undertook proof of concept systems in speech to text and machine learning for QA task, with initial results confirming the usability of the Kencorpus to the machine learning community. Kencorpus is the first such corpus of its kind for these low resource languages and forms a basis of learning and sharing experiences for similar works.
KenSwQuAD -- A Question Answering Dataset for Swahili Low Resource Language
May 04, 2022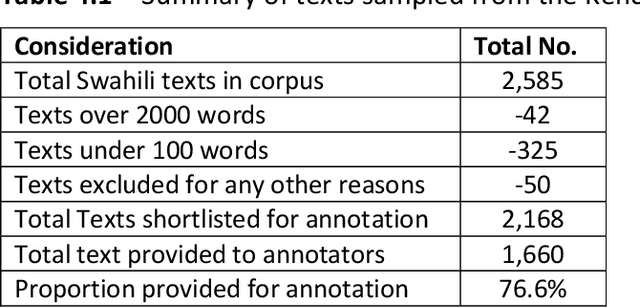
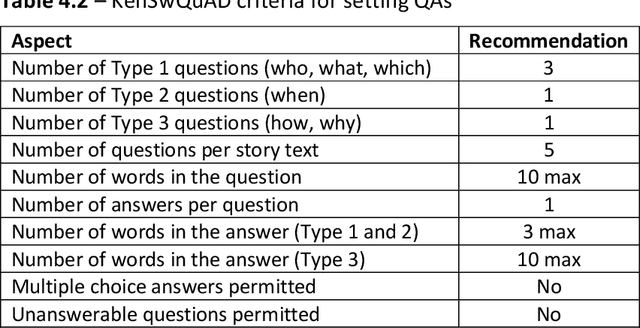
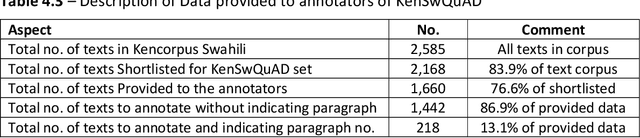

Abstract:This research developed a Kencorpus Swahili Question Answering Dataset KenSwQuAD from raw data of Swahili language, which is a low resource language predominantly spoken in Eastern African and also has speakers in other parts of the world. Question Answering datasets are important for machine comprehension of natural language processing tasks such as internet search and dialog systems. However, before such machine learning systems can perform these tasks, they need training data such as the gold standard Question Answering (QA) set that is developed in this research. The research engaged annotators to formulate question answer pairs from Swahili texts that had been collected by the Kencorpus project, a Kenyan languages corpus that collected data from three Kenyan languages. The total Swahili data collection had 2,585 texts, out of which we annotated 1,445 story texts with at least 5 QA pairs each, resulting into a final dataset of 7,526 QA pairs. A quality assurance set of 12.5% of the annotated texts was subjected to re-evaluation by different annotators who confirmed that the QA pairs were all correctly annotated. A proof of concept on applying the set to machine learning on the question answering task confirmed that the dataset can be used for such practical tasks. The research therefore developed KenSwQuAD, a question-answer dataset for Swahili that is useful to the natural language processing community who need training and gold standard sets for their machine learning applications. The research also contributed to the resourcing of the Swahili language which is important for communication around the globe. Updating this set and providing similar sets for other low resource languages is an important research area that is worthy of further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge