Lianlian Jiang
Day-Ahead Electricity Price Forecasting for Volatile Markets Using Foundation Models with Regularization Strategy
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Electricity price forecasting (EPF) is essential for energy markets stakeholders (e.g. grid operators, energy traders, policymakers) but remains challenging due to the inherent volatility and nonlinearity of price signals. Traditional statistical and deep learning (DL) models often struggle to capture complex temporal dependencies and integrate heterogeneous data effectively. While time series foundation models (TSFMs) have shown strong performance in general time series forecasting tasks, such as traffic forecasting and weather forecasting. However, their effectiveness in day-ahead EPF, particularly in volatile markets, remains underexplored. This paper presents a spike regularization strategy and evaluates a wide range of TSFMs, including Tiny Time Mixers (TTMs), MOIRAI, MOMENT, and TimesFM, against traditional statistical and DL models such as Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA), Long-short Term Memory (LSTM), and Convolutional Neural Network - LSTM (CNN-LSTM) using half-hourly wholesale market data with volatile trends in Singapore. Exogenous factors (e.g. weather and calendar variables) are also incorporated into models where applicable. Results demonstrate that TSFMs consistently outperform traditional approaches, achieving up to 37.4% improvement in MAPE across various evaluation settings. The findings offer practical guidance for improving forecast accuracy and decision-making in volatile electricity markets.
LSTMSPLIT: Effective SPLIT Learning based LSTM on Sequential Time-Series Data
Mar 08, 2022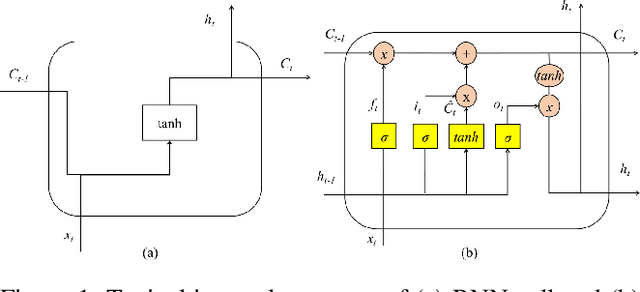
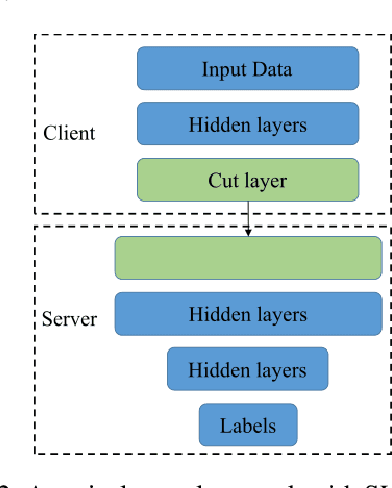
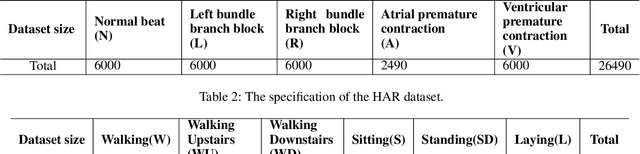
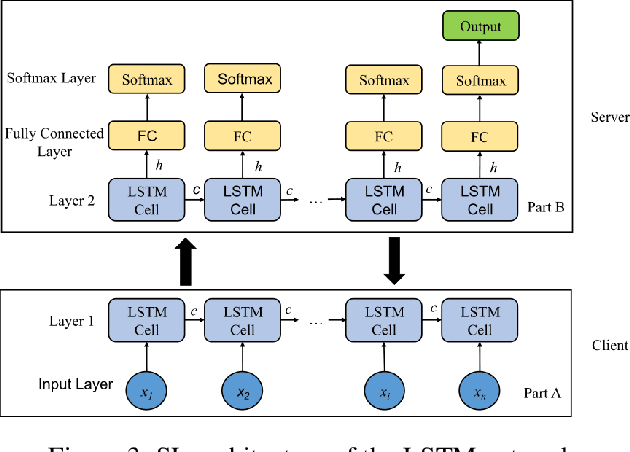
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) and split learning (SL) are the two popular distributed machine learning (ML) approaches that provide some data privacy protection mechanisms. In the time-series classification problem, many researchers typically use 1D convolutional neural networks (1DCNNs) based on the SL approach with a single client to reduce the computational overhead at the client-side while still preserving data privacy. Another method, recurrent neural network (RNN), is utilized on sequentially partitioned data where segments of multiple-segment sequential data are distributed across various clients. However, to the best of our knowledge, it is still not much work done in SL with long short-term memory (LSTM) network, even the LSTM network is practically effective in processing time-series data. In this work, we propose a new approach, LSTMSPLIT, that uses SL architecture with an LSTM network to classify time-series data with multiple clients. The differential privacy (DP) is applied to solve the data privacy leakage. The proposed method, LSTMSPLIT, has achieved better or reasonable accuracy compared to the Split-1DCNN method using the electrocardiogram dataset and the human activity recognition dataset. Furthermore, the proposed method, LSTMSPLIT, can also achieve good accuracy after applying differential privacy to preserve the user privacy of the cut layer of the LSTMSPLIT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge