Liangzi Rong
A Strong Baseline for Crowd Counting and Unsupervised People Localization
Nov 07, 2020
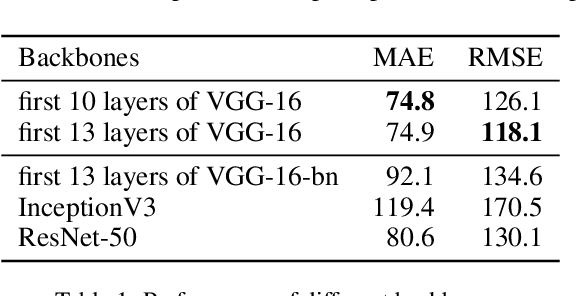
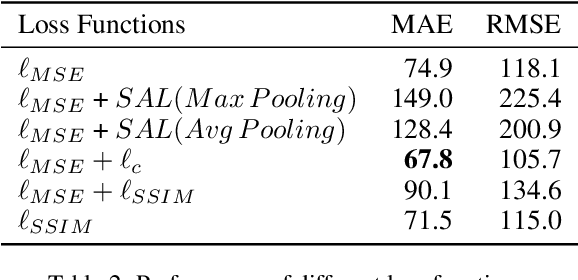

Abstract:In this paper, we explore a strong baseline for crowd counting and an unsupervised people localization algorithm based on estimated density maps. Firstly, existing methods achieve state-of-the-art performance based on different backbones and kinds of training tricks. We collect different backbones and training tricks and evaluate the impact of changing them and develop an efficient pipeline for crowd counting, which decreases MAE and RMSE significantly on multiple datasets. We also propose a clustering algorithm named isolated KMeans to locate the heads in density maps. This method can divide the density maps into subregions and find the centers under local count constraints without training any parameter and can be integrated with existing methods easily.
Coarse- and Fine-grained Attention Network with Background-aware Loss for Crowd Density Map Estimation
Nov 07, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel method Coarse- and Fine-grained Attention Network (CFANet) for generating high-quality crowd density maps and people count estimation by incorporating attention maps to better focus on the crowd area. We devise a from-coarse-to-fine progressive attention mechanism by integrating Crowd Region Recognizer (CRR) and Density Level Estimator (DLE) branch, which can suppress the influence of irrelevant background and assign attention weights according to the crowd density levels, because generating accurate fine-grained attention maps directly is normally difficult. We also employ a multi-level supervision mechanism to assist the backpropagation of gradient and reduce overfitting. Besides, we propose a Background-aware Structural Loss (BSL) to reduce the false recognition ratio while improving the structural similarity to groundtruth. Extensive experiments on commonly used datasets show that our method can not only outperform previous state-of-the-art methods in terms of count accuracy but also improve the image quality of density maps as well as reduce the false recognition ratio.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge