Leyla Rabiei
Iran Telecommunication Research Center
Colloquial Persian POS Corpus: A Novel Corpus for Colloquial Persian Part of Speech Tagging
Oct 01, 2023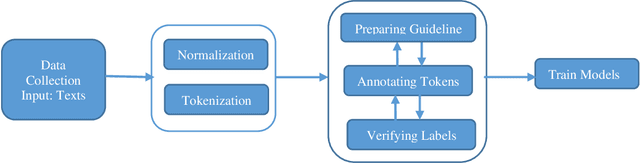

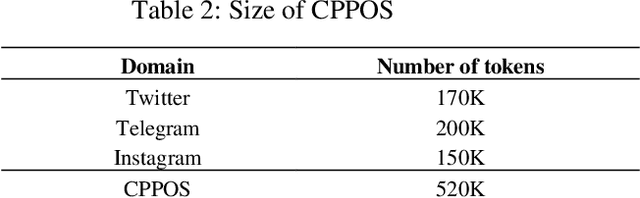
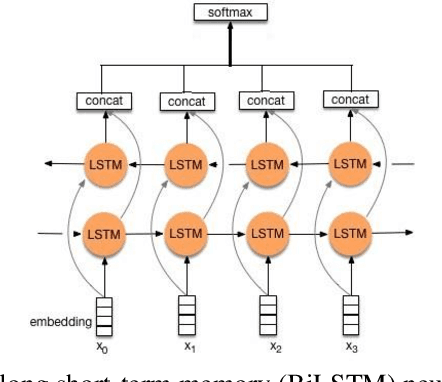
Abstract:Introduction: Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging, the process of classifying words into their respective parts of speech (e.g., verb or noun), is essential in various natural language processing applications. POS tagging is a crucial preprocessing task for applications like machine translation, question answering, sentiment analysis, etc. However, existing corpora for POS tagging in Persian mainly consist of formal texts, such as daily news and newspapers. As a result, smart POS tools, machine learning models, and deep learning models trained on these corpora may not perform optimally for processing colloquial text in social network analysis. Method: This paper introduces a novel corpus, "Colloquial Persian POS" (CPPOS), specifically designed to support colloquial Persian text. The corpus includes formal and informal text collected from various domains such as political, social, and commercial on Telegram, Twitter, and Instagram more than 520K labeled tokens. After collecting posts from these social platforms for one year, special preprocessing steps were conducted, including normalization, sentence tokenizing, and word tokenizing for social text. The tokens and sentences were then manually annotated and verified by a team of linguistic experts. This study also defines a POS tagging guideline for annotating the data and conducting the annotation process. Results: To evaluate the quality of CPPOS, various deep learning models, such as the RNN family, were trained using the constructed corpus. A comparison with another well-known Persian POS corpus named "Bijankhan" and the Persian Hazm POS tool trained on Bijankhan revealed that our model trained on CPPOS outperforms them. With the new corpus and the BiLSTM deep neural model, we achieved a 14% improvement over the previous dataset.
Constructing Colloquial Dataset for Persian Sentiment Analysis of Social Microblogs
Jun 22, 2023Abstract:Introduction: Microblogging websites have massed rich data sources for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In this regard, sentiment classification has frequently proven inefficient because microblog posts typically lack syntactically consistent terms and representatives since users on these social networks do not like to write lengthy statements. Also, there are some limitations to low-resource languages. The Persian language has exceptional characteristics and demands unique annotated data and models for the sentiment analysis task, which are distinctive from text features within the English dialect. Method: This paper first constructs a user opinion dataset called ITRC-Opinion by collaborative environment and insource way. Our dataset contains 60,000 informal and colloquial Persian texts from social microblogs such as Twitter and Instagram. Second, this study proposes a new deep convolutional neural network (CNN) model for more effective sentiment analysis of colloquial text in social microblog posts. The constructed datasets are used to evaluate the presented model. Furthermore, some models, such as LSTM, CNN-RNN, BiLSTM, and BiGRU with different word embeddings, including Fasttext, Glove, and Word2vec, investigated our dataset and evaluated the results. Results: The results demonstrate the benefit of our dataset and the proposed model (72% accuracy), displaying meaningful improvement in sentiment classification performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge