Levi Kieft
A Passive Mechanical Add-on for Treadmill Exercise (P-MATE) in Stroke Rehabilitation
Jan 06, 2025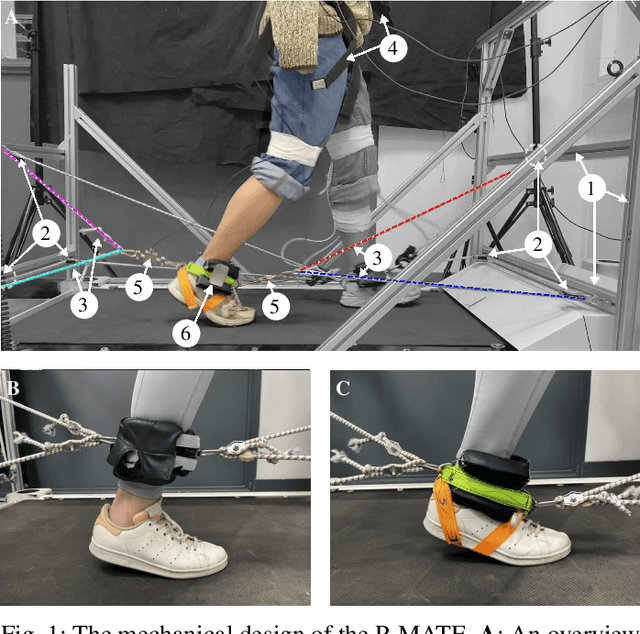
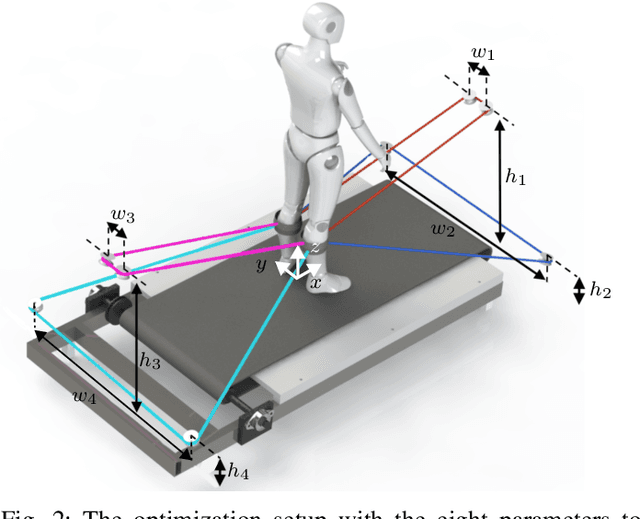
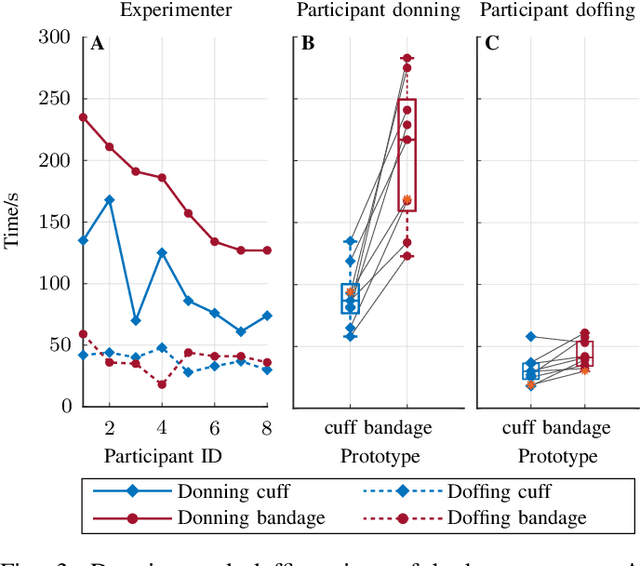
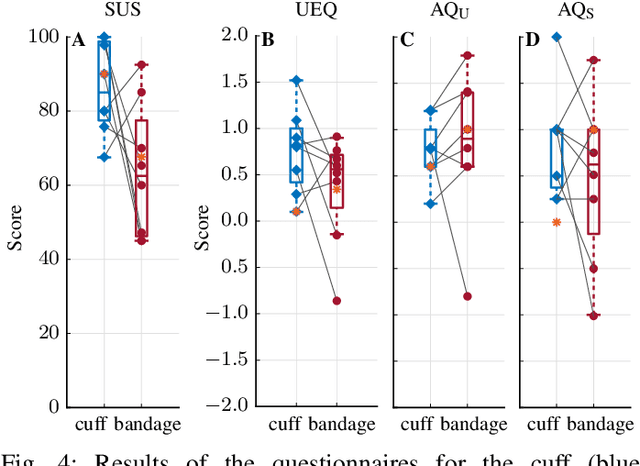
Abstract:Robotic rehabilitation can deliver high-dose gait therapy and improve motor function after a stroke. However, for many devices, high costs and lengthy setup times limit clinical adoption. Thus, we designed, built, and evaluated the Passive Mechanical Add-on for Treadmill Exercise (P-MATE), a low-cost passive end-effector add-on for treadmills that couples the movement of the paretic and non-paretic legs via a reciprocating system of elastic cables and pulleys. Two human-device mechanical interfaces were designed to attach the elastic cables to the user. The P-MATE and two interface prototypes were tested with a physical therapist and eight unimpaired participants. Biomechanical data, including kinematics and interaction forces, were collected alongside standardized questionnaires to assess usability and user experience. Both interfaces were quick and easy to attach, though user experience differed, highlighting the need for personalization. We also identified areas for future improvement, including pretension adjustments, tendon derailing prevention, and understanding long-term impacts on user gait. Our preliminary findings underline the potential of the P-MATE to provide effective, accessible, and sustainable stroke gait rehabilitation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge