Lechi Li
Deep Fusion of Multi-Object Densities Using Transformer
Sep 23, 2022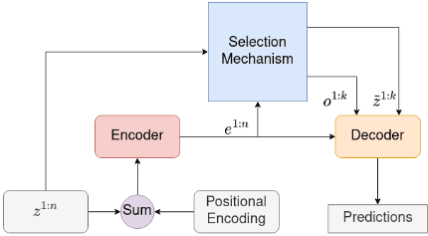
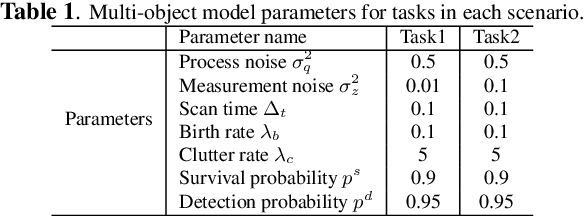
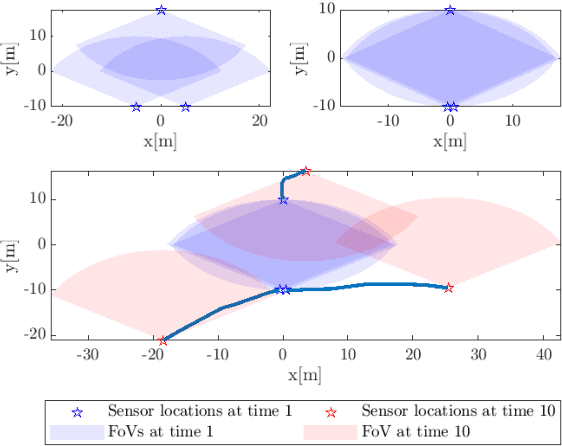
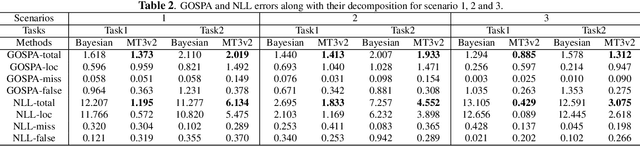
Abstract:In this paper, we demonstrate that deep learning based method can be used to fuse multi-object densities. Given a scenario with several sensors with possibly different field-of-views, tracking is performed locally in each sensor by a tracker, which produces random finite set multi-object densities. To fuse outputs from different trackers, we adapt a recently proposed transformer-based multi-object tracker, where the fusion result is a global multi-object density, describing the set of all alive objects at the current time. We compare the performance of the transformer-based fusion method with a well-performing model-based Bayesian fusion method in several simulated scenarios with different parameter settings using synthetic data. The simulation results show that the transformer-based fusion method outperforms the model-based Bayesian method in our experimental scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge