Lazar Đoković
Sarcasm Detection in a Less-Resourced Language
Oct 16, 2024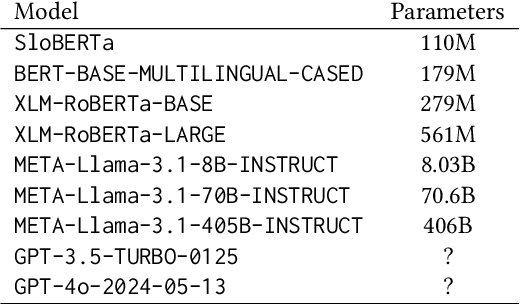
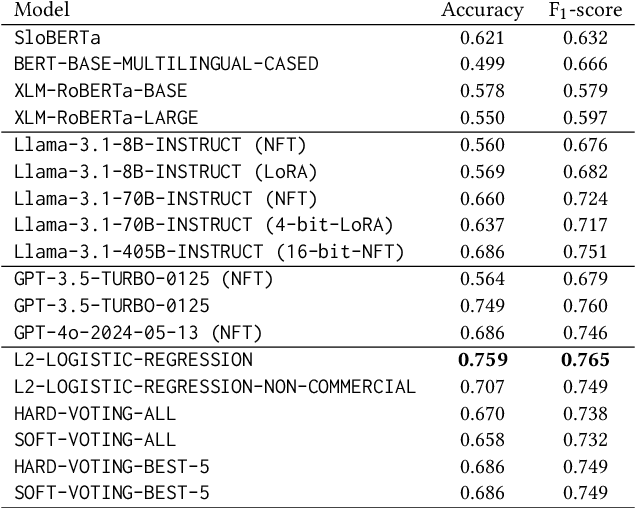
Abstract:The sarcasm detection task in natural language processing tries to classify whether an utterance is sarcastic or not. It is related to sentiment analysis since it often inverts surface sentiment. Because sarcastic sentences are highly dependent on context, and they are often accompanied by various non-verbal cues, the task is challenging. Most of related work focuses on high-resourced languages like English. To build a sarcasm detection dataset for a less-resourced language, such as Slovenian, we leverage two modern techniques: a machine translation specific medium-size transformer model, and a very large generative language model. We explore the viability of translated datasets and how the size of a pretrained transformer affects its ability to detect sarcasm. We train ensembles of detection models and evaluate models' performance. The results show that larger models generally outperform smaller ones and that ensembling can slightly improve sarcasm detection performance. Our best ensemble approach achieves an $\text{F}_1$-score of 0.765 which is close to annotators' agreement in the source language.
* 4 pages, published in the Slovenian Conference on Artificial Intelligence
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge