Laura Verde
Reproducible Machine Learning-based Voice Pathology Detection: Introducing the Pitch Difference Feature
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we propose a robust set of features derived from a thorough research of contemporary practices in voice pathology detection. The feature set is based on the combination of acoustic handcrafted features. Additionally, we introduce pitch difference as a novel feature. We combine this feature set, containing data from the publicly available Saarbr\"ucken Voice Database (SVD), with preprocessing using the K-Means Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique algorithm to address class imbalance. Moreover, we applied multiple ML models as binary classifiers. We utilized support vector machine, k-nearest neighbors, naive Bayes, decision tree, random forest and AdaBoost classifiers. To determine the best classification approach, we performed grid search on feasible hyperparameters of respective classifiers and subsections of features. Our approach has achieved the state-of-the-art performance, measured by unweighted average recall in voice pathology detection on SVD database. We intentionally omit accuracy as it is highly biased metric in case of unbalanced data compared to aforementioned metrics. The results are further enhanced by eliminating the potential overestimation of the results with repeated stratified cross-validation. This advancement demonstrates significant potential for the clinical deployment of ML methods, offering a valuable tool for an objective examination of voice pathologies. To support our claims, we provide a publicly available GitHub repository with DOI 10.5281/zenodo.13771573. Finally, we provide REFORMS checklist.
Towards an extension of Fault Trees in the Predictive Maintenance Scenario
Mar 20, 2024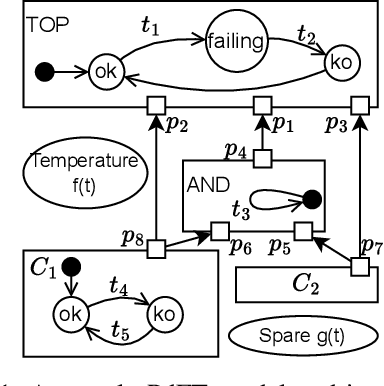
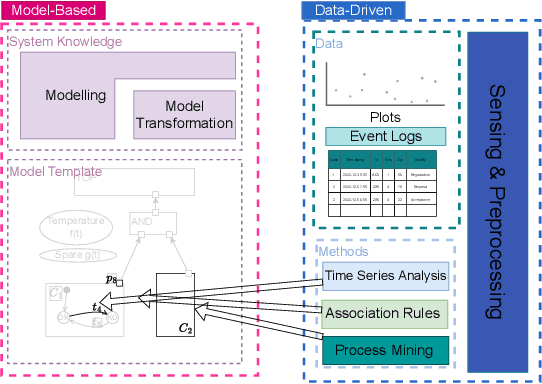
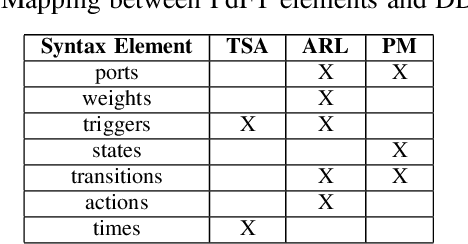
Abstract:One of the most appreciated features of Fault Trees (FTs) is their simplicity, making them fit into industrial processes. As such processes evolve in time, considering new aspects of large modern systems, modelling techniques based on FTs have adapted to these needs. This paper proposes an extension of FTs to take into account the problem of Predictive Maintenance, one of the challenges of the modern dependability field of study. The paper sketches the Predictive Fault Tree language and proposes some use cases to support their modelling and analysis in concrete industrial settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge