Ladislau Matekovits
Simple Wideband RCS Reduction by Phase Gradient Modulated Surface
Jun 27, 2021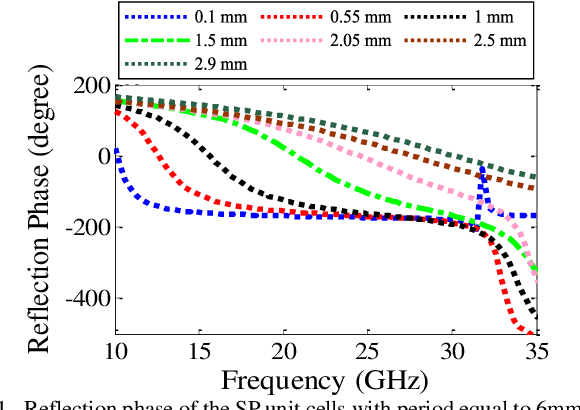
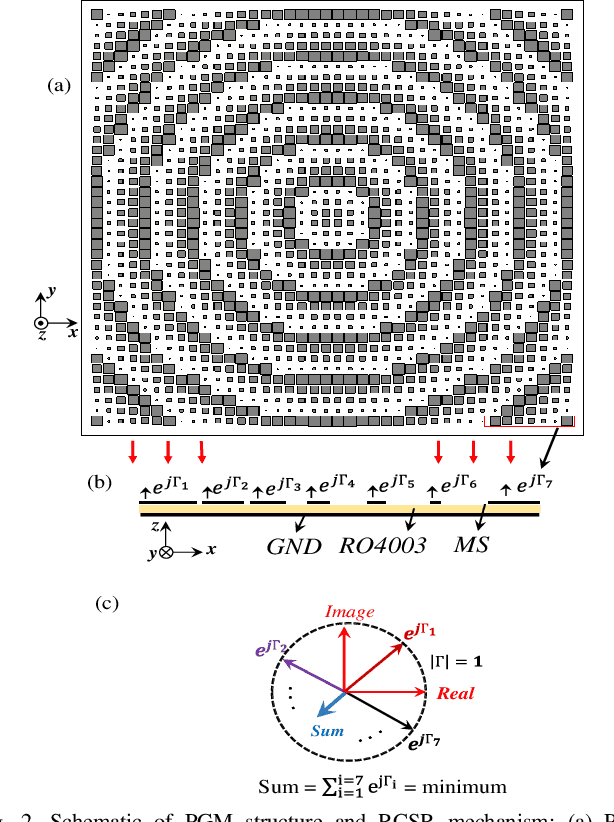
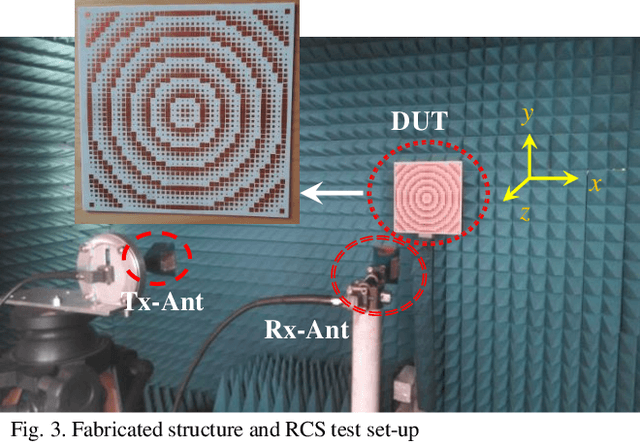
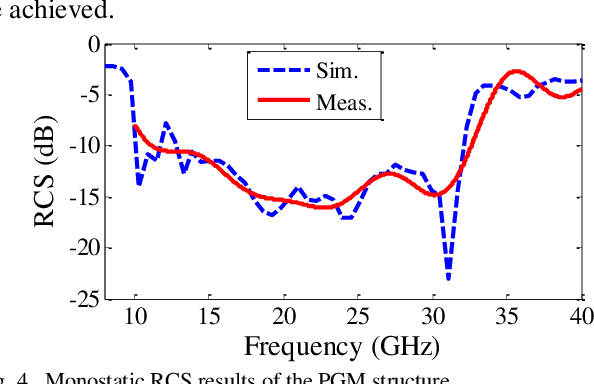
Abstract:This paper presents the design and implementation of a simple, single-layer, broadband (97%, 11.3-32.3 GHz) Radar Cross Section Reduction (RCSR) Modulated Surface (MS). It uses modulation of the edge-length of the square patch (SP) radiators within adjacent unit cells. By using Sinusoidal Modulation (SM) of the edge length of the unit cells, the unit cells sequences with phase gradient, that plays an effective role in improving the RCSR, can be used for wideband RCSR achievement. The proposed structure with the dimension of 250*250mm2 that consists of 40 * 40 unit cells with period of 6mm printed on a RO4003 substrate of 1.6mm thickness and has been considered. Measurements on a prototype were conducted considering both mono- and bi-static arrangements for oblique incidences for both TM and TE polarization tests. A good agreement between simulation and measurement results proves the validity of the design criteria.
Bi-static Radar Cross Section Test Method by Using Historic Marconi Set-up and Time Gating
Jun 27, 2021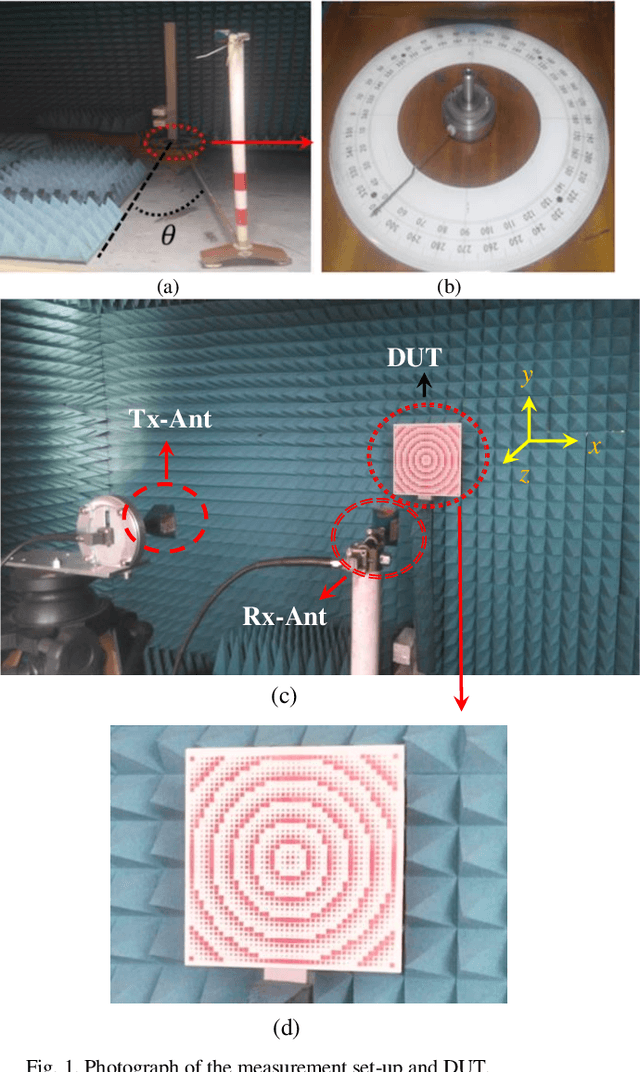
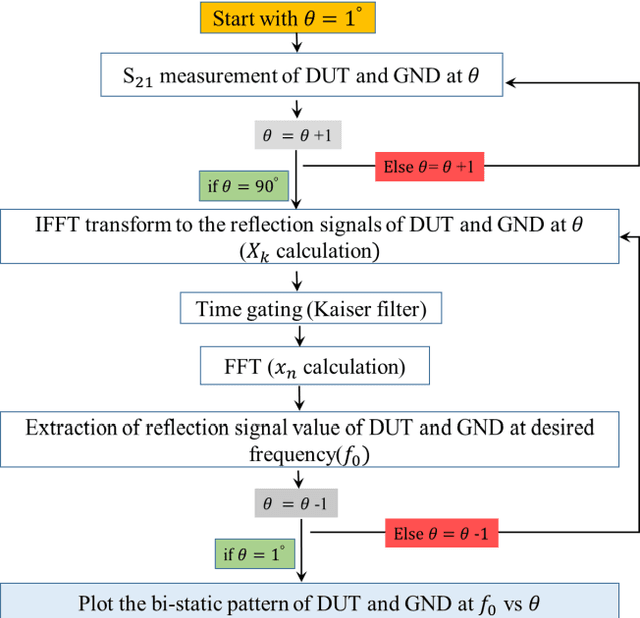
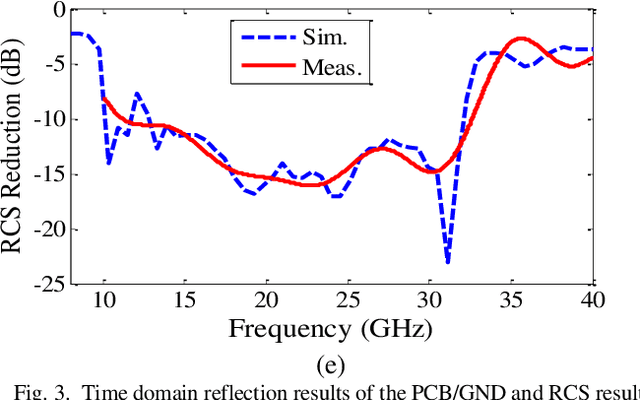
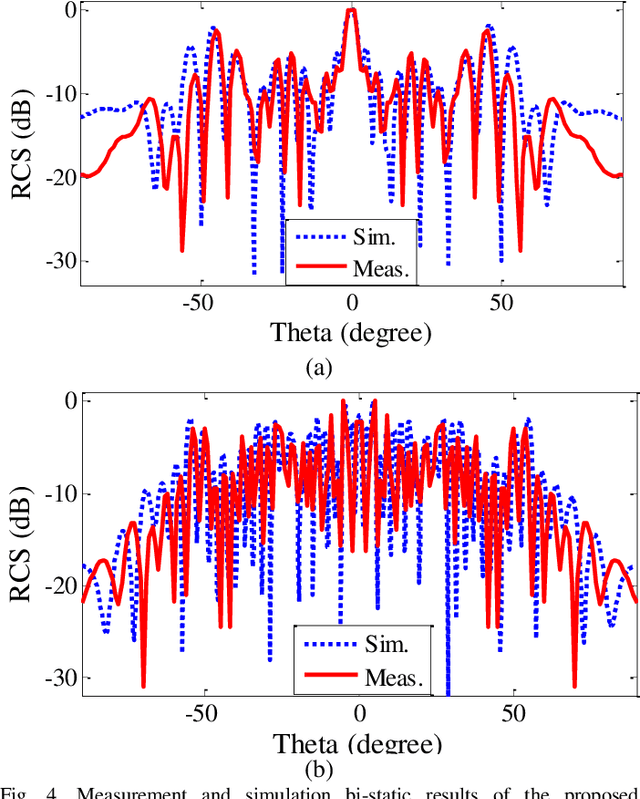
Abstract:In this paper, a low-cost, simple and reliable bi-static Radar Cross Section (RCS) measurement method making use a historic Marconi set-up is presented. It uses a transmitting (Tx) antenna (located at a constant position, at a reference angle of {\theta} = 0o) and a receiver (Rx) antenna (mounted on a moveable arm calibrated in the azimuthal direction with an accuracy of 0.1o). A time gating method is used to extract the information from the reflection in the time domain; applying time filter allows removing the antenna side lobe effects and other ambient noise. In this method, the Rx antenna (on the movable arm) is used to measure the reflected field in the angular range from 1o to 90o of reflection from the structure (printed PCB) and from the reference configuration represented by a ground (GND) plane of the same dimension. The time gating method is then applied to each pair of PCB / GND measurements to extract the bi-static RCS pattern of the structure at a given frequency. Here comparison of measurement results carried out at 18 GHz and 32 GHz with simulation indicates the successful performance of the proposed method. It can be used as a low-cost, reliable and available option in future measurement and scientific research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge