Kunihito Kato
Vision-Language In-Context Learning Driven Few-Shot Visual Inspection Model
Feb 13, 2025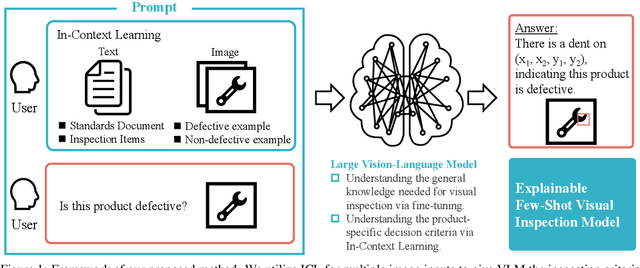
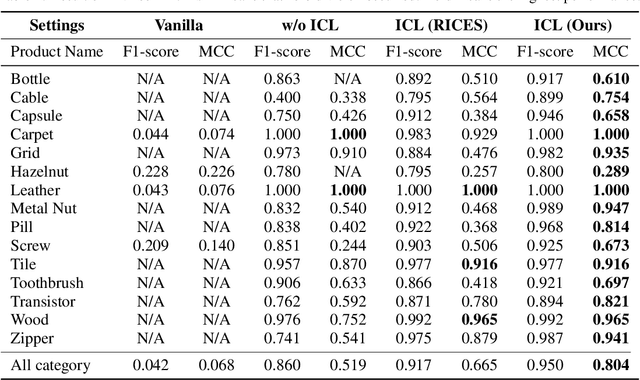
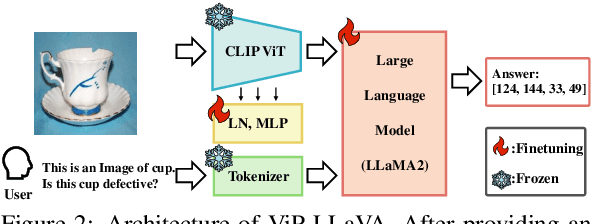
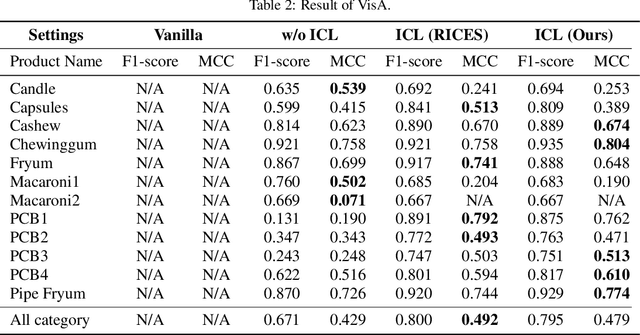
Abstract:We propose general visual inspection model using Vision-Language Model~(VLM) with few-shot images of non-defective or defective products, along with explanatory texts that serve as inspection criteria. Although existing VLM exhibit high performance across various tasks, they are not trained on specific tasks such as visual inspection. Thus, we construct a dataset consisting of diverse images of non-defective and defective products collected from the web, along with unified formatted output text, and fine-tune VLM. For new products, our method employs In-Context Learning, which allows the model to perform inspections with an example of non-defective or defective image and the corresponding explanatory texts with visual prompts. This approach eliminates the need to collect a large number of training samples and re-train the model for each product. The experimental results show that our method achieves high performance, with MCC of 0.804 and F1-score of 0.950 on MVTec AD in a one-shot manner. Our code is available at~https://github.com/ia-gu/Vision-Language-In-Context-Learning-Driven-Few-Shot-Visual-Inspection-Model.
Benchmarking of Query Strategies: Towards Future Deep Active Learning
Dec 10, 2023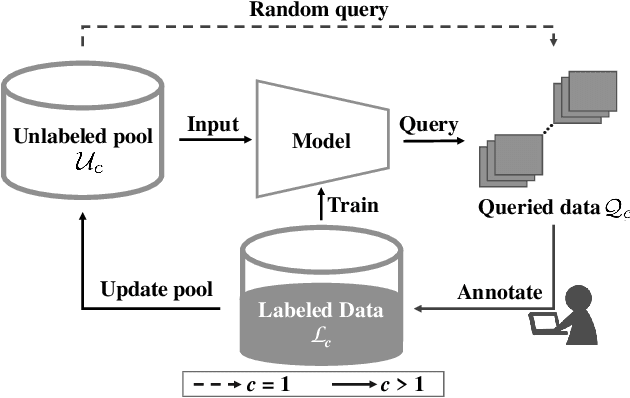
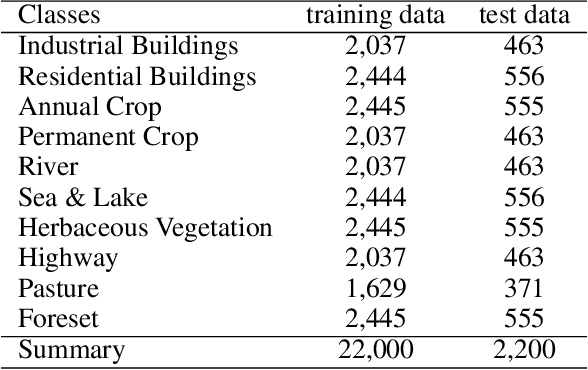
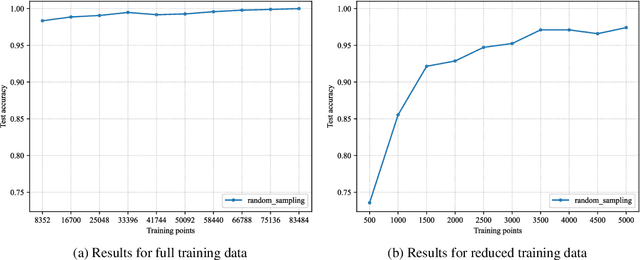
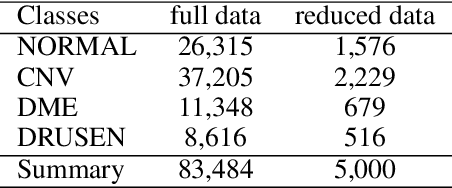
Abstract:In this study, we benchmark query strategies for deep actice learning~(DAL). DAL reduces annotation costs by annotating only high-quality samples selected by query strategies. Existing research has two main problems, that the experimental settings are not standardized, making the evaluation of existing methods is difficult, and that most of experiments were conducted on the CIFAR or MNIST datasets. Therefore, we develop standardized experimental settings for DAL and investigate the effectiveness of various query strategies using six datasets, including those that contain medical and visual inspection images. In addition, since most current DAL approaches are model-based, we perform verification experiments using fully-trained models for querying to investigate the effectiveness of these approaches for the six datasets. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/ia-gu/Benchmarking-of-Query-Strategies-Towards-Future-Deep-Active-Learning}
Hierarchical Pyramid Representations for Semantic Segmentation
Apr 05, 2021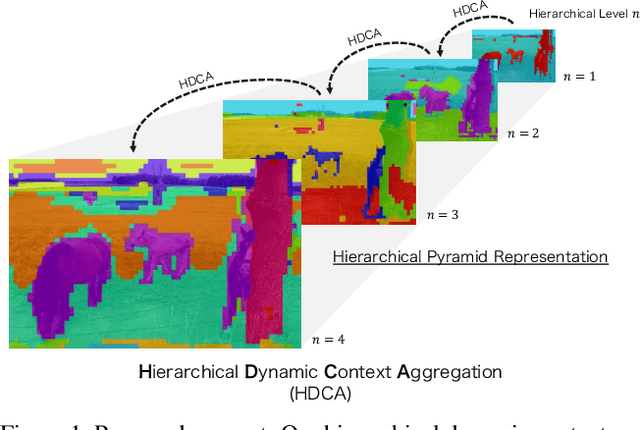
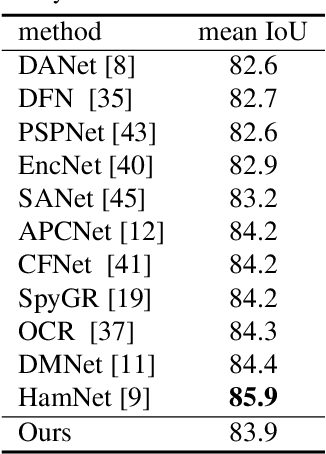
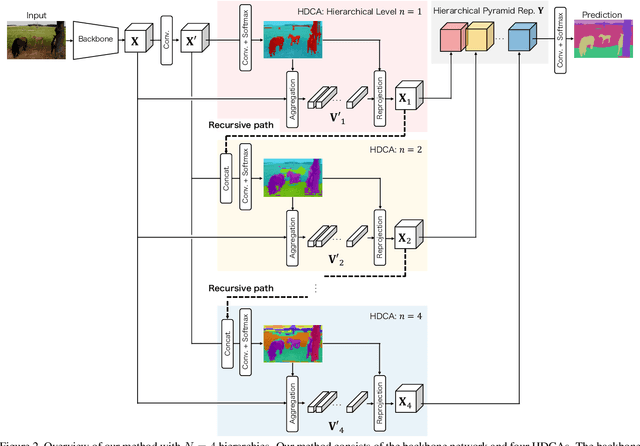
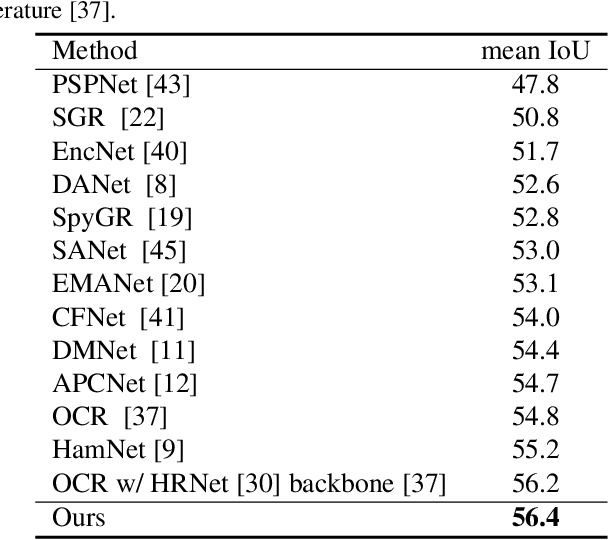
Abstract:Understanding the context of complex and cluttered scenes is a challenging problem for semantic segmentation. However, it is difficult to model the context without prior and additional supervision because the scene's factors, such as the scale, shape, and appearance of objects, vary considerably in these scenes. To solve this, we propose to learn the structures of objects and the hierarchy among objects because context is based on these intrinsic properties. In this study, we design novel hierarchical, contextual, and multiscale pyramidal representations to capture the properties from an input image. Our key idea is the recursive segmentation in different hierarchical regions based on a predefined number of regions and the aggregation of the context in these regions. The aggregated contexts are used to predict the contextual relationship between the regions and partition the regions in the following hierarchical level. Finally, by constructing the pyramid representations from the recursively aggregated context, multiscale and hierarchical properties are attained. In the experiments, we confirmed that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in PASCAL Context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge