Kieren Davies
More Effective Ontology Authoring with Test-Driven Development
Dec 14, 2018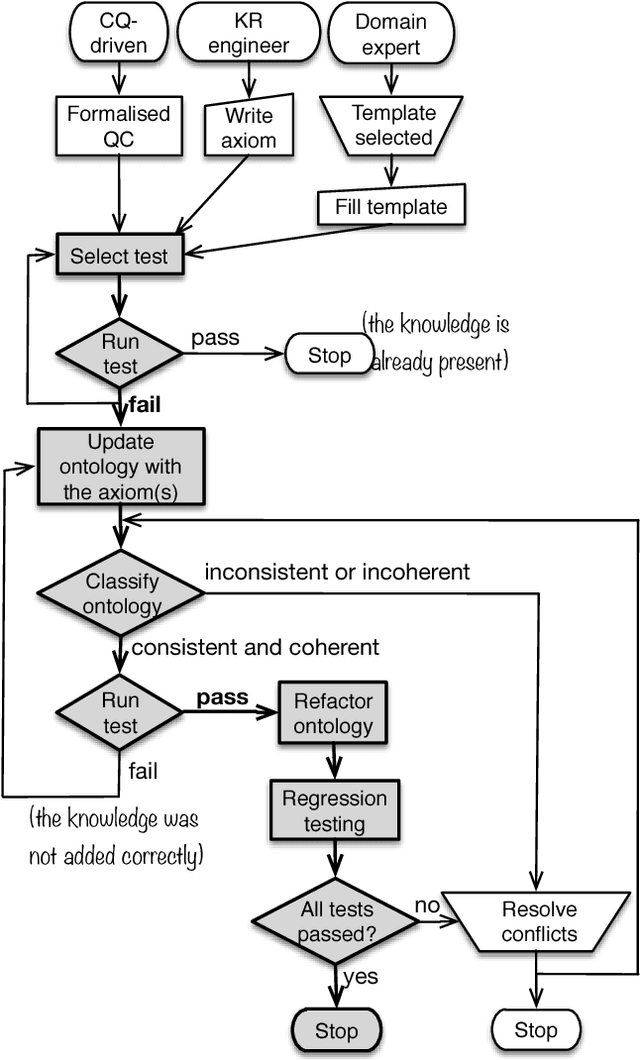
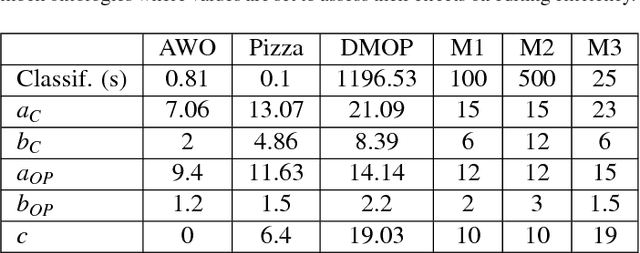
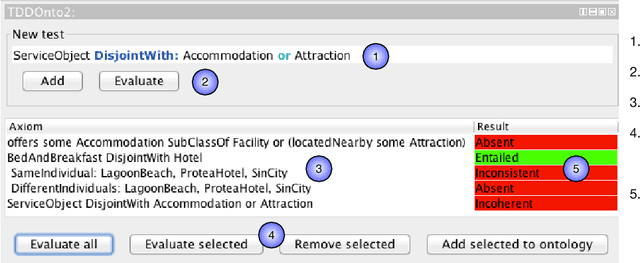
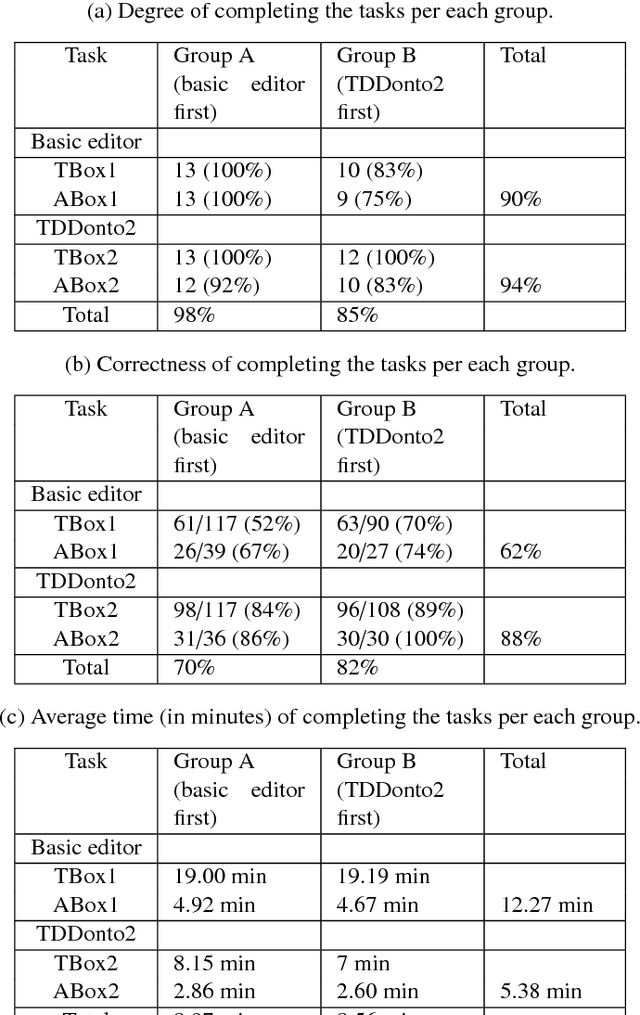
Abstract:Ontology authoring is a complex process, where commonly the automated reasoner is invoked for verification of newly introduced changes, therewith amounting to a time-consuming test-last approach. Test-Driven Development (TDD) for ontology authoring is a recent {\em test-first} approach that aims to reduce authoring time and increase authoring efficiency. Current TDD testing falls short on coverage of OWL features and possible test outcomes, the rigorous foundation thereof, and evaluations to ascertain its effectiveness. We aim to address these issues in one instantiation of TDD for ontology authoring. We first propose a succinct, logic-based model of TDD testing and present novel TDD algorithms so as to cover also any OWL 2 class expression for the TBox and for the principal ABox assertions, and prove their correctness. The algorithms use methods from the OWL API directly such that reclassification is not necessary for test execution, therewith reducing ontology authoring time. The algorithms were implemented in TDDonto2, a Prot\'eg\'e plugin. TDDonto2 was evaluated on editing efficiency and by users. The editing efficiency study demonstrated that it is faster than a typical ontology authoring interface, especially for medium size and large ontologies. The user evaluation demonstrated that modellers make significantly less errors with TDDonto2 compared to the standard Prot\'eg\'e interface and complete their tasks better using less time. Thus, the results indicate that Test-Driven Development is a promising approach in an ontology development methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge