Khaled Salah
BehavDT: A Behavioral Decision Tree Learning to Build User-Centric Context-Aware Predictive Model
Dec 17, 2019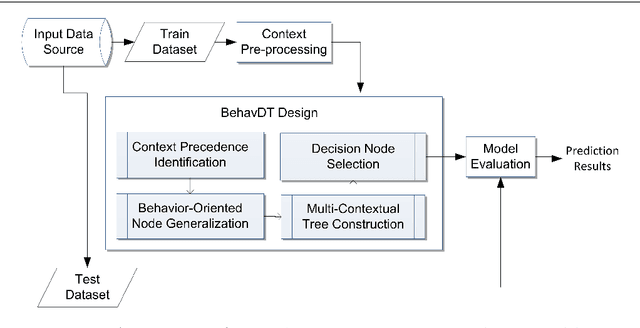
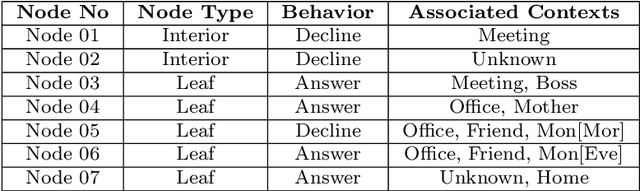
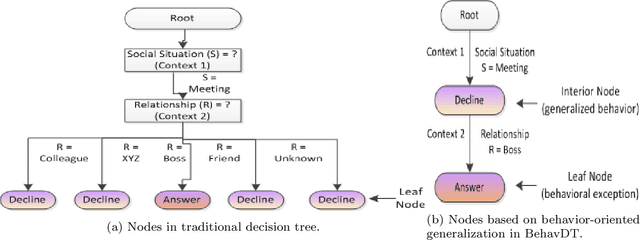
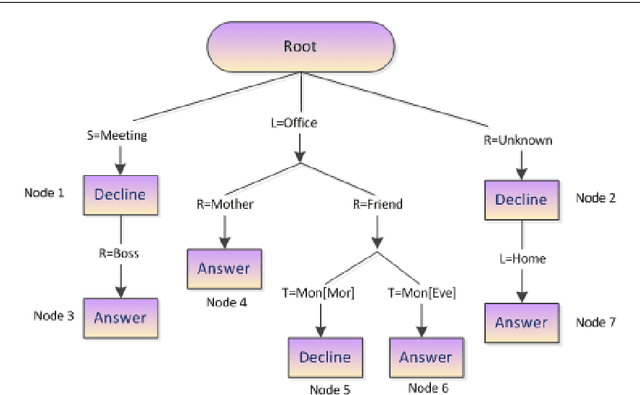
Abstract:This paper formulates the problem of building a context-aware predictive model based on user diverse behavioral activities with smartphones. In the area of machine learning and data science, a tree-like model as that of decision tree is considered as one of the most popular classification techniques, which can be used to build a data-driven predictive model. The traditional decision tree model typically creates a number of leaf nodes as decision nodes that represent context-specific rigid decisions, and consequently may cause overfitting problem in behavior modeling. However, in many practical scenarios within the context-aware environment, the generalized outcomes could play an important role to effectively capture user behavior. In this paper, we propose a behavioral decision tree, "BehavDT" context-aware model that takes into account user behavior-oriented generalization according to individual preference level. The BehavDT model outputs not only the generalized decisions but also the context-specific decisions in relevant exceptional cases. The effectiveness of our BehavDT model is studied by conducting experiments on individual user real smartphone datasets. Our experimental results show that the proposed BehavDT context-aware model is more effective when compared with the traditional machine learning approaches, in predicting user diverse behaviors considering multi-dimensional contexts.
AppsPred: Predicting Context-Aware Smartphone Apps using Random Forest Learning
Aug 26, 2019



Abstract:Due to the popularity of context-awareness in the Internet of Things (IoT) and the recent advanced features in the most popular IoT device, i.e., smartphone, modeling and predicting personalized usage behavior based on relevant contexts can be highly useful in assisting them to carry out daily routines and activities. Usage patterns of different categories smartphone apps such as social networking, communication, entertainment, or daily life services related apps usually vary greatly between individuals. People use these apps differently in different contexts, such as temporal context, spatial context, individual mood and preference, work status, Internet connectivity like Wifi? status, or device related status like phone profile, battery level etc. Thus, we consider individuals' apps usage as a multi-class context-aware problem for personalized modeling and prediction. Random Forest learning is one of the most popular machine learning techniques to build a multi-class prediction model. Therefore, in this paper, we present an effective context-aware smartphone apps prediction model, and name it "AppsPred" using random forest machine learning technique that takes into account optimal number of trees based on such multi-dimensional contexts to build the resultant forest. The effectiveness of this model is examined by conducting experiments on smartphone apps usage datasets collected from individual users. The experimental results show that our AppsPred significantly outperforms other popular machine learning classification approaches like ZeroR, Naive Bayes, Decision Tree, Support Vector Machines, Logistic Regression while predicting smartphone apps in various context-aware test cases.
* 28 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge