Kaveen Perera
Robust Palm-Vein Recognition Using the MMD Filter: Improving SIFT-Based Feature Matching
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:A major challenge with palm vein images is that slight movements of the fingers and thumb, or variations in hand posture, can stretch the skin in different areas and alter the vein patterns. This can result in an infinite number of variations in palm vein images for a given individual. This paper introduces a novel filtering technique for SIFT-based feature matching, known as the Mean and Median Distance (MMD) Filter. This method evaluates the differences in keypoint coordinates and computes the mean and median in each direction to eliminate incorrect matches. Experiments conducted on the 850nm subset of the CASIA dataset indicate that the proposed MMD filter effectively preserves correct points while reducing false positives detected by other filtering methods. A comparison with existing SIFT-based palm vein recognition systems demonstrates that the proposed MMD filter delivers outstanding performance, achieving lower Equal Error Rate (EER) values. This article presents an extended author's version based on our previous work, A Keypoint Filtering Method for SIFT based Palm-Vein Recognition.
ILACS-LGOT: A Multi-Layer Contrast Enhancement Approach for Palm-Vein Images
Feb 26, 2025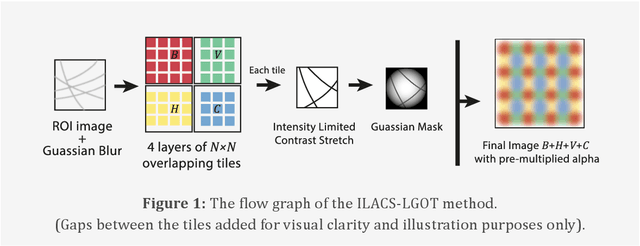



Abstract:This article presents an extended author's version based on our previous work, where we introduced the Multiple Overlapping Tiles (MOT) method for palm vein image enhancement. To better reflect the specific operations involved, we rename MOT to ILACS-LGOT (Intensity-Limited Adaptive Contrast Stretching with Layered Gaussian-weighted Overlapping Tiles). This revised terminology more accurately represents the method's approach to contrast enhancement and blocky effect mitigation. Additionally, this article provides a more detailed analysis, including expanded evaluations, graphical representations, and sample-based comparisons, demonstrating the effectiveness of ILACS-LGOT over existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge