Kasun Wickramasinghe
How Good is BLI as an Alignment Measure: A Study in Word Embedding Paradigm
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Sans a dwindling number of monolingual embedding studies originating predominantly from the low-resource domains, it is evident that multilingual embedding has become the de facto choice due to its adaptability to the usage of code-mixed languages, granting the ability to process multilingual documents in a language-agnostic manner, as well as removing the difficult task of aligning monolingual embeddings. But is this victory complete? Are the multilingual models better than aligned monolingual models in every aspect? Can the higher computational cost of multilingual models always be justified? Or is there a compromise between the two extremes? Bilingual Lexicon Induction is one of the most widely used metrics in terms of evaluating the degree of alignment between two embedding spaces. In this study, we explore the strengths and limitations of BLI as a measure to evaluate the degree of alignment of two embedding spaces. Further, we evaluate how well traditional embedding alignment techniques, novel multilingual models, and combined alignment techniques perform BLI tasks in the contexts of both high-resource and low-resource languages. In addition to that, we investigate the impact of the language families to which the pairs of languages belong. We identify that BLI does not measure the true degree of alignment in some cases and we propose solutions for them. We propose a novel stem-based BLI approach to evaluate two aligned embedding spaces that take into account the inflected nature of languages as opposed to the prevalent word-based BLI techniques. Further, we introduce a vocabulary pruning technique that is more informative in showing the degree of the alignment, especially performing BLI on multilingual embedding models. Often, combined embedding alignment techniques perform better while in certain cases multilingual embeddings perform better (mainly low-resource language cases).
Sinhala Transliteration: A Comparative Analysis Between Rule-based and Seq2Seq Approaches
Dec 31, 2024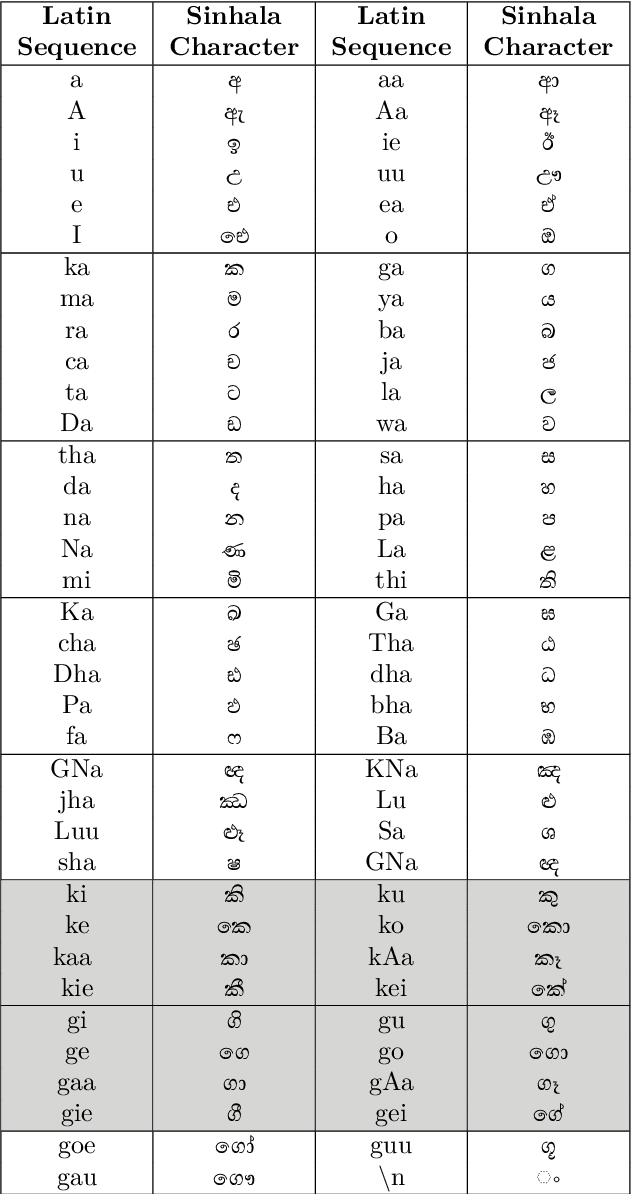
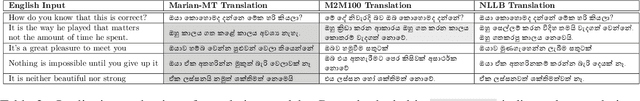

Abstract:Due to reasons of convenience and lack of tech literacy, transliteration (i.e., Romanizing native scripts instead of using localization tools) is eminently prevalent in the context of low-resource languages such as Sinhala, which have their own writing script. In this study, our focus is on Romanized Sinhala transliteration. We propose two methods to address this problem: Our baseline is a rule-based method, which is then compared against our second method where we approach the transliteration problem as a sequence-to-sequence task akin to the established Neural Machine Translation (NMT) task. For the latter, we propose a Transformer-based Encode-Decoder solution. We witnessed that the Transformer-based method could grab many ad-hoc patterns within the Romanized scripts compared to the rule-based method. The code base associated with this paper is available on GitHub - https://github.com/kasunw22/Sinhala-Transliterator/
Sinhala-English Word Embedding Alignment: Introducing Datasets and Benchmark for a Low Resource Language
Nov 17, 2023Abstract:Since their inception, embeddings have become a primary ingredient in many flavours of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks supplanting earlier types of representation. Even though multilingual embeddings have been used for the increasing number of multilingual tasks, due to the scarcity of parallel training data, low-resource languages such as Sinhala, tend to focus more on monolingual embeddings. Then when it comes to the aforementioned multi-lingual tasks, it is challenging to utilize these monolingual embeddings given that even if the embedding spaces have a similar geometric arrangement due to an identical training process, the embeddings of the languages considered are not aligned. This is solved by the embedding alignment task. Even in this, high-resource language pairs are in the limelight while low-resource languages such as Sinhala which is in dire need of help seem to have fallen by the wayside. In this paper, we try to align Sinhala and English word embedding spaces based on available alignment techniques and introduce a benchmark for Sinhala language embedding alignment. In addition to that, to facilitate the supervised alignment, as an intermediate task, we also introduce Sinhala-English alignment datasets. These datasets serve as our anchor datasets for supervised word embedding alignment. Even though we do not obtain results comparable to the high-resource languages such as French, German, or Chinese, we believe our work lays the groundwork for more specialized alignment between English and Sinhala embeddings.
Sinhala-English Parallel Word Dictionary Dataset
Aug 04, 2023Abstract:Parallel datasets are vital for performing and evaluating any kind of multilingual task. However, in the cases where one of the considered language pairs is a low-resource language, the existing top-down parallel data such as corpora are lacking in both tally and quality due to the dearth of human annotation. Therefore, for low-resource languages, it is more feasible to move in the bottom-up direction where finer granular pairs such as dictionary datasets are developed first. They may then be used for mid-level tasks such as supervised multilingual word embedding alignment. These in turn can later guide higher-level tasks in the order of aligning sentence or paragraph text corpora used for Machine Translation (MT). Even though more approachable than generating and aligning a massive corpus for a low-resource language, for the same reason of apathy from larger research entities, even these finer granular data sets are lacking for some low-resource languages. We have observed that there is no free and open dictionary data set for the low-resource language, Sinhala. Thus, in this work, we introduce three parallel English-Sinhala word dictionaries (En-Si-dict-large, En-Si-dict-filtered, En-Si-dict-FastText) which help in multilingual Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks related to English and Sinhala languages. In this paper, we explain the dataset creation pipeline as well as the experimental results of the tests we have carried out to verify the quality of the data sets. The data sets and the related scripts are available at https://github.com/kasunw22/sinhala-para-dict.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge