Kaiyu Shen
Mining Functionally Related Genes with Semi-Supervised Learning
Nov 05, 2020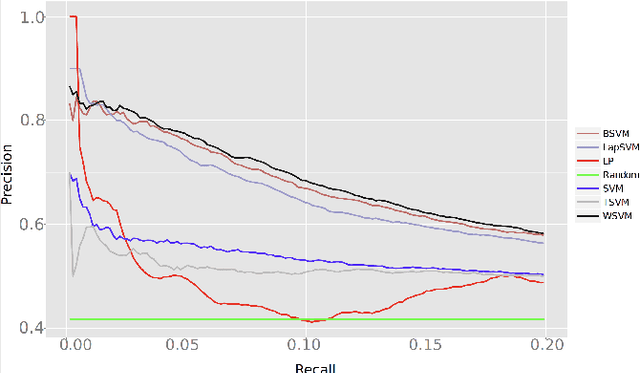
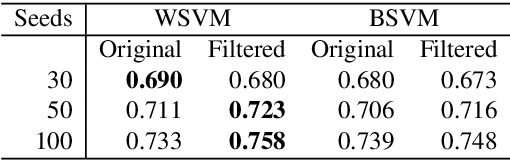
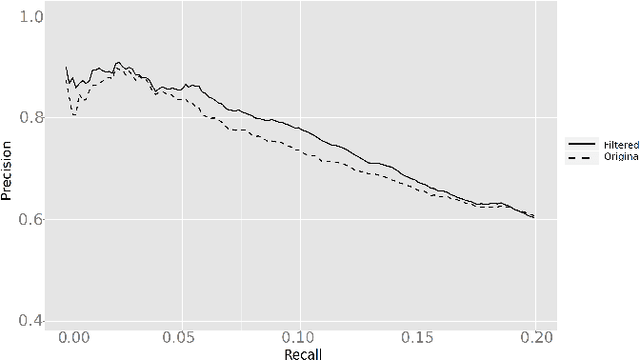
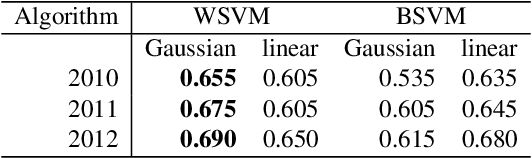
Abstract:The study of biological processes can greatly benefit from tools that automatically predict gene functions or directly cluster genes based on shared functionality. Existing data mining methods predict protein functionality by exploiting data obtained from high-throughput experiments or meta-scale information from public databases. Most existing prediction tools are targeted at predicting protein functions that are described in the gene ontology (GO). However, in many cases biologists wish to discover functionally related genes for which GO terms are inadequate. In this paper, we introduce a rich set of features and use them in conjunction with semisupervised learning approaches in order to expand an initial set of seed genes to a larger cluster of functionally related genes. Among all the semi-supervised methods that were evaluated, the framework of learning with positive and unlabeled examples (LPU) is shown to be especially appropriate for mining functionally related genes. When evaluated on experimentally validated benchmark data, the LPU approaches1 significantly outperform a standard supervised learning algorithm as well as an established state-of-the-art method. Given an initial set of seed genes, our best performing approach could be used to mine functionally related genes in a wide range of organisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge