Jyh-Shing Jang
k-Same-Siamese-GAN: k-Same Algorithm with Generative Adversarial Network for Facial Image De-identification with Hyperparameter Tuning and Mixed Precision Training
Mar 27, 2019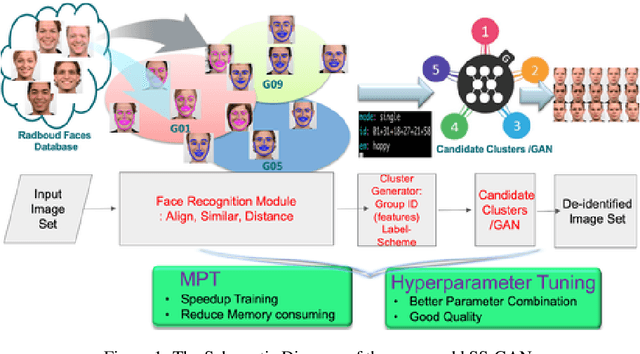
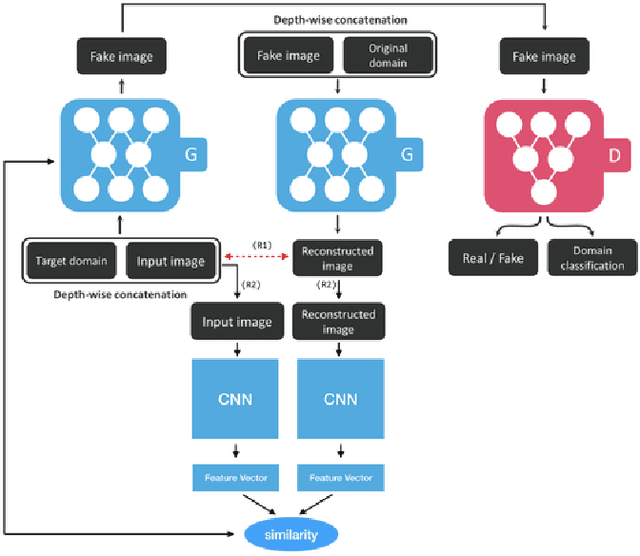
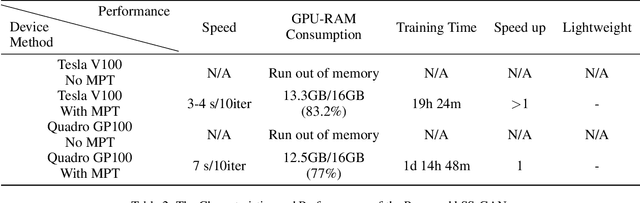
Abstract:In recent years, advances in camera and computing hardware have made it easy to capture and store amounts of image and video data. Consider a data holder, such as a hospital or a government entity, who has a privately held collection of personal data. Then, how can we ensure that the data holder does conceal the identity of each individual in the imagery of personal data while still preserving certain useful aspects of the data after de-identification? In this work, we proposed a novel approach towards high-resolution facial image de-identification, called k-Same-Siamese-GAN (kSS-GAN), which leverages k-Same-Anonymity mechanism, Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), and hyperparameter tuning. To speed up training and reduce memory consumption, the mixed precision training (MPT) technique is also applied to make kSS-GAN provide guarantees regarding privacy protection on close-form identities and be trained much more efficiently as well. Finally, we dedicated our system to an actual dataset: RafD dataset for performance testing. Besides protecting privacy of high resolution of facial images, the proposed system is also justified for its ability in automating parameter tuning and breaking through the limitation of the number of adjustable parameters.
A Hierarchical Approach to Designing Approximate Reasoning-Based Controllers for Dynamic Physical Systems
Mar 27, 2013



Abstract:This paper presents a new technique for the design of approximate reasoning based controllers for dynamic physical systems with interacting goals. In this approach, goals are achieved based on a hierarchy defined by a control knowledge base and remain highly interactive during the execution of the control task. The approach has been implemented in a rule-based computer program which is used in conjunction with a prototype hardware system to solve the cart-pole balancing problem in real-time. It provides a complementary approach to the conventional analytical control methodology, and is of substantial use where a precise mathematical model of the process being controlled is not available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge