Julian Stecklina
Towards Faster Reasoners By Using Transparent Huge Pages
Apr 29, 2020
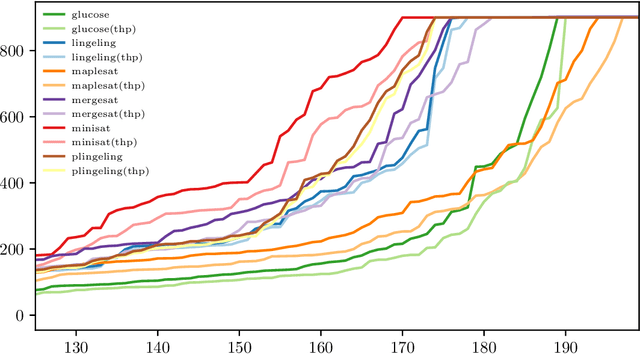
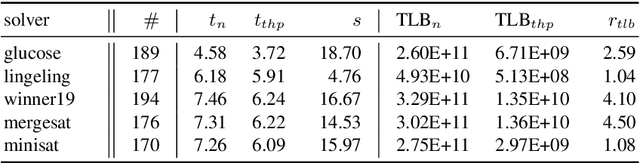
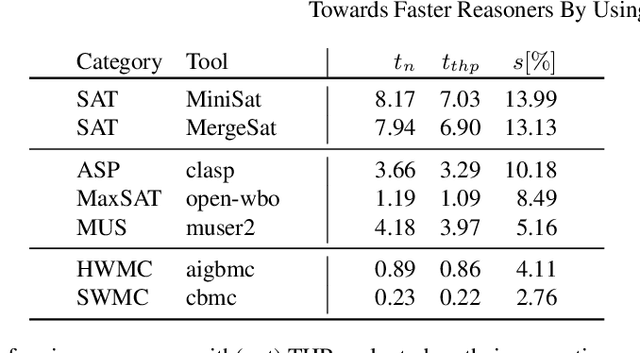
Abstract:Various state-of-the-art automated reasoning (AR) tools are widely used as backend tools in research of knowledge representation and reasoning as well as in industrial applications. In testing and verification, those tools often run continuously or nightly. In this work, we present an approach to reduce the runtime of AR tools by 10% on average and up to 20% for long running tasks. Our improvement addresses the high memory usage that comes with the data structures used in AR tools, which are based on conflict driven no-good learning. We establish a general way to enable faster memory access by using the memory cache line of modern hardware more effectively. Therefore, we extend the standard C library (glibc) by dynamically allowing to use a memory management feature called huge pages. Huge pages allow to reduce the overhead that is required to translate memory addresses between the virtual memory of the operating system and the physical memory of the hardware. In that way, we can reduce runtime, costs, and energy consumption of AR tools and applications with similar memory access patterns simply by linking the tool against this new glibc library when compiling it. In every day industrial applications this easily allows to be more eco-friendly in computation. To back up the claimed speed-up, we present experimental results for tools that are commonly used in the AR community, including the domains ASP, BMC, MaxSAT, SAT, and SMT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge