Julian Kulozik
Compensation Effect Amplification Control (CEAC): A movement-based approach for coordinated position and velocity control of the elbow of upper-limb prostheses
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Despite advances in upper-limb (UL) prosthetic design, achieving intuitive control of intermediate joints - such as the wrist and elbow - remains challenging, particularly for continuous and velocity-modulated movements. We introduce a novel movement-based control paradigm entitled Compensation Effect Amplification Control (CEAC) that leverages users' trunk flexion and extension as input for controlling prosthetic elbow velocity. Considering that the trunk can be both a functional and compensatory joint when performing upper-limb actions, CEAC amplifies the natural coupling between trunk and prosthesis while introducing a controlled delay that allows users to modulate both the position and velocity of the prosthetic joint. We evaluated CEAC in a generic drawing task performed by twelve able-bodied participants using a supernumerary prosthesis with an active elbow. Additionally a multiple-target-reaching task was performed by a subset of ten participants. Results demonstrate task performances comparable to those obtained with natural arm movements, even when gesture velocity or drawing size were varied, while maintaining ergonomic trunk postures. Analysis revealed that CEAC effectively restores joint coordinated action, distributes movement effort between trunk and elbow, enabling intuitive trajectory control without requiring extreme compensatory movements. Overall, CEAC offers a promising control strategy for intermediate joints of UL prostheses, particularly in tasks requiring continuous and precise coordination.
Evaluating the precision of the HTC VIVE Ultimate Tracker with robotic and human movements under varied environmental conditions
Sep 04, 2024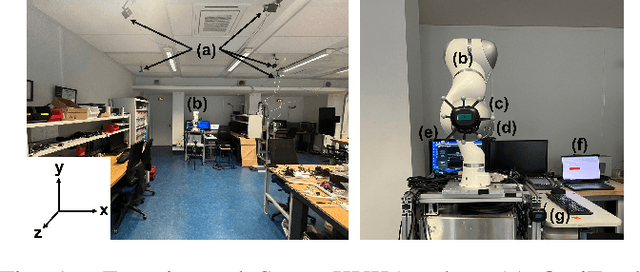
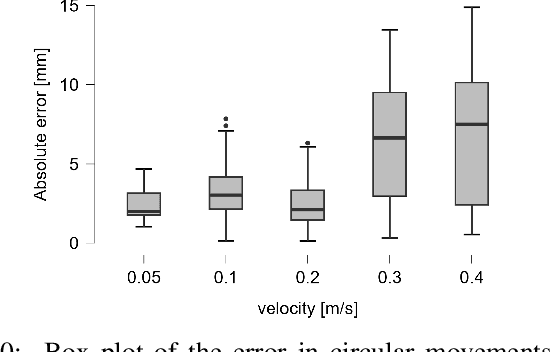
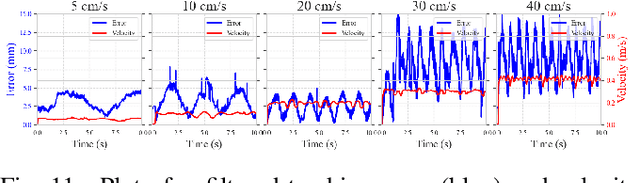
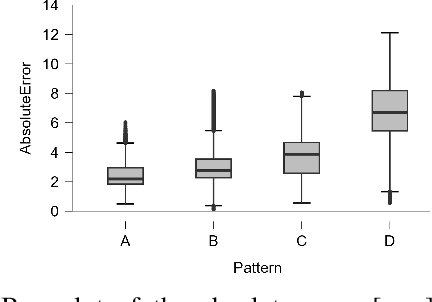
Abstract:The HTC VIVE Ultimate Tracker, utilizing inside-out tracking with internal stereo cameras providing 6 DoF tracking without external cameras, offers a cost-efficient and straightforward setup for motion tracking. Initially designed for the gaming and VR industry, we explored its application beyond VR, providing source code for data capturing in both C++ and Python without requiring a VR headset. This study is the first to evaluate the tracker's precision across various experimental scenarios. To assess the robustness of the tracking precision, we employed a robotic arm as a precise and repeatable source of motion. Using the OptiTrack system as a reference, we conducted tests under varying experimental conditions: lighting, movement velocity, environmental changes caused by displacing objects in the scene, and human movement in front of the trackers, as well as varying the displacement size relative to the calibration center. On average, the HTC VIVE Ultimate Tracker achieved a precision of 4.98 mm +/- 4 mm across various conditions. The most critical factors affecting accuracy were lighting conditions, movement velocity, and range of motion relative to the calibration center. For practical evaluation, we captured human movements with 5 trackers in realistic motion capture scenarios. Our findings indicate sufficient precision for capturing human movements, validated through two tasks: a low-dynamic pick-and-place task and high-dynamic fencing movements performed by an elite athlete. Even though its precision is lower than that of conventional fixed-camera-based motion capture systems and its performance is influenced by several factors, the HTC VIVE Ultimate Tracker demonstrates adequate accuracy for a variety of motion tracking applications. Its ability to capture human or object movements outside of VR or MOCAP environments makes it particularly versatile.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge