Ju Won Seo
Classification Method of Road Surface Condition and Type with LiDAR Using Spatiotemporal Information
Aug 11, 2023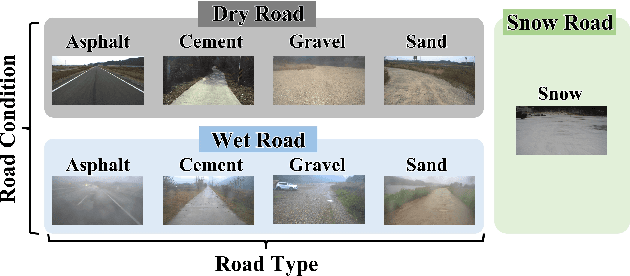
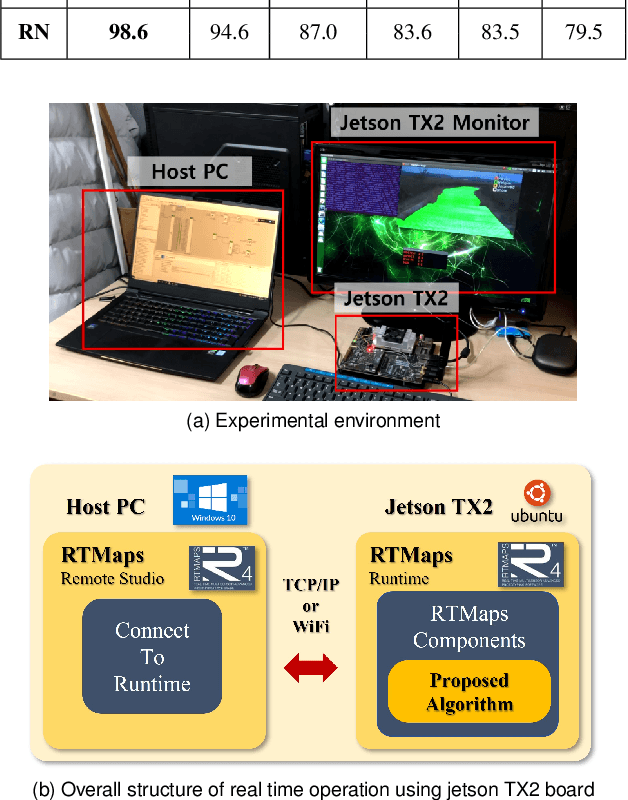
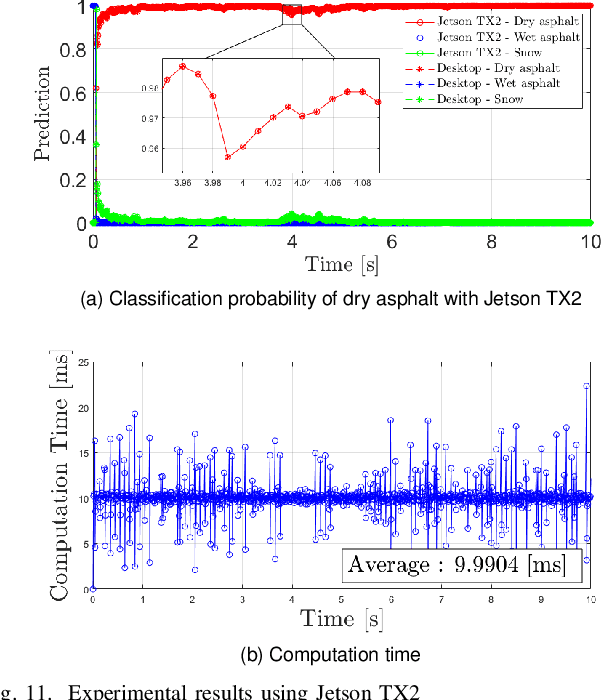
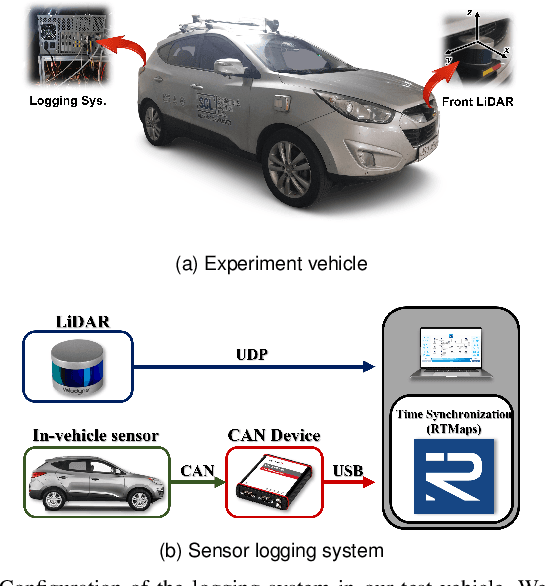
Abstract:This paper proposes a spatiotemporal architecture with a deep neural network (DNN) for road surface conditions and types classification using LiDAR. It is known that LiDAR provides information on the reflectivity and number of point clouds depending on a road surface. Thus, this paper utilizes the information to classify the road surface. We divided the front road area into four subregions. First, we constructed feature vectors using each subregion's reflectivity, number of point clouds, and in-vehicle information. Second, the DNN classifies road surface conditions and types for each subregion. Finally, the output of the DNN feeds into the spatiotemporal process to make the final classification reflecting vehicle speed and probability given by the outcomes of softmax functions of the DNN output layer. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we performed a comparative study with five other algorithms. With the proposed DNN, we obtained the highest accuracy of 98.0\% and 98.6\% for two subregions near the vehicle. In addition, we implemented the proposed method on the Jetson TX2 board to confirm that it is applicable in real-time.
Reachable Set-based Path Planning for Automated Vertical Parking System
Aug 11, 2023



Abstract:This paper proposes a local path planning method with a reachable set for Automated vertical Parking Systems (APS). First, given a parking lot layout with a goal position, we define an intermediate pose for the APS to accomplish reverse parking with a single maneuver, i.e., without changing the gear shift. Then, we introduce a reachable set which is a set of points consisting of the grid points of all possible intermediate poses. Once the APS approaches the goal position, it must select an intermediate pose in the reachable set. A minimization problem was formulated and solved to choose the intermediate pose. We performed various scenarios with different parking lot conditions. We used the Hybrid-A* algorithm for the global path planning to move the vehicle from the starting pose to the intermediate pose and utilized clothoid-based local path planning to move from the intermediate pose to the goal pose. Additionally, we designed a controller to follow the generated path and validated its tracking performance. It was confirmed that the tracking error in the mean root square for the lateral position was bounded within 0.06m and for orientation within 0.01rad.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge