Joydeb Kumar Sana
Patient Similarity Computation for Clinical Decision Support: An Efficient Use of Data Transformation, Combining Static and Time Series Data
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Patient similarity computation (PSC) is a fundamental problem in healthcare informatics. The aim of the patient similarity computation is to measure the similarity among patients according to their historical clinical records, which helps to improve clinical decision support. This paper presents a novel distributed patient similarity computation (DPSC) technique based on data transformation (DT) methods, utilizing an effective combination of time series and static data. Time series data are sensor-collected patients' information, including metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, Oxygen saturation, respiration, etc. The static data are mainly patient background and demographic data, including age, weight, height, gender, etc. Static data has been used for clustering the patients. Before feeding the static data to the machine learning model adaptive Weight-of-Evidence (aWOE) and Z-score data transformation (DT) methods have been performed, which improve the prediction performances. In aWOE-based patient similarity models, sensitive patient information has been processed using aWOE which preserves the data privacy of the trained models. We used the Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) approach, which is robust and very popular, for time series similarity. However, DTW is not suitable for big data due to the significant computational run-time. To overcome this problem, distributed DTW computation is used in this study. For Coronary Artery Disease, our DT based approach boosts prediction performance by as much as 11.4%, 10.20%, and 12.6% in terms of AUC, accuracy, and F-measure, respectively. In the case of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), our proposed method achieves performance enhancement up to 15.9%, 10.5%, and 21.9% for the same measures, respectively. The proposed method reduces the computation time by as high as 40%.
Privacy-Preserving Customer Churn Prediction Model in the Context of Telecommunication Industry
Nov 03, 2024Abstract:Data is the main fuel of a successful machine learning model. A dataset may contain sensitive individual records e.g. personal health records, financial data, industrial information, etc. Training a model using this sensitive data has become a new privacy concern when someone uses third-party cloud computing. Trained models also suffer privacy attacks which leads to the leaking of sensitive information of the training data. This study is conducted to preserve the privacy of training data in the context of customer churn prediction modeling for the telecommunications industry (TCI). In this work, we propose a framework for privacy-preserving customer churn prediction (PPCCP) model in the cloud environment. We have proposed a novel approach which is a combination of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and adaptive Weight-of-Evidence (aWOE). Synthetic data is generated from GANs, and aWOE is applied on the synthetic training dataset before feeding the data to the classification algorithms. Our experiments were carried out using eight different machine learning (ML) classifiers on three openly accessible datasets from the telecommunication sector. We then evaluated the performance using six commonly employed evaluation metrics. In addition to presenting a data privacy analysis, we also performed a statistical significance test. The training and prediction processes achieve data privacy and the prediction classifiers achieve high prediction performance (87.1\% in terms of F-Measure for GANs-aWOE based Na\"{\i}ve Bayes model). In contrast to earlier studies, our suggested approach demonstrates a prediction enhancement of up to 28.9\% and 27.9\% in terms of accuracy and F-measure, respectively.
Data transformation based optimized customer churn prediction model for the telecommunication industry
Jan 11, 2022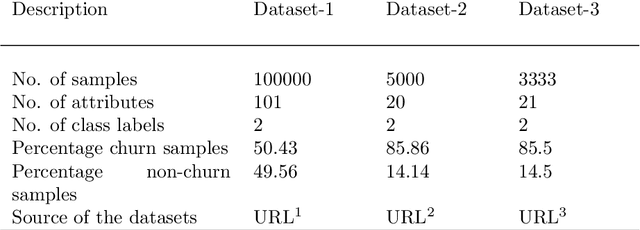
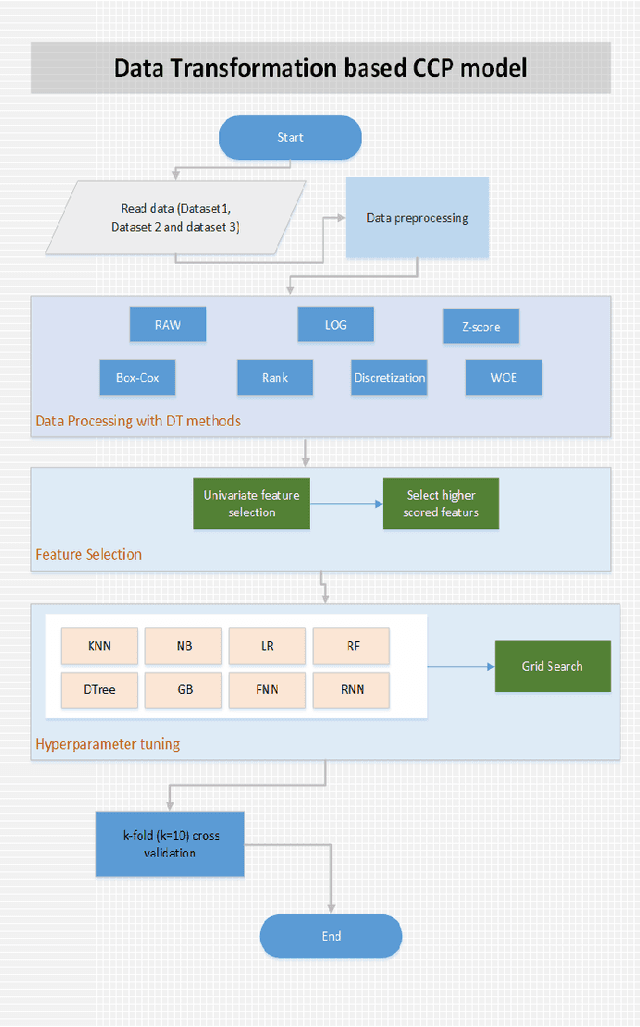
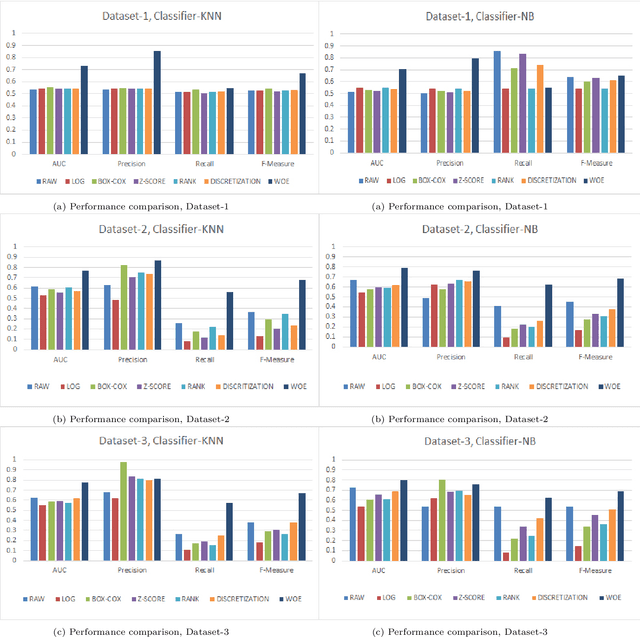
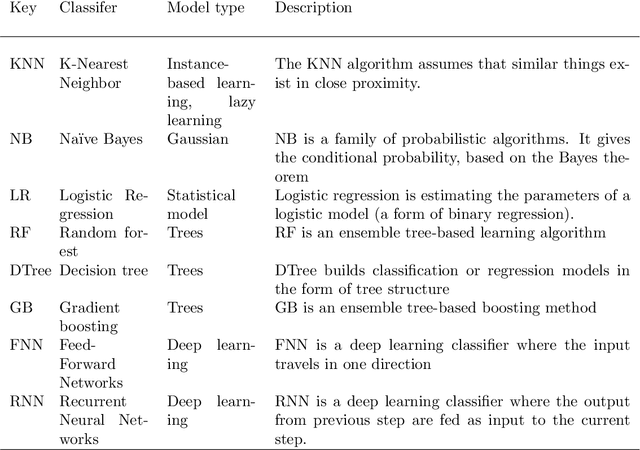
Abstract:Data transformation (DT) is a process that transfers the original data into a form which supports a particular classification algorithm and helps to analyze the data for a special purpose. To improve the prediction performance we investigated various data transform methods. This study is conducted in a customer churn prediction (CCP) context in the telecommunication industry (TCI), where customer attrition is a common phenomenon. We have proposed a novel approach of combining data transformation methods with the machine learning models for the CCP problem. We conducted our experiments on publicly available TCI datasets and assessed the performance in terms of the widely used evaluation measures (e.g. AUC, precision, recall, and F-measure). In this study, we presented comprehensive comparisons to affirm the effect of the transformation methods. The comparison results and statistical test proved that most of the proposed data transformation based optimized models improve the performance of CCP significantly. Overall, an efficient and optimized CCP model for the telecommunication industry has been presented through this manuscript.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge