José A. García Gutiérrez
Evolutionary Computation in Astronomy and Astrophysics: A Review
Apr 10, 2012
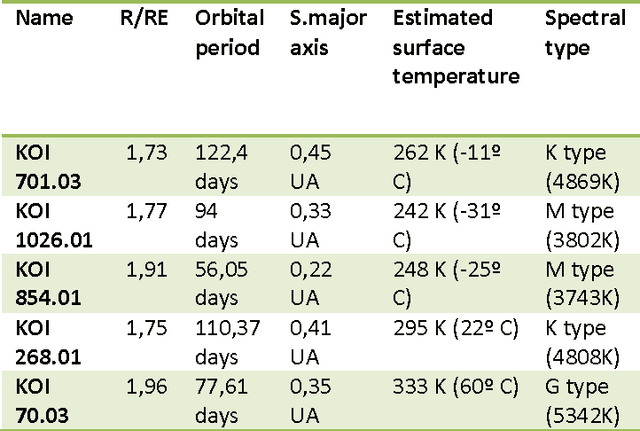


Abstract:In general Evolutionary Computation (EC) includes a number of optimization methods inspired by biological mechanisms of evolution. The methods catalogued in this area use the Darwinian principles of life evolution to produce algorithms that returns high quality solutions to hard-to-solve optimization problems. The main strength of EC is precisely that they provide good solutions even if the computational resources (e.g., running time) are limited. Astronomy and Astrophysics are two fields that often require optimizing problems of high complexity or analyzing a huge amount of data and the so-called complete optimization methods are inherently limited by the size of the problem/data. For instance, reliable analysis of large amounts of data is central to modern astrophysics and astronomical sciences in general. EC techniques perform well where other optimization methods are inherently limited (as complete methods applied to NP-hard problems), and in the last ten years, numerous proposals have come up that apply with greater or lesser success methodologies of evolutional computation to common engineering problems. Some of these problems, such as the estimation of non-lineal parameters, the development of automatic learning techniques, the implementation of control systems, or the resolution of multi-objective optimization problems, have had (and have) a special repercussion in the fields. For these reasons EC emerges as a feasible alternative for traditional methods. In this paper, we discuss some promising applications in this direction and a number of recent works in this area; the paper also includes a general description of EC to provide a global perspective to the reader and gives some guidelines of application of EC techniques for future research
Design of Emergent and Adaptive Virtual Players in a War RTS Game
Jan 15, 2012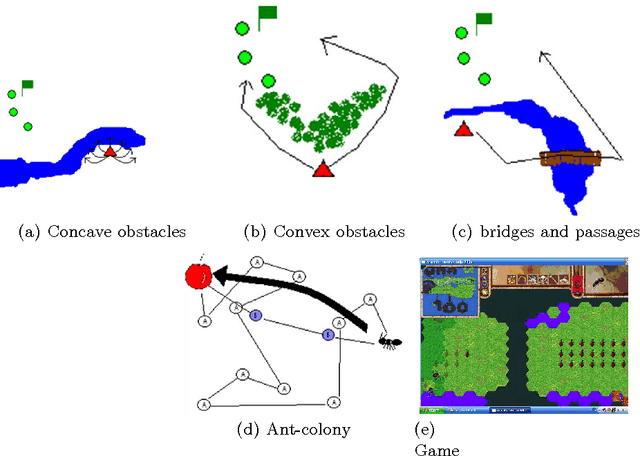

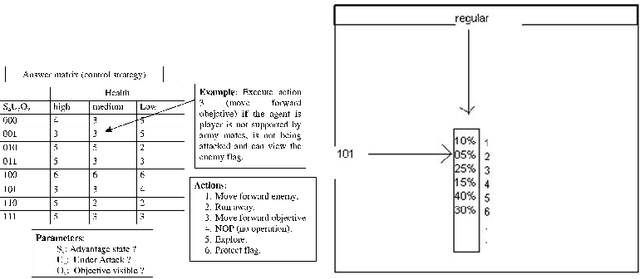
Abstract:Basically, in (one-player) war Real Time Strategy (wRTS) games a human player controls, in real time, an army consisting of a number of soldiers and her aim is to destroy the opponent's assets where the opponent is a virtual (i.e., non-human player controlled) player that usually consists of a pre-programmed decision-making script. These scripts have usually associated some well-known problems (e.g., predictability, non-rationality, repetitive behaviors, and sensation of artificial stupidity among others). This paper describes a method for the automatic generation of virtual players that adapt to the player skills; this is done by building initially a model of the player behavior in real time during the game, and further evolving the virtual player via this model in-between two games. The paper also shows preliminary results obtained on a one player wRTS game constructed specifically for experimentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge