Jonathan Serugunda
On-site Energy Utilization Evaluation of Telecommunication Base Station: A Case Study of Western Uganda
Aug 15, 2023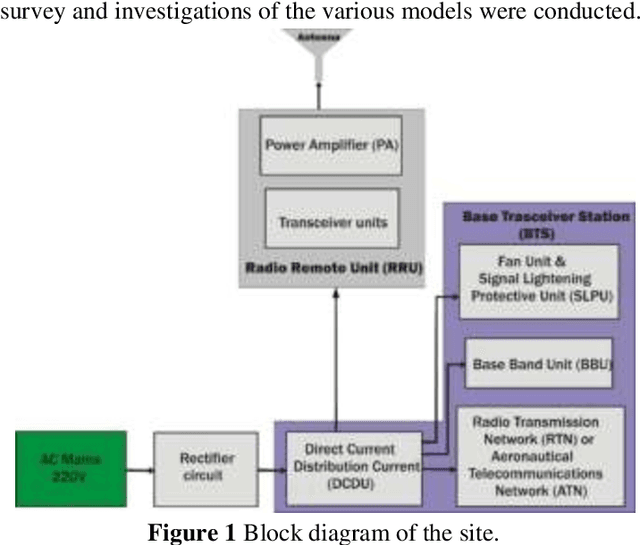


Abstract:Due to the widespread installation of Base Stations, the power consumption of cellular communication is increasing rapidly (BSs). Power consumption rises as traffic does, however, this scenario varies from geolocation to geolocation because sites in rural and urban areas have variable traffic loads. Therefore, in order to address various power consumption issues, it is necessary to analyze these sites and offer valid data that network operators can employ. This study took into account the impact of traffic load on energy consumption both in rural and urban locations in western Uganda because prior models did not adequately account for the impact of traffic load on both rural and urban sites. Regression models are used to examine these effects of traffic load on power consumption. Based on measurements taken for twenty-eight days in a row in six urban and rural areas, linear models have been presented. The findings showed that both rural and urban BTS were well-fitted by the suggested linear models. Depending on the layouts of the sites, it was found that energy consumption varied along with traffic, with the number of transceivers present having an impact on both the traffic load and energy consumption.
An Overview of Machine Learning-aided Optical Performance Monitoring Techniques
Jun 20, 2021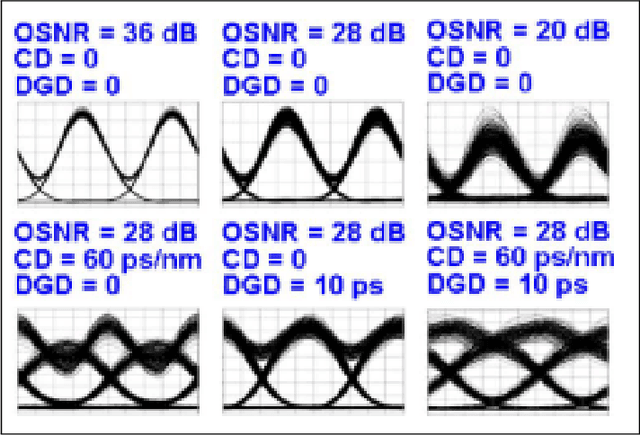
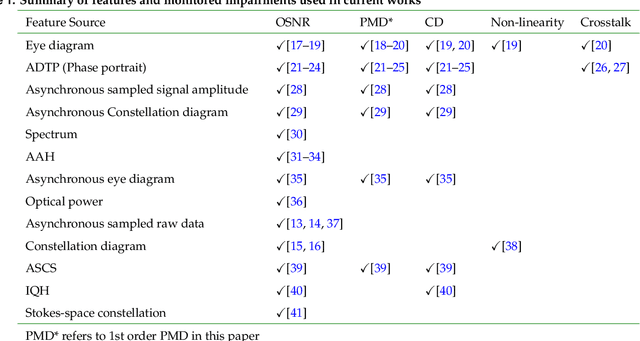


Abstract:Future communication systems are faced with increased demand for high capacity, dynamic bandwidth, reliability and heterogeneous traffic. To meet these requirements, networks have become more complex and thus require new design methods and monitoring techniques, as they evolve towards becoming autonomous. Machine learning has come to the forefront in recent years as a promising technology to aid in this evolution. Optical fiber communications can already provide the high capacity required for most applications, however, there is a need for increased scalability and adaptability to changing user demands and link conditions. Accurate performance monitoring is an integral part of this transformation. In this paper we review optical performance monitoring techniques where machine learning algorithms have been applied. Moreover, since alot of OPM depends on knowledge of the signal type, we also review work for modulation format recognition and bitrate identification. We additionally briefly introduce a neuromorphic approach to OPM as an emerging technique that has only recently been applied to this domain.
Face Recognition as a Method of Authentication in a Web-Based System
Mar 28, 2021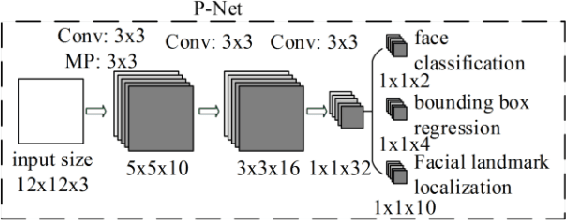
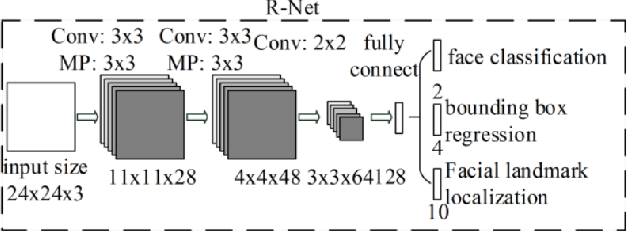


Abstract:Online information systems currently heavily rely on the username and password traditional method for protecting information and controlling access. With the advancement in biometric technology and popularity of fields like AI and Machine Learning, biometric security is becoming increasingly popular because of the usability advantage. This paper reports how machine learning based face recognition can be integrated into a web-based system as a method of authentication to reap the benefits of improved usability. This paper includes a comparison of combinations of detection and classification algorithms with FaceNet for face recognition. The results show that a combination of MTCNN for detection, Facenet for generating embeddings, and LinearSVC for classification outperforms other combinations with a 95% accuracy. The resulting classifier is integrated into the web-based system and used for authenticating users.
A Deep Learning-based Detector for Brown Spot Disease in Passion Fruit Plant Leaves
Jul 29, 2020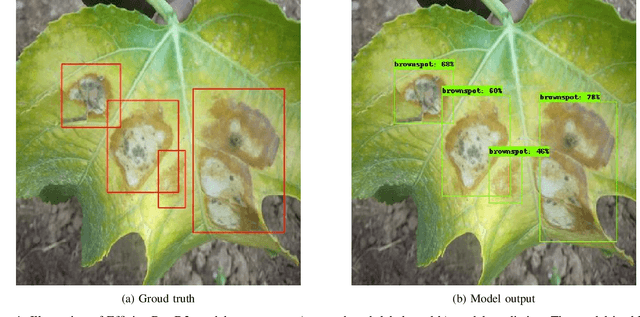
Abstract:Pests and diseases pose a key challenge to passion fruit farmers across Uganda and East Africa in general. They lead to loss of investment as yields reduce and losses increases. As the majority of the farmers, including passion fruit farmers, in the country are smallholder farmers from low-income households, they do not have the sufficient information and means to combat these challenges. While, passion fruits have the potential to improve the well-being of these farmers as they have a short maturity period and high market value , without the required knowledge about the health of their crops, farmers cannot intervene promptly to turn the situation around. For this work, we have partnered with the Uganda National Crop Research Institute (NaCRRI) to develop a dataset of expertly labelled passion fruit plant leaves and fruits, both diseased and healthy. We have made use of their extension service to collect images from 5 districts in Uganda, With the dataset in place, we are employing state-of-the-art techniques in machine learning, and specifically deep learning, techniques at scale for object detection and classification to correctly determine the health status of passion fruit plants and provide an accurate diagnosis for positive detections.This work focuses on two major diseases woodiness (viral) and brown spot (fungal) diseases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge