Jonathan Lu
A Comparative Study of Translation Bias and Accuracy in Multilingual Large Language Models for Cross-Language Claim Verification
Oct 14, 2024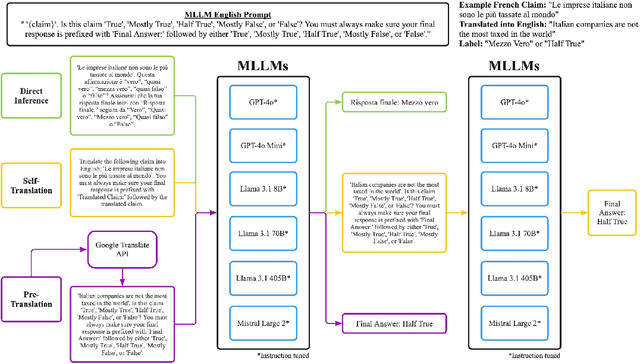
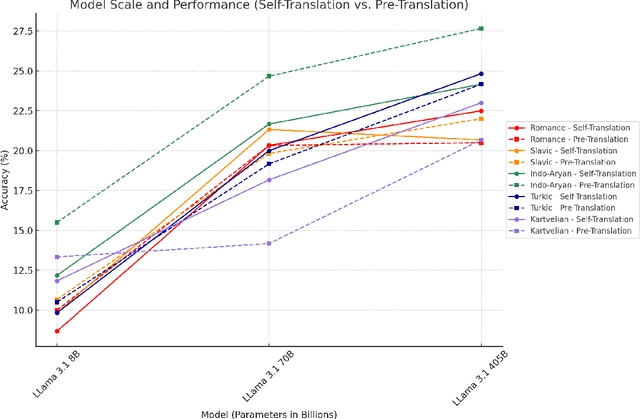


Abstract:The rise of digital misinformation has heightened interest in using multilingual Large Language Models (LLMs) for fact-checking. This study systematically evaluates translation bias and the effectiveness of LLMs for cross-lingual claim verification across 15 languages from five language families: Romance, Slavic, Turkic, Indo-Aryan, and Kartvelian. Using the XFACT dataset to assess their impact on accuracy and bias, we investigate two distinct translation methods: pre-translation and self-translation. We use mBERT's performance on the English dataset as a baseline to compare language-specific accuracies. Our findings reveal that low-resource languages exhibit significantly lower accuracy in direct inference due to underrepresentation in the training data. Furthermore, larger models demonstrate superior performance in self-translation, improving translation accuracy and reducing bias. These results highlight the need for balanced multilingual training, especially in low-resource languages, to promote equitable access to reliable fact-checking tools and minimize the risk of spreading misinformation in different linguistic contexts.
Fine-Tuning Language Models for Ethical Ambiguity: A Comparative Study of Alignment with Human Responses
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:Language models often misinterpret human intentions due to their handling of ambiguity, a limitation well-recognized in NLP research. While morally clear scenarios are more discernible to LLMs, greater difficulty is encountered in morally ambiguous contexts. In this investigation, we explored LLM calibration to show that human and LLM judgments are poorly aligned in such scenarios. We used two curated datasets from the Scruples project for evaluation: DILEMMAS, which involves pairs of distinct moral scenarios to assess the model's ability to compare and contrast ethical situations, and ANECDOTES, which presents individual narratives to evaluate the model's skill in drawing out details, interpreting, and analyzing distinct moral scenarios. Model answer probabilities were extracted for all possible choices and compared with human annotations to benchmark the alignment of three models: Llama-3.1-8b, Zephyr-7b-beta, and Mistral-7b. Significant improvements were observed after fine-tuning, with notable enhancements in both cross-entropy and Dirichlet scores, particularly in the latter. Notably, after fine-tuning, the performance of Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 was on par with GPT-4o. However, the experimental models that were examined were all still outperformed by the BERT and RoBERTa models in terms of cross-entropy scores. Our fine-tuning approach, which improves the model's understanding of text distributions in a text-to-text format, effectively enhances performance and alignment in complex decision-making contexts, underscoring the need for further research to refine ethical reasoning techniques and capture human judgment nuances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge