Aryan Singhal
Semantic Search and Recommendation Algorithm
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a new semantic search algorithm that uses Word2Vec and Annoy Index to improve the efficiency of information retrieval from large datasets. The proposed approach addresses the limitations of traditional search methods by offering enhanced speed, accuracy, and scalability. Testing on datasets up to 100GB demonstrates the method's effectiveness in processing vast amounts of data while maintaining high precision and performance.
A Comparative Study of Translation Bias and Accuracy in Multilingual Large Language Models for Cross-Language Claim Verification
Oct 14, 2024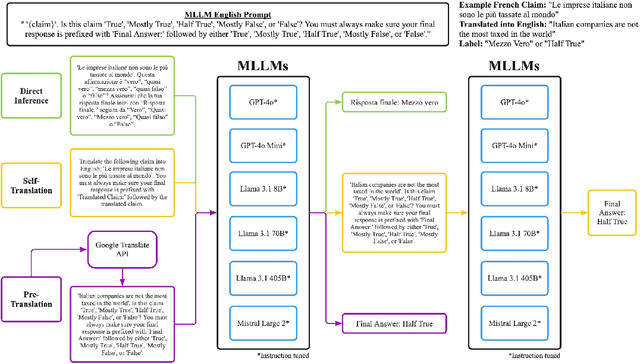
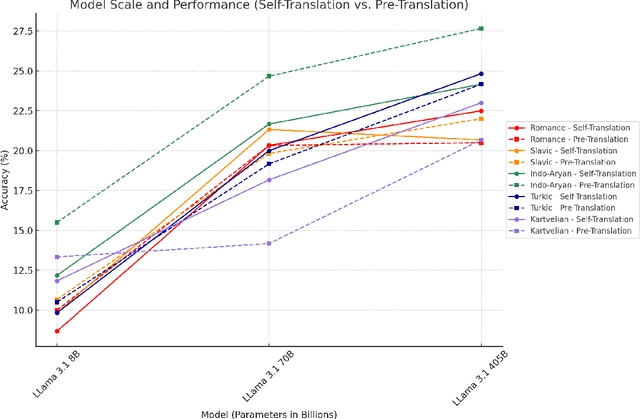


Abstract:The rise of digital misinformation has heightened interest in using multilingual Large Language Models (LLMs) for fact-checking. This study systematically evaluates translation bias and the effectiveness of LLMs for cross-lingual claim verification across 15 languages from five language families: Romance, Slavic, Turkic, Indo-Aryan, and Kartvelian. Using the XFACT dataset to assess their impact on accuracy and bias, we investigate two distinct translation methods: pre-translation and self-translation. We use mBERT's performance on the English dataset as a baseline to compare language-specific accuracies. Our findings reveal that low-resource languages exhibit significantly lower accuracy in direct inference due to underrepresentation in the training data. Furthermore, larger models demonstrate superior performance in self-translation, improving translation accuracy and reducing bias. These results highlight the need for balanced multilingual training, especially in low-resource languages, to promote equitable access to reliable fact-checking tools and minimize the risk of spreading misinformation in different linguistic contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge