John M. O'Toole
Irish Centre for Maternal and Child Health Research, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University College Cork, Ireland
Honest and Reliable Evaluation and Expert Equivalence Testing of Automated Neonatal Seizure Detection
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Reliable evaluation of machine learning models for neonatal seizure detection is critical for clinical adoption. Current practices often rely on inconsistent and biased metrics, hindering model comparability and interpretability. Expert-level claims about AI performance are frequently made without rigorous validation, raising concerns about their reliability. This study aims to systematically evaluate common performance metrics and propose best practices tailored to the specific challenges of neonatal seizure detection. Using real and synthetic seizure annotations, we assessed standard performance metrics, consensus strategies, and human-expert level equivalence tests under varying class imbalance, inter-rater agreement, and number of raters. Matthews and Pearson's correlation coefficients outperformed the area under the curve in reflecting performance under class imbalance. Consensus types are sensitive to the number of raters and agreement level among them. Among human-expert level equivalence tests, the multi-rater Turing test using Fleiss k best captured expert-level AI performance. We recommend reporting: (1) at least one balanced metric, (2) Sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV, (3) Multi-rater Turing test results using Fleiss k, and (4) All the above on held-out validation set. This proposed framework provides an important prerequisite to clinical validation by enabling a thorough and honest appraisal of AI methods for neonatal seizure detection.
Scaling convolutional neural networks achieves expert-level seizure detection in neonatal EEG
May 16, 2024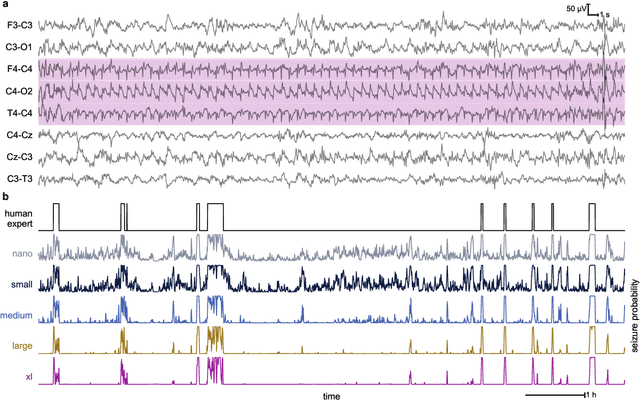
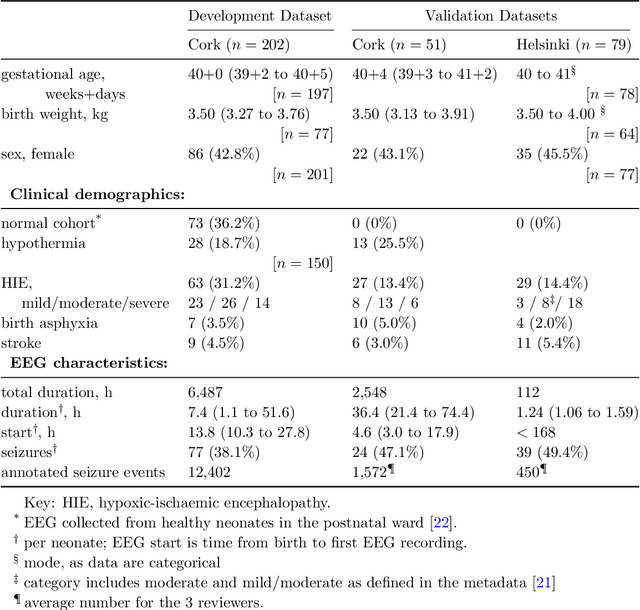
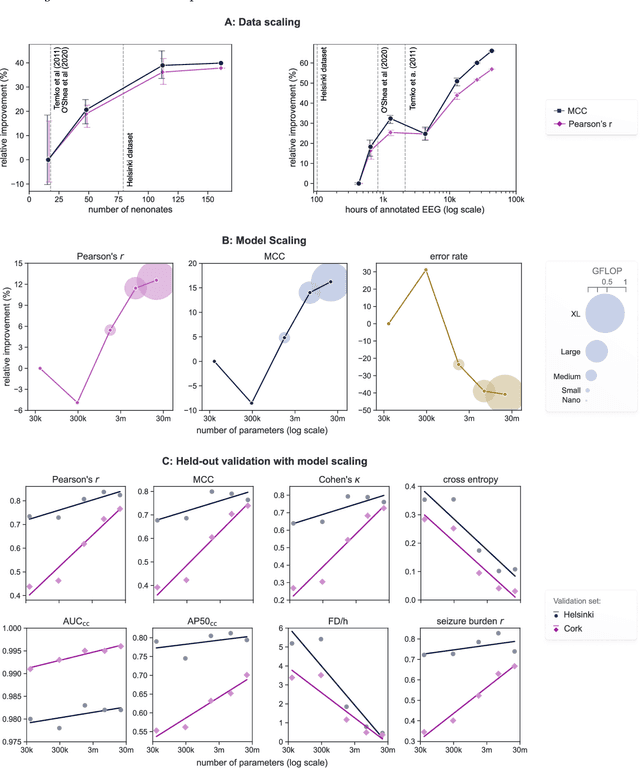
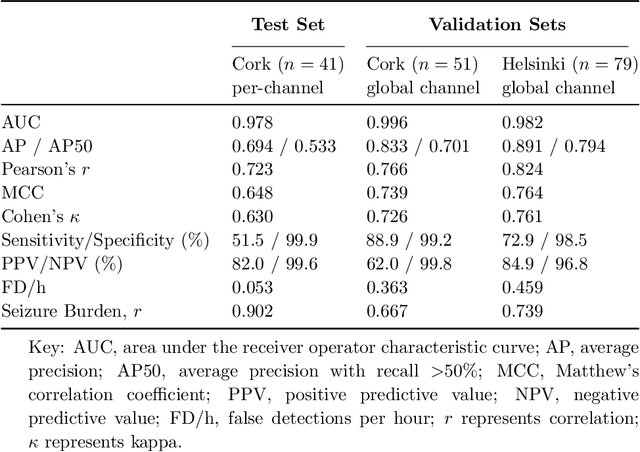
Abstract:Background: Neonatal seizures are a neurological emergency that require urgent treatment. They are hard to diagnose clinically and can go undetected if EEG monitoring is unavailable. EEG interpretation requires specialised expertise which is not widely available. Algorithms to detect EEG seizures can address this limitation but have yet to reach widespread clinical adoption. Methods: Retrospective EEG data from 332 neonates was used to develop and validate a seizure-detection model. The model was trained and tested with a development dataset ($n=202$) that was annotated with over 12k seizure events on a per-channel basis. This dataset was used to develop a convolutional neural network (CNN) using a modern architecture and training methods. The final model was then validated on two independent multi-reviewer datasets ($n=51$ and $n=79$). Results: Increasing dataset and model size improved model performance: Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) and Pearson's correlation ($r$) increased by up to 50% with data scaling and up to 15% with model scaling. Over 50k hours of annotated single-channel EEG was used for training a model with 21 million parameters. State-of-the-art was achieved on an open-access dataset (MCC=0.764, $r=0.824$, and AUC=0.982). The CNN attains expert-level performance on both held-out validation sets, with no significant difference in inter-rater agreement among the experts and among experts and algorithm ($\Delta \kappa < -0.095$, $p>0.05$). Conclusion: With orders of magnitude increases in data and model scale we have produced a new state-of-the-art model for neonatal seizure detection. Expert-level equivalence on completely unseen data, a first in this field, provides a strong indication that the model is ready for further clinical validation.
Random Convolution Kernels with Multi-Scale Decomposition for Preterm EEG Inter-burst Detection
Aug 04, 2021
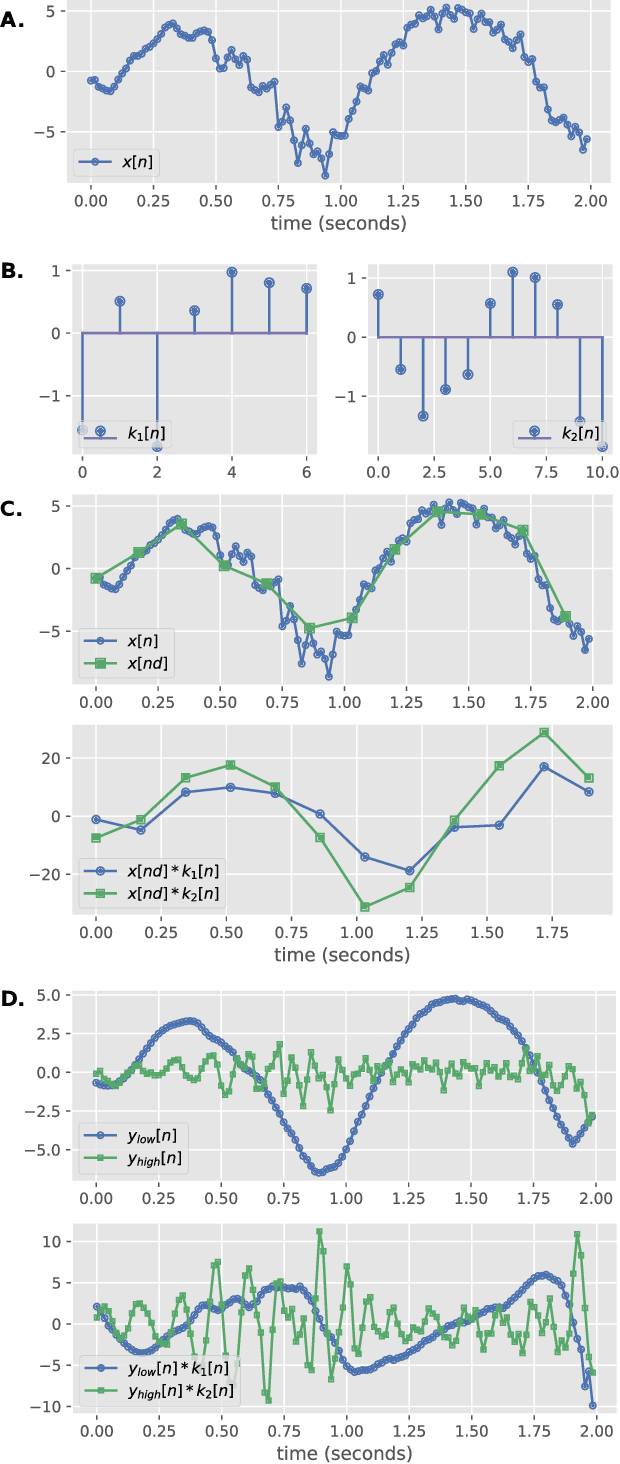
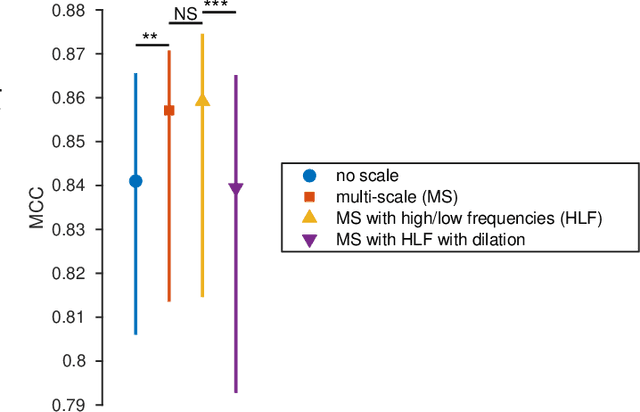
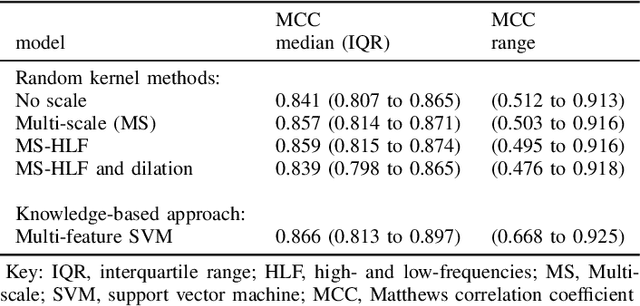
Abstract:Linear classifiers with random convolution kernels are computationally efficient methods that need no design or domain knowledge. Unlike deep neural networks, there is no need to hand-craft a network architecture; the kernels are randomly generated and only the linear classifier needs training. A recently proposed method, RandOm Convolutional KErnel Transforms (ROCKETs), has shown high accuracy across a range of time-series data sets. Here we propose a multi-scale version of this method, using both high- and low-frequency components. We apply our methods to inter-burst detection in a cohort of preterm EEG recorded from 36 neonates <30 weeks gestational age. Two features from the convolution of 10,000 random kernels are combined using ridge regression. The proposed multi-scale ROCKET method out-performs the method without scale: median (interquartile range, IQR) Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) of 0.859 (0.815 to 0.874) for multi-scale versus 0.841 (0.807 to 0.865) without scale, p<0.001. The proposed method lags behind an existing feature-based machine learning method developed with deep domain knowledge, but is fast to train and can quickly set an initial baseline threshold of performance for generic and biomedical time-series classification.
Tracé alternant detector for grading hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal EEG
May 31, 2021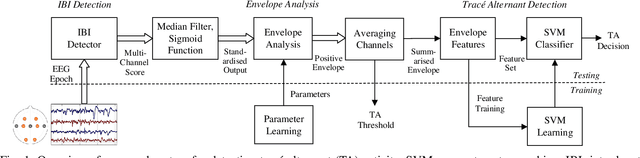
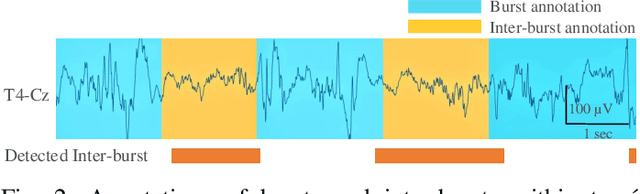
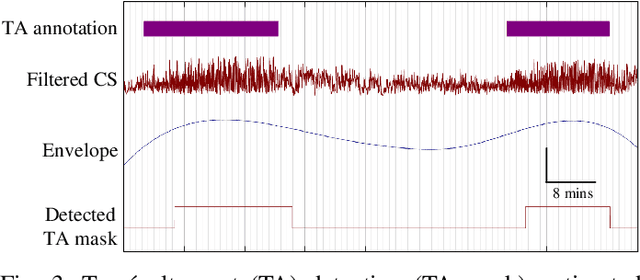
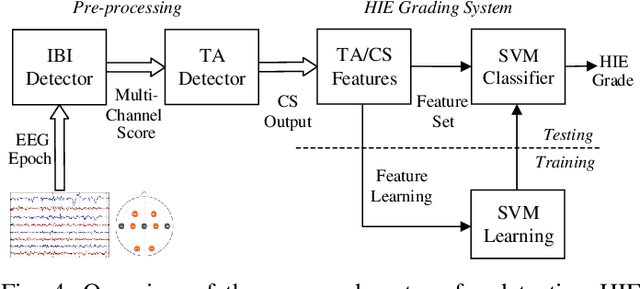
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) is an important clinical tool to capture sleep-wake cycling. It can also be used for grading injury, known as hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy(HIE), caused by lack of oxygen or blood to the brain during birth. Trac\'e alternant (TA) is a distinctive component of normal quiet sleep which consists of alternating periods of high-voltage activity (bursts) separated by lower-voltage activity (inter-bursts). This study presents an automated method to grade the severity of injury in HIE, using an automated method to first detect activity. The TA detector uses the output of an existing method to detect inter-bursts. Features are extracted from a processed output and then combined in a support vector machine (SVM). Next, we develop an HIE grading system using the TA detector by combining different features from the temporal organisation of the detected TA mask, again using an SVM. Training and testing for both models use a leave-one-baby-out cross-validation procedure, with model hyper-parameters selected from nested cross validations. The TA detector, tested on EEG from 71 healthy term neonates, has an accuracy of 79.1% (Cohen's \k{appa}=0.55). the grading system, tested on EEG from 54 term neonates in intensive care, has an accuracy of 81.5% (\k{appa}=0.74). These results validate how detecting the presence or absence of TA can be used to quantify the grade of HIE injury in neonatal EEG and open up the possibility of a clinically-meaningful grading system.
Grading the severity of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborn EEG using a convolutional neural network
May 12, 2020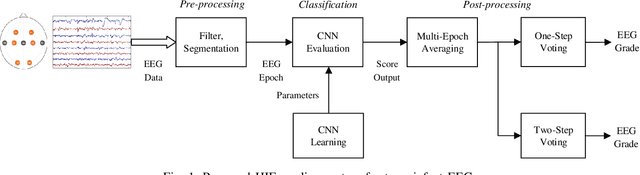
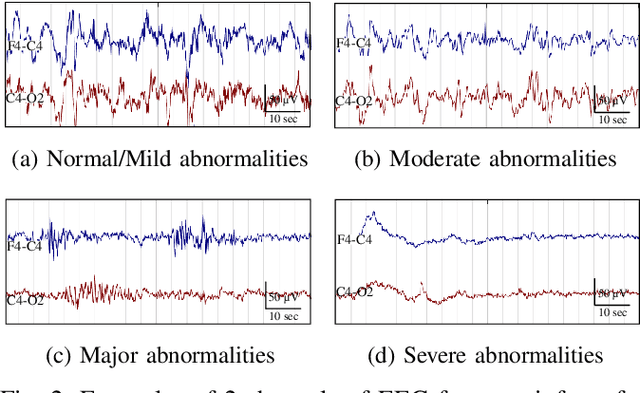
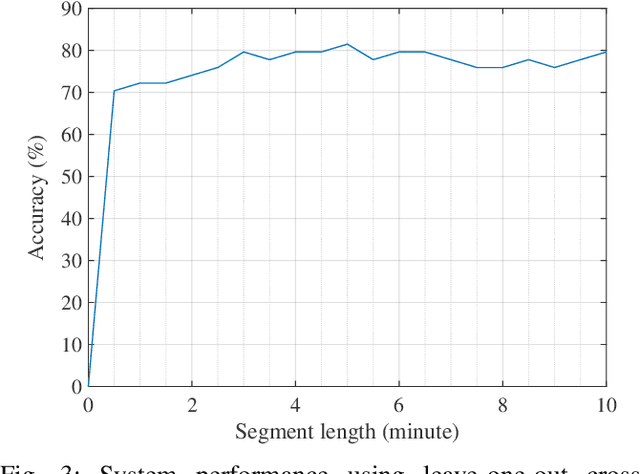
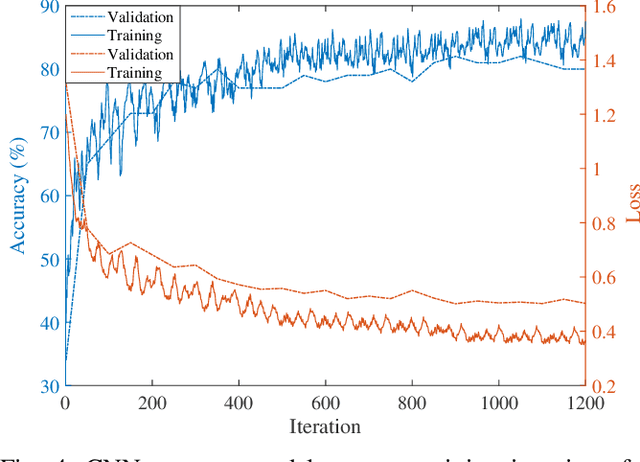
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) is a valuable clinical tool for grading injury caused by lack of blood and oxygen to the brain during birth. This study presents a novel end-to-end architecture, using a deep convolutional neural network, that learns hierarchical representations within raw EEG data. The system classifies 4 grades of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and is evaluated on a multi-channel EEG dataset of 63 hours from 54 newborns. The proposed method achieves a testing accuracy of 79.6% with one-step voting and 81.5% with two-step voting. These results show how a feature-free approach can be used to classify different grades of injury in newborn EEG with comparable accuracy to existing feature-based systems. Automated grading of newborn background EEG could help with the early identification of those infants in need of interventional therapies such as hypothermia.
Identifying trace alternant activity in neonatal EEG using an inter-burst detection approach
May 12, 2020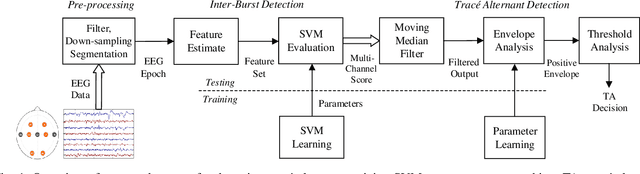
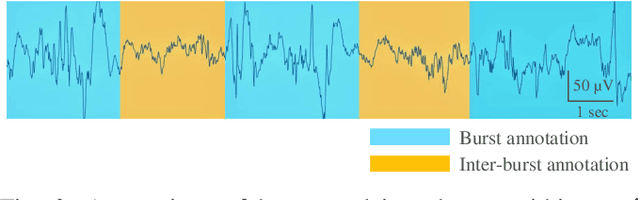
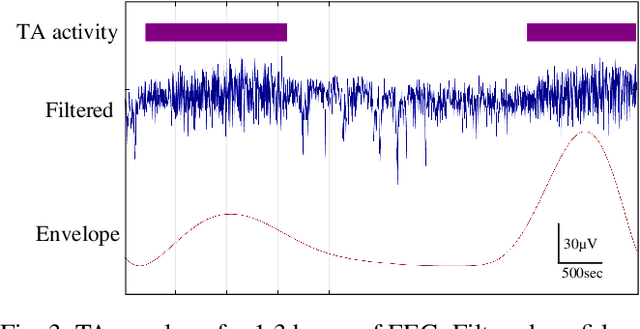
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) is an important clinical tool for reviewing sleep-wake cycling in neonates in intensive care. Trace alternant (TA)-a characteristic pattern of EEG activity during quiet sleep in term neonates-is defined by alternating periods of short-duration, high-voltage activity (bursts) separated by lower-voltage activity (inter-bursts). This study presents a novel approach for detecting TA activity by first detecting the inter-bursts and then processing the temporal map of the bursts and inter-bursts. EEG recordings from 72 healthy term neonates were used to develop and evaluate performance of 1) an inter-burst detection method which is then used for 2) detection of TA activity. First, multiple amplitude and spectral features were combined using a support vector machine (SVM) to classify bursts from inter-bursts within TA activity, resulting in a median area under the operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.95 (95% confidence interval, CI: 0.93 to 0.98). Second, post-processing of the continuous SVM output, the confidence score, was used to produce a TA envelope. This envelope was used to detect TA activity within the continuous EEG with a median AUC of 0.84 (95% CI: 0.80 to 0.88). These results validate how an inter-burst detection approach combined with post processing can be used to classify TA activity. Detecting the presence or absence of TA will help quantify disruption of the clinically important sleep-wake cycle.
Machine learning without a feature set for detecting bursts in the EEG of preterm infants
Jul 16, 2019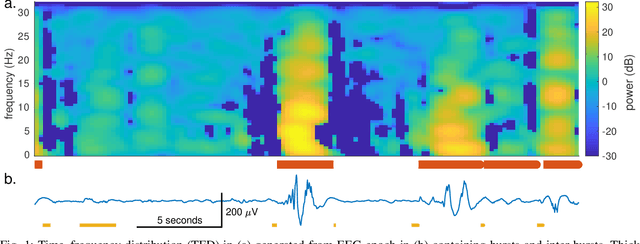
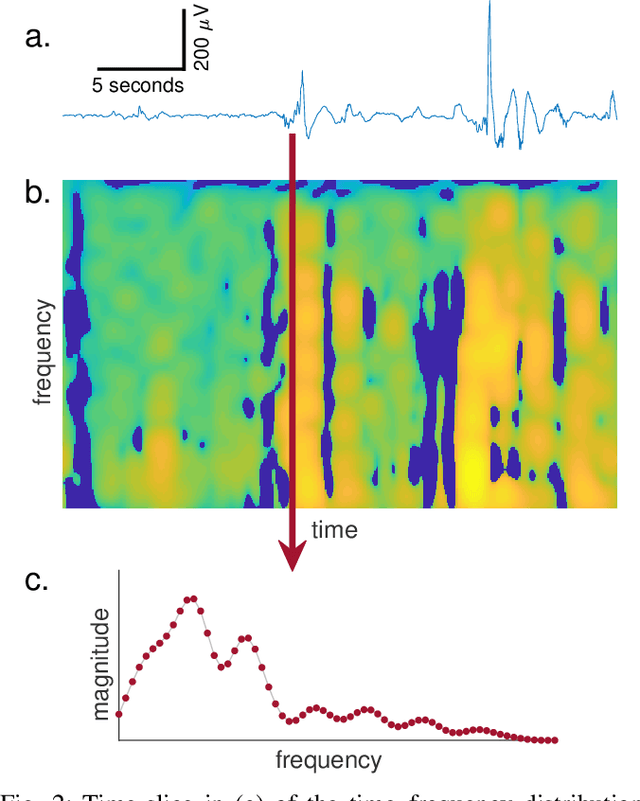
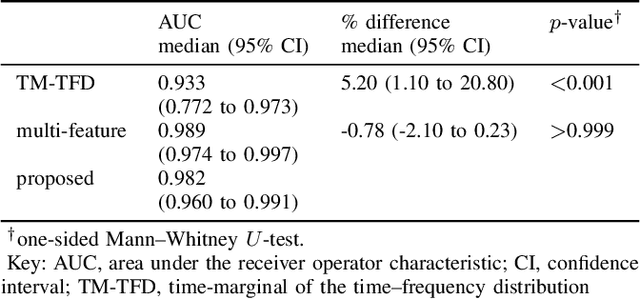
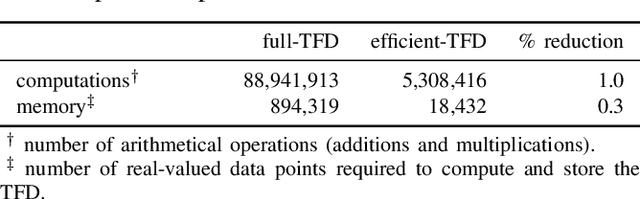
Abstract:Deep neural networks enable learning directly on the data without the domain knowledge needed to construct a feature set. This approach has been extremely successful in almost all machine learning applications. We propose a new framework that also learns directly from the data, without extracting a feature set. We apply this framework to detecting bursts in the EEG of premature infants. The EEG is recorded within days of birth in a cohort of infants without significant brain injury and born <30 weeks of gestation. The method first transforms the time-domain signal to the time--frequency domain and then trains a machine learning method, a gradient boosting machine, on each time-slice of the time--frequency distribution. We control for oversampling the time--frequency distribution with a significant reduction (<1%) in memory and computational complexity. The proposed method achieves similar accuracy to an existing multi-feature approach: area under the characteristic curve of 0.98 (with 95% confidence interval of 0.96 to 0.99), with a median sensitivity of 95% and median specificity of 94%. The proposed framework presents an accurate, simple, and computational efficient implementation as an alternative to both the deep learning approach and to the manual generation of a feature set.
Suitability of an inter-burst detection method for grading hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborn EEG
Jul 05, 2019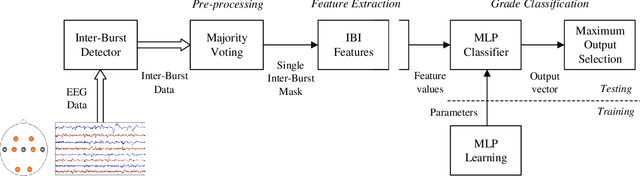
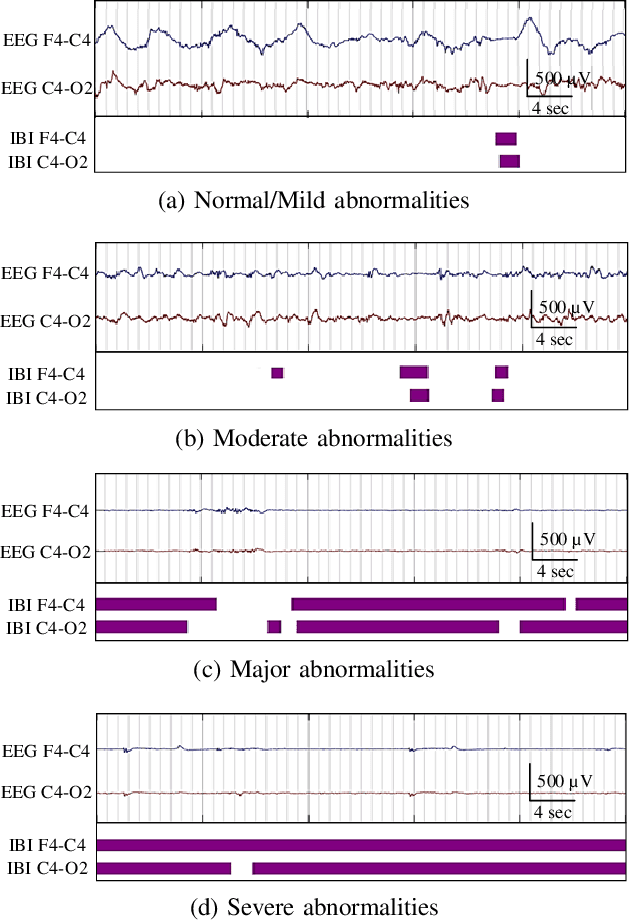
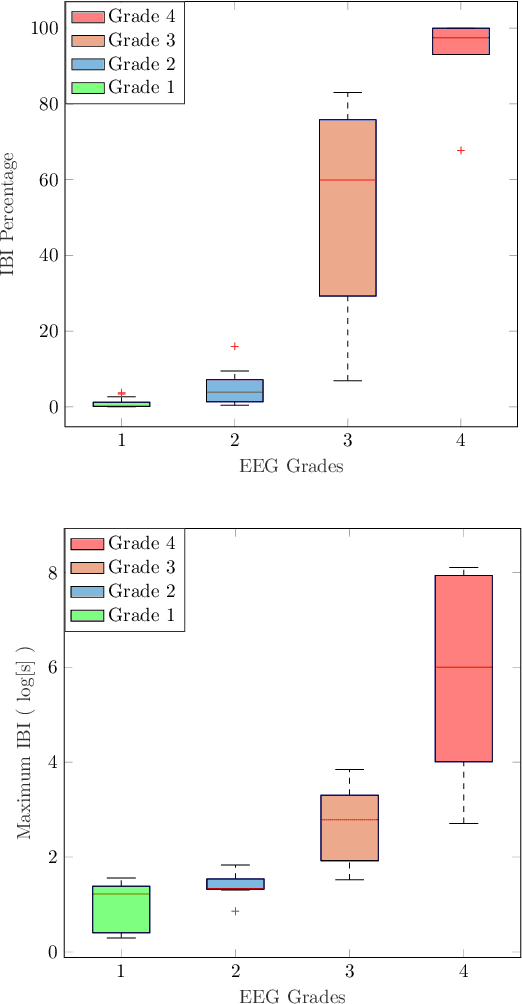
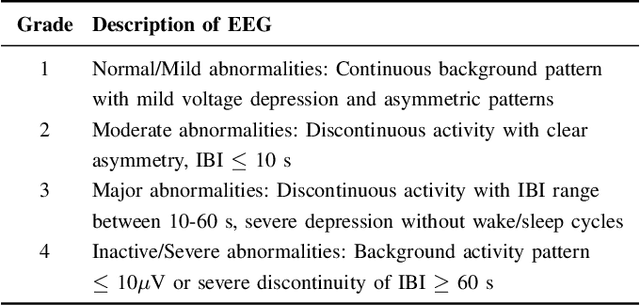
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) is an important clinical tool for grading injury caused by lack of oxygen or blood to the brain during birth. Characteristics of low-voltage waveforms, known as inter-bursts, are related to different grades of injury. This study assesses the suitability of an existing inter-burst detection method, developed from preterm infants born <30 weeks of gestational age, to detect inter-bursts in term infants. Different features from the temporal organisation of the inter-bursts are combined using a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) machine learning algorithm to classify four grades of injury in the EEG. We find that the best performing feature, percentage of inter-bursts, has an accuracy of 59.3%. Combining this with the maximum duration of inter-bursts in the MLP produces a testing accuracy of 77.8%, with similar performance to existing multi-feature methods. These results validate the use of the preterm detection method in term EEG and show how simple measures of the inter-burst interval can be used to classify different grades of injury.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge