Johannes A. Langendijk
SynthRAD2025 Grand Challenge dataset: generating synthetic CTs for radiotherapy
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Medical imaging is essential in modern radiotherapy, supporting diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring. Synthetic imaging, particularly synthetic computed tomography (sCT), is gaining traction in radiotherapy. The SynthRAD2025 dataset and Grand Challenge promote advancements in sCT generation by providing a benchmarking platform for algorithms using cone-beam CT (CBCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The dataset includes 2362 cases: 890 MRI-CT and 1472 CBCT-CT pairs from head-and-neck, thoracic, and abdominal cancer patients treated at five European university medical centers (UMC Groningen, UMC Utrecht, Radboud UMC, LMU University Hospital Munich, and University Hospital of Cologne). Data were acquired with diverse scanners and protocols. Pre-processing, including rigid and deformable image registration, ensures high-quality, modality-aligned images. Extensive quality assurance validates image consistency and usability. All imaging data is provided in MetaImage (.mha) format, ensuring compatibility with medical image processing tools. Metadata, including acquisition parameters and registration details, is available in structured CSV files. To maintain dataset integrity, SynthRAD2025 is divided into training (65%), validation (10%), and test (25%) sets. The dataset is accessible at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14918089 under the SynthRAD2025 collection. This dataset supports benchmarking and the development of synthetic imaging techniques for radiotherapy applications. Use cases include sCT generation for MRI-only and MR-guided photon/proton therapy, CBCT-based dose calculations, and adaptive radiotherapy workflows. By integrating diverse acquisition settings, SynthRAD2025 fosters robust, generalizable image synthesis algorithms, advancing personalized cancer care and adaptive radiotherapy.
Slice-by-slice deep learning aided oropharyngeal cancer segmentation with adaptive thresholding for spatial uncertainty on FDG PET and CT images
Jul 04, 2022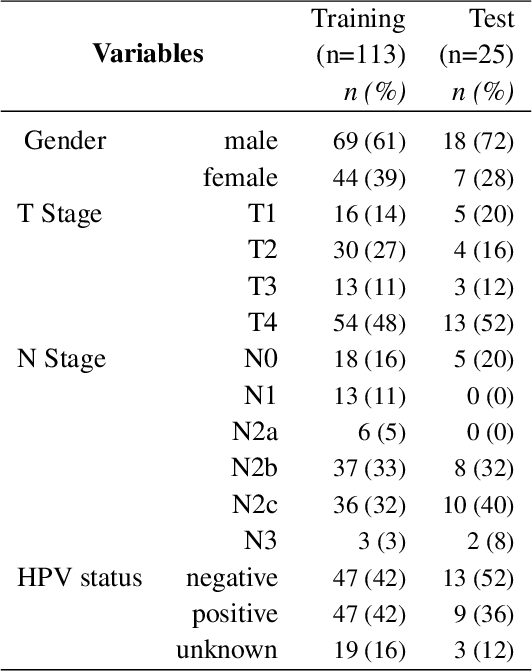
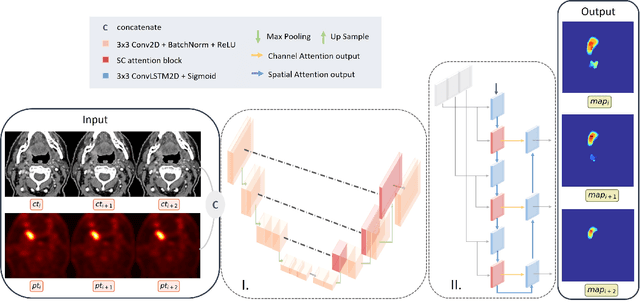
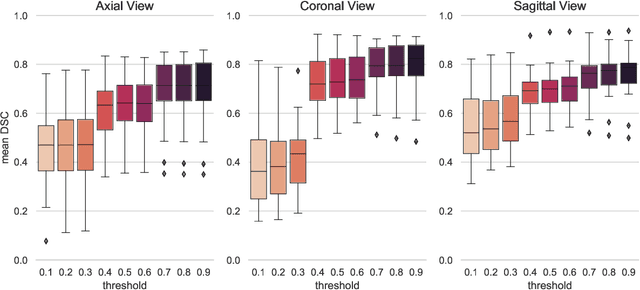
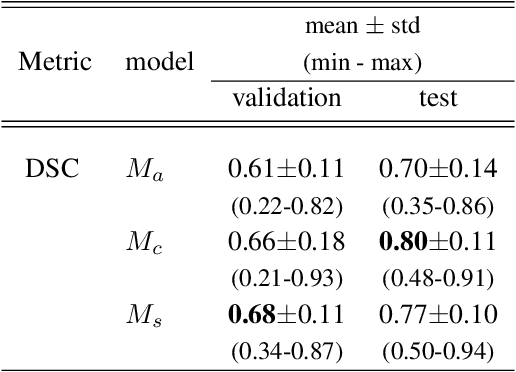
Abstract:Tumor segmentation is a fundamental step for radiotherapy treatment planning. To define an accurate segmentation of the primary tumor (GTVp) of oropharyngeal cancer patients (OPC), simultaneous assessment of different image modalities is needed, and each image volume is explored slice-by-slice from different orientations. Moreover, the manual fixed boundary of segmentation neglects the spatial uncertainty known to occur in tumor delineation. This study proposes a novel automatic deep learning (DL) model to assist radiation oncologists in a slice-by-slice adaptive GTVp segmentation on registered FDG PET/CT images. We included 138 OPC patients treated with (chemo)radiation in our institute. Our DL framework exploits both inter and intra-slice context. Sequences of 3 consecutive 2D slices of concatenated FDG PET/CT images and GTVp contours were used as input. A 3-fold cross validation was performed three times, training on sequences extracted from the Axial (A), Sagittal (S), and Coronal (C) plane of 113 patients. Since consecutive sequences in a volume contain overlapping slices, each slice resulted in three outcome predictions that were averaged. In the A, S, and C planes, the output shows areas with different probabilities of predicting the tumor. The performance of the models was assessed on 25 patients at different probability thresholds using the mean Dice Score Coefficient (DSC). Predictions were the closest to the ground truth at a probability threshold of 0.9 (DSC of 0.70 in the A, 0.77 in the S, and 0.80 in the C plane). The promising results of the proposed DL model show that the probability maps on registered FDG PET/CT images could guide radiation oncologists in a slice-by-slice adaptive GTVp segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge