Joao Paulo Papa
LibOPT: An Open-Source Platform for Fast Prototyping Soft Optimization Techniques
Apr 18, 2017Abstract:Optimization techniques play an important role in several scientific and real-world applications, thus becoming of great interest for the community. As a consequence, a number of open-source libraries are available in the literature, which ends up fostering the research and development of new techniques and applications. In this work, we present a new library for the implementation and fast prototyping of nature-inspired techniques called LibOPT. Currently, the library implements 15 techniques and 112 benchmarking functions, as well as it also supports 11 hypercomplex-based optimization approaches, which makes it one of the first of its kind. We showed how one can easily use and also implement new techniques in LibOPT under the C paradigm. Examples are provided with samples of source-code using benchmarking functions.
Temperature-Based Deep Boltzmann Machines
Sep 04, 2016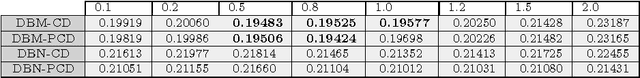
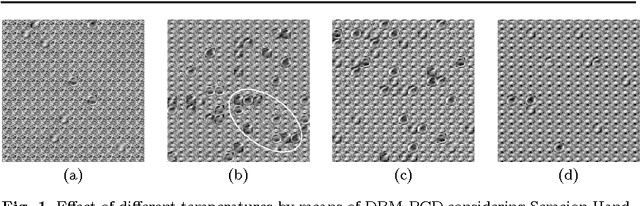
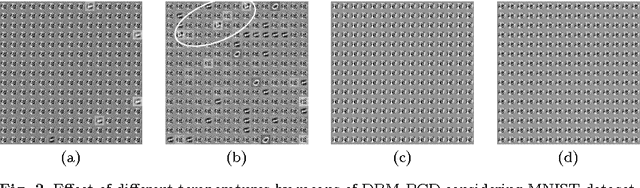
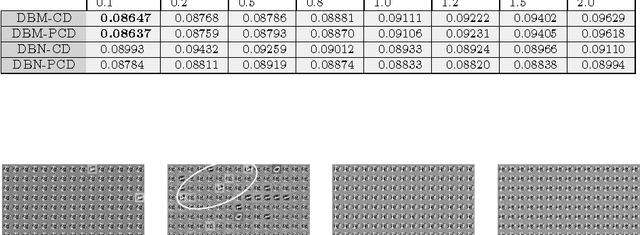
Abstract:Deep learning techniques have been paramount in the last years, mainly due to their outstanding results in a number of applications, that range from speech recognition to face-based user identification. Despite other techniques employed for such purposes, Deep Boltzmann Machines are among the most used ones, which are composed of layers of Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) stacked on top of each other. In this work, we evaluate the concept of temperature in DBMs, which play a key role in Boltzmann-related distributions, but it has never been considered in this context up to date. Therefore, the main contribution of this paper is to take into account this information and to evaluate its influence in DBMs considering the task of binary image reconstruction. We expect this work can foster future research considering the usage of different temperatures during learning in DBMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge