João Antônio Chagas Nunes
AM-MobileNet1D: A Portable Model for Speaker Recognition
Mar 31, 2020



Abstract:Speaker Recognition and Speaker Identification are challenging tasks with essential applications such as automation, authentication, and security. Deep learning approaches like SincNet and AM-SincNet presented great results on these tasks. The promising performance took these models to real-world applications that becoming fundamentally end-user driven and mostly mobile. The mobile computation requires applications with reduced storage size, non-processing and memory intensive and efficient energy-consuming. The deep learning approaches, in contrast, usually are energy expensive, demanding storage, processing power, and memory. To address this demand, we propose a portable model called Additive Margin MobileNet1D (AM-MobileNet1D) to Speaker Identification on mobile devices. We evaluated the proposed approach on TIMIT and MIT datasets obtaining equivalent or better performances concerning the baseline methods. Additionally, the proposed model takes only 11.6 megabytes on disk storage against 91.2 from SincNet and AM-SincNet architectures, making the model seven times faster, with eight times fewer parameters.
Additive Margin SincNet for Speaker Recognition
Jan 28, 2019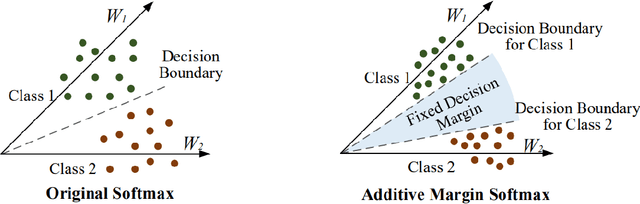
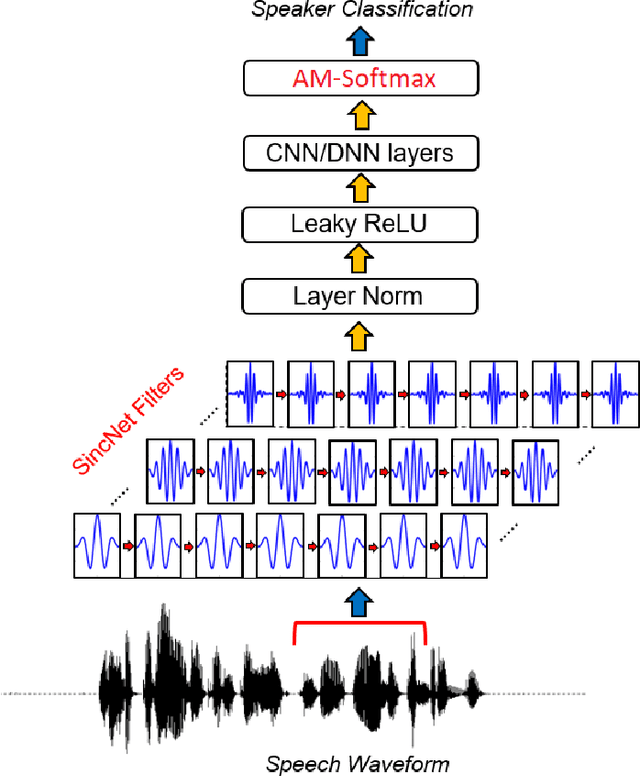
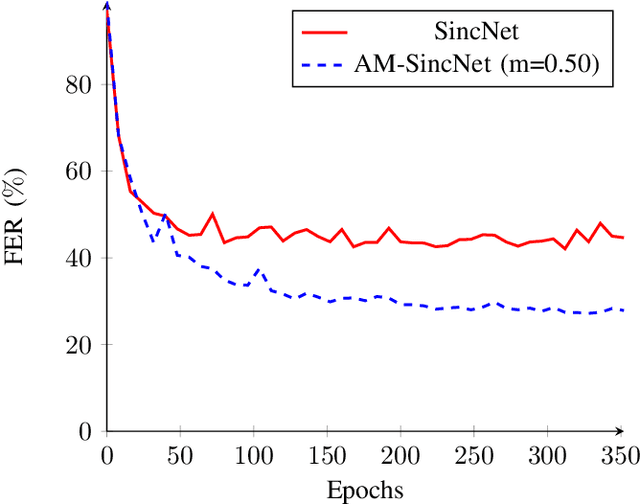
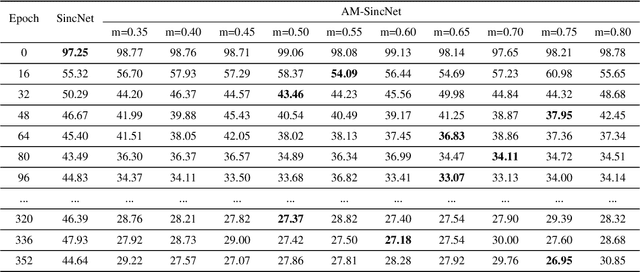
Abstract:Speaker Recognition is a challenging task with essential applications such as authentication, automation, and security. The SincNet is a new deep learning based model which has produced promising results to tackle the mentioned task. To train deep learning systems, the loss function is essential to the network performance. The Softmax loss function is a widely used function in deep learning methods, but it is not the best choice for all kind of problems. For distance-based problems, one new Softmax based loss function called Additive Margin Softmax (AM-Softmax) is proving to be a better choice than the traditional Softmax. The AM-Softmax introduces a margin of separation between the classes that forces the samples from the same class to be closer to each other and also maximizes the distance between classes. In this paper, we propose a new approach for speaker recognition systems called AM-SincNet, which is based on the SincNet but uses an improved AM-Softmax layer. The proposed method is evaluated in the TIMIT dataset and obtained an improvement of approximately 40% in the Frame Error Rate compared to SincNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge