Jingshan Chen
Model Predictive Path-Following Control for a Quadrotor
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Automating drone-assisted processes is a complex task. Many solutions rely on trajectory generation and tracking, whereas in contrast, path-following control is a particularly promising approach, offering an intuitive and natural approach to automate tasks for drones and other vehicles. While different solutions to the path-following problem have been proposed, most of them lack the capability to explicitly handle state and input constraints, are formulated in a conservative two-stage approach, or are only applicable to linear systems. To address these challenges, the paper is built upon a Model Predictive Control-based path-following framework and extends its application to the Crazyflie quadrotor, which is investigated in hardware experiments. A cascaded control structure including an underlying attitude controller is included in the Model Predictive Path-Following Control formulation to meet the challenging real-time demands of quadrotor control. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through real-world experiments, representing, to the best of the authors' knowledge, a novel application of this MPC-based path-following approach to the quadrotor. Additionally, as an extension to the original method, to allow for deviations of the path in cases where the precise following of the path might be overly restrictive, a corridor path-following approach is presented.
An Online Optimization-Based Trajectory Planning Approach for Cooperative Landing Tasks
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a real-time trajectory planning scheme for a heterogeneous multi-robot system (consisting of a quadrotor and a ground mobile robot) for a cooperative landing task, where the landing position, landing time, and coordination between the robots are determined autonomously under the consideration of feasibility and user specifications. The proposed framework leverages the potential of the complementarity constraint as a decision-maker and an indicator for diverse cooperative tasks and extends it to the collaborative landing scenario. In a potential application of the proposed methodology, a ground mobile robot may serve as a mobile charging station and coordinates in real-time with a quadrotor to be charged, facilitating a safe and efficient rendezvous and landing. We verified the generated trajectories in simulation and real-world applications, demonstrating the real-time capabilities of the proposed landing planning framework.
Time-Optimal Handover Trajectory Planning for Aerial Manipulators based on Discrete Mechanics and Complementarity Constraints
Sep 01, 2022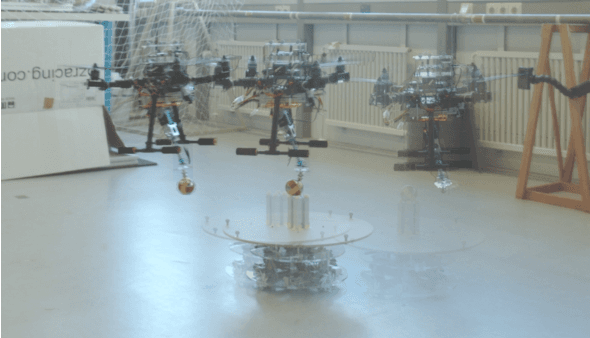
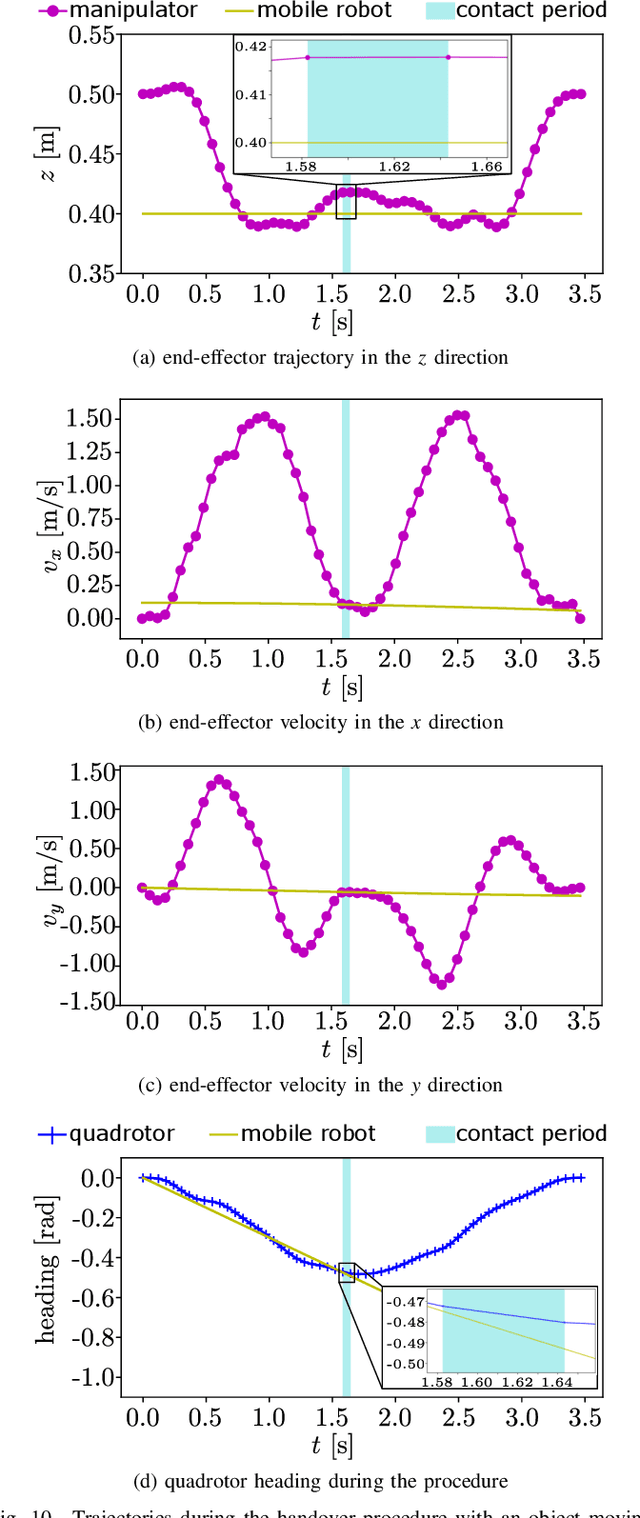
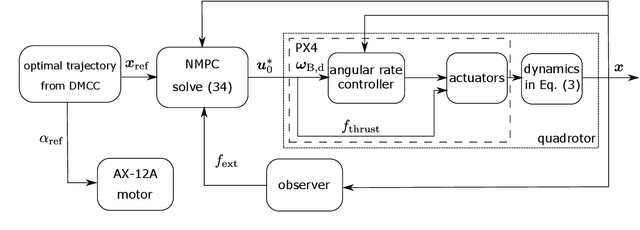
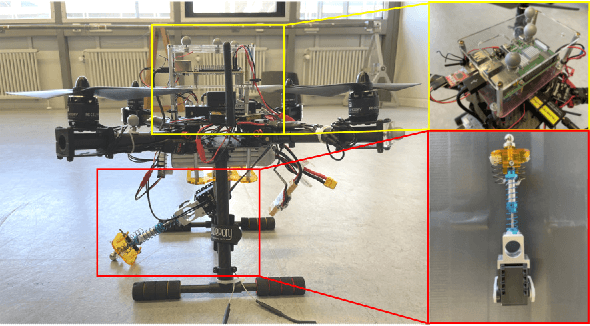
Abstract:Planning a time-optimal trajectory for aerial robots is critical in many drone applications, such as rescue missions and package delivery, which have been widely researched in recent years. However, it still involves several challenges, particularly when it comes to incorporating special task requirements into the planning as well as the aerial robot's dynamics. In this work, we study a case where an aerial manipulator shall hand over a parcel from a moving mobile robot in a time-optimal manner. Rather than setting up the approach trajectory manually, which makes it difficult to determine the optimal total travel time to accomplish the desired task within dynamic limits, we propose an optimization framework, which combines discrete mechanics and complementarity constraints (DMCC) together. In the proposed framework, the system dynamics is constrained with the discrete variational Lagrangian mechanics that provides reliable estimation results also according to our experiments. The handover opportunities are automatically determined and arranged based on the desired complementarity constraints. Finally, the performance of the proposed framework is verified with numerical simulations and hardware experiments with our self-designed aerial manipulators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge