Ji-Hun Oh
Finer Disentanglement of Aleatoric Uncertainty Can Accelerate Chemical Histopathology Imaging
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Label-free chemical imaging holds significant promise for improving digital pathology workflows. However, data acquisition speed remains a limiting factor for smooth clinical transition. To address this gap, we propose an adaptive strategy: initially scan the low information (LI) content of the entire tissue quickly, identify regions with high aleatoric uncertainty (AU), and selectively re-image them at better quality to capture higher information (HI) details. The primary challenge lies in distinguishing between high-AU regions that can be mitigated through HI imaging and those that cannot. However, since existing uncertainty frameworks cannot separate such AU subcategories, we propose a fine-grained disentanglement method based on post-hoc latent space analysis to unmix resolvable from irresolvable high-AU regions. We apply our approach to efficiently image infrared spectroscopic data of breast tissues, achieving superior segmentation performance using the acquired HI data compared to a random baseline. This represents the first algorithmic study focused on fine-grained AU disentanglement within dynamic image spaces (LI-to-HI), with novel application to streamline histopathology.
Detecting Hallucinations in Virtual Histology with Neural Precursors
Nov 22, 2024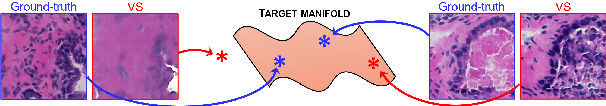
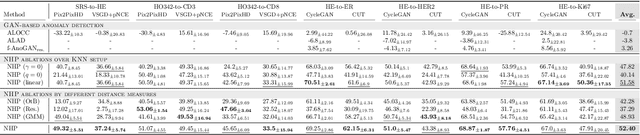
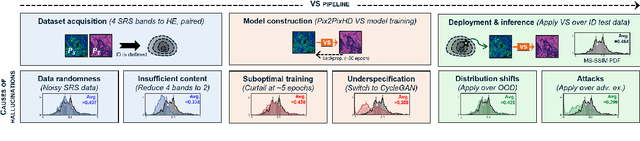
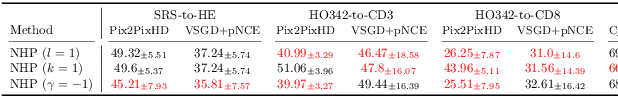
Abstract:Significant biomedical research and clinical care rely on the histopathologic examination of tissue structure using microscopy of stained tissue. Virtual staining (VS) offers a promising alternative with the potential to reduce cost and eliminate the use of toxic reagents. However, the critical challenge of hallucinations limits confidence in its use, necessitating a VS co-pilot to detect these hallucinations. Here, we first formally establish the problem of hallucination detection in VS. Next, we introduce a scalable, post-hoc hallucination detection method that identifies a Neural Hallucination Precursor (NHP) from VS model embeddings for test-time detection. We report extensive validation across diverse and challenging VS settings to demonstrate NHP's effectiveness and robustness. Furthermore, we show that VS models with fewer hallucinations do not necessarily disclose them better, risking a false sense of security when reporting just the former metric. This highlights the need for a reassessment of current VS evaluation practices.
Are We Ready for Out-of-Distribution Detection in Digital Pathology?
Jul 18, 2024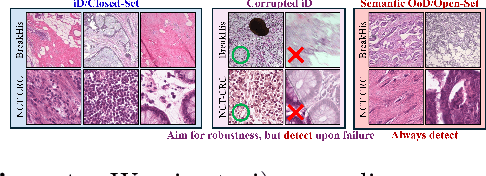

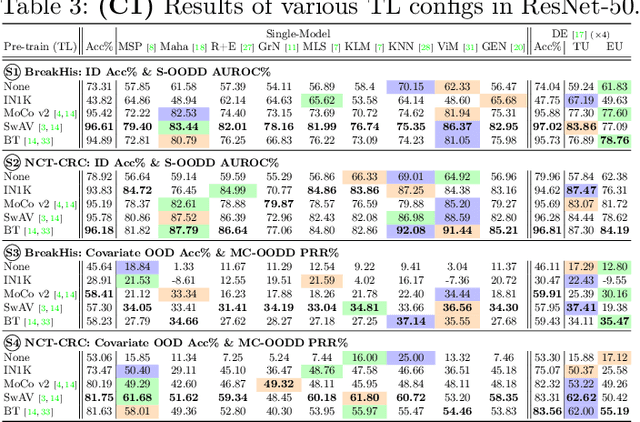
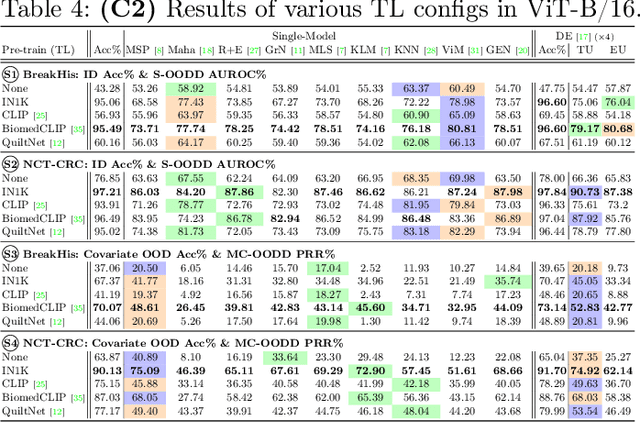
Abstract:The detection of semantic and covariate out-of-distribution (OOD) examples is a critical yet overlooked challenge in digital pathology (DP). Recently, substantial insight and methods on OOD detection were presented by the ML community, but how do they fare in DP applications? To this end, we establish a benchmark study, our highlights being: 1) the adoption of proper evaluation protocols, 2) the comparison of diverse detectors in both a single and multi-model setting, and 3) the exploration into advanced ML settings like transfer learning (ImageNet vs. DP pre-training) and choice of architecture (CNNs vs. transformers). Through our comprehensive experiments, we contribute new insights and guidelines, paving the way for future research and discussion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge