Jhony Giraldo
Automatic segmentation of lizard spots using an active contour model
Mar 02, 2016
Abstract:Animal biometrics is a challenging task. In the literature, many algorithms have been used, e.g. penguin chest recognition, elephant ears recognition and leopard stripes pattern recognition, but to use technology to a large extent in this area of research, still a lot of work has to be done. One important target in animal biometrics is to automate the segmentation process, so in this paper we propose a segmentation algorithm for extracting the spots of Diploglossus millepunctatus, an endangered lizard species. The automatic segmentation is achieved with a combination of preprocessing, active contours and morphology. The parameters of each stage of the segmentation algorithm are found using an optimization procedure, which is guided by the ground truth. The results show that automatic segmentation of spots is possible. A 78.37 % of correct segmentation in average is reached.
A Markov Random Field and Active Contour Image Segmentation Model for Animal Spots Patterns
Oct 26, 2015

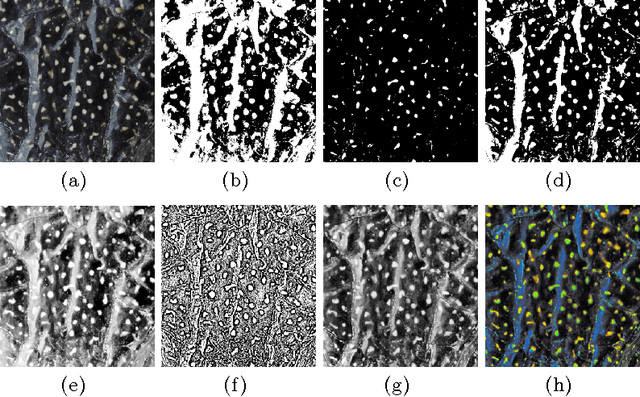
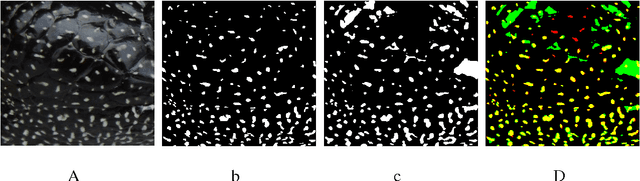
Abstract:Non-intrusive biometrics of animals using images allows to analyze phenotypic populations and individuals with patterns like stripes and spots without affecting the studied subjects. However, non-intrusive biometrics demand a well trained subject or the development of computer vision algorithms that ease the identification task. In this work, an analysis of classic segmentation approaches that require a supervised tuning of their parameters such as threshold, adaptive threshold, histogram equalization, and saturation correction is presented. In contrast, a general unsupervised algorithm using Markov Random Fields (MRF) for segmentation of spots patterns is proposed. Active contours are used to boost results using MRF output as seeds. As study subject the Diploglossus millepunctatus lizard is used. The proposed method achieved a maximum efficiency of $91.11\%$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge