A Markov Random Field and Active Contour Image Segmentation Model for Animal Spots Patterns
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2015

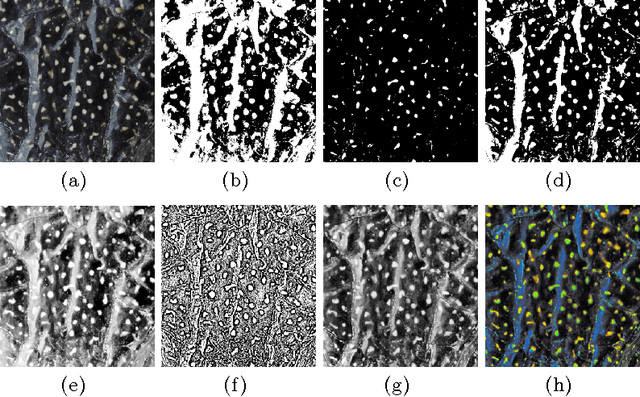
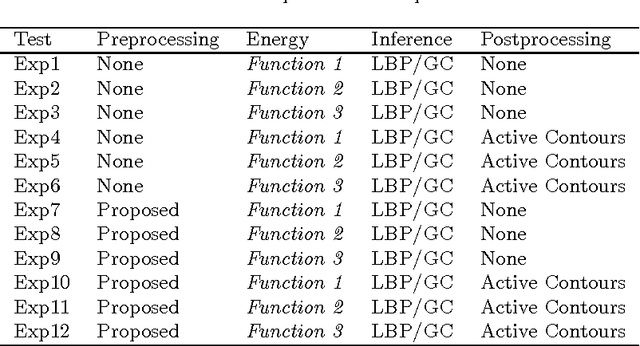
Non-intrusive biometrics of animals using images allows to analyze phenotypic populations and individuals with patterns like stripes and spots without affecting the studied subjects. However, non-intrusive biometrics demand a well trained subject or the development of computer vision algorithms that ease the identification task. In this work, an analysis of classic segmentation approaches that require a supervised tuning of their parameters such as threshold, adaptive threshold, histogram equalization, and saturation correction is presented. In contrast, a general unsupervised algorithm using Markov Random Fields (MRF) for segmentation of spots patterns is proposed. Active contours are used to boost results using MRF output as seeds. As study subject the Diploglossus millepunctatus lizard is used. The proposed method achieved a maximum efficiency of $91.11\%$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge