Jayden L. Macklin-Cordes
Challenges of sampling and how phylogenetic comparative methods help: With a case study of the Pama-Nyungan laminal contrast
Jan 01, 2022



Abstract:Phylogenetic comparative methods are new in our field and are shrouded, for most linguists, in at least a little mystery. Yet the path that led to their discovery in comparative biology is so similar to the methodological history of balanced sampling, that it is only an accident of history that they were not discovered by a typologist. Here we clarify the essential logic behind phylogenetic comparative methods and their fundamental relatedness to a deep intellectual tradition focussed on sampling. Then we introduce concepts, methods and tools which will enable typologists to use these methods in everyday typological research. The key commonality of phylogenetic comparative methods and balanced sampling is that they attempt to deal with statistical non-independence due to genealogy. Whereas sampling can never achieve independence and requires most comparative data to be discarded, phylogenetic comparative methods achieve independence while retaining and using all data. We discuss the essential notions of phylogenetic signal; uncertainty about trees; typological averages and proportions that are sensitive to genealogy; comparison across language families; and the effects of areality. Extensive supplementary materials illustrate computational tools for practical analysis and we illustrate the methods discussed with a typological case study of the laminal contrast in Pama-Nyungan.
Re-evaluating phoneme frequencies
Jun 09, 2020



Abstract:Causal processes can give rise to distinctive distributions in the linguistic variables that they affect. Consequently, a secure understanding of a variable's distribution can hold a key to understanding the forces that have causally shaped it. A storied distribution in linguistics has been Zipf's law, a kind of power law. In the wake of a major debate in the sciences around power-law hypotheses and the unreliability of earlier methods of evaluating them, here we re-evaluate the distributions claimed to characterize phoneme frequencies. We infer the fit of power laws and three alternative distributions to 168 Australian languages, using a maximum likelihood framework. We find evidence supporting earlier results, but also qualifying and nuancing them. Most notably, phonemic inventories appear to have a Zipfian-like frequency structure among their most-frequent members (though perhaps also a lognormal structure) but a geometric (or exponential) structure among the least-frequent. We highlight implications for causal accounts.
Phylogenetic signal in phonotactics
Feb 03, 2020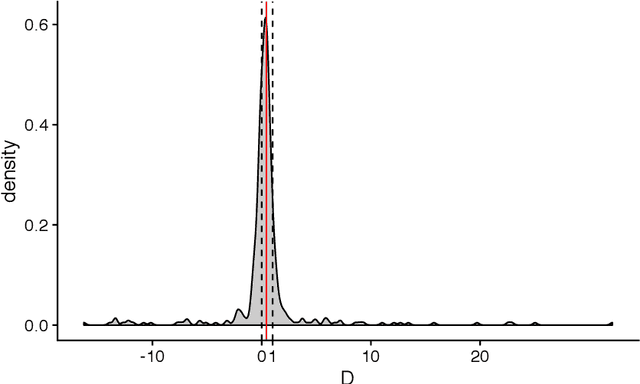
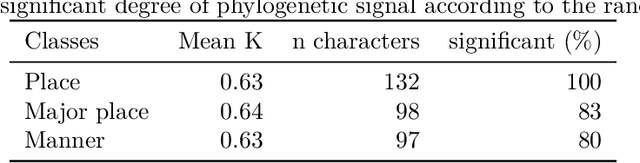
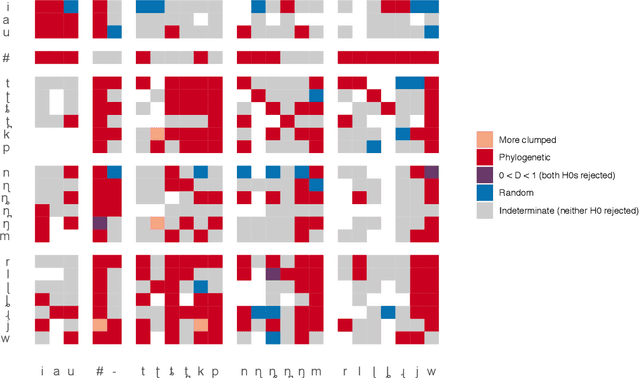
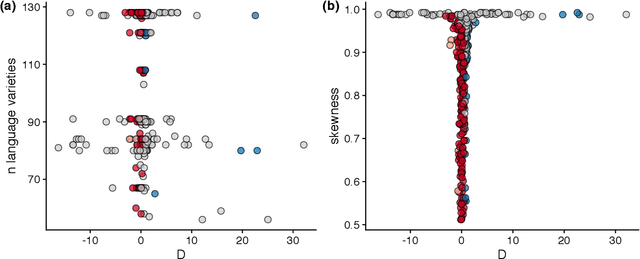
Abstract:Phylogenetic methods have broad potential in linguistics beyond tree inference. Here, we show how a phylogenetic approach opens the possibility of gaining historical insights from entirely new kinds of linguistic data--in this instance, statistical phonotactics. We extract phonotactic data from 128 Pama-Nyungan vocabularies and apply tests for phylogenetic signal, quantifying the degree to which the data reflect phylogenetic history. We test three datasets: (1) binary variables recording the presence or absence of biphones (two-segment sequences) in a lexicon (2) frequencies of transitions between segments, and (3) frequencies of transitions between natural sound classes. Australian languages have been characterised as having a high degree of phonotactic homogeneity. Nevertheless, we detect phylogenetic signal in all datasets. Phylogenetic signal is higher in finer-grained frequency data than in binary data, and highest in natural-class-based data. These results demonstrate the viability of employing a new source of readily extractable data in historical and comparative linguistics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge