Jawad Haidar
MaskUno: Switch-Split Block For Enhancing Instance Segmentation
Jul 31, 2024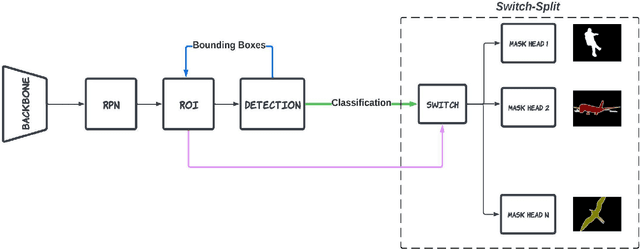



Abstract:Instance segmentation is an advanced form of image segmentation which, beyond traditional segmentation, requires identifying individual instances of repeating objects in a scene. Mask R-CNN is the most common architecture for instance segmentation, and improvements to this architecture include steps such as benefiting from bounding box refinements, adding semantics, or backbone enhancements. In all the proposed variations to date, the problem of competing kernels (each class aims to maximize its own accuracy) persists when models try to synchronously learn numerous classes. In this paper, we propose mitigating this problem by replacing mask prediction with a Switch-Split block that processes refined ROIs, classifies them, and assigns them to specialized mask predictors. We name the method MaskUno and test it on various models from the literature, which are then trained on multiple classes using the benchmark COCO dataset. An increase in the mean Average Precision (mAP) of 2.03% was observed for the high-performing DetectoRS when trained on 80 classes. MaskUno proved to enhance the mAP of instance segmentation models regardless of the number and typ
OSPC: Online Sequential Photometric Calibration
May 28, 2023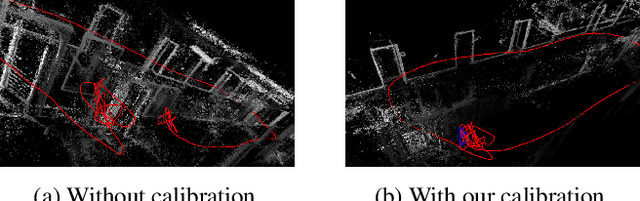
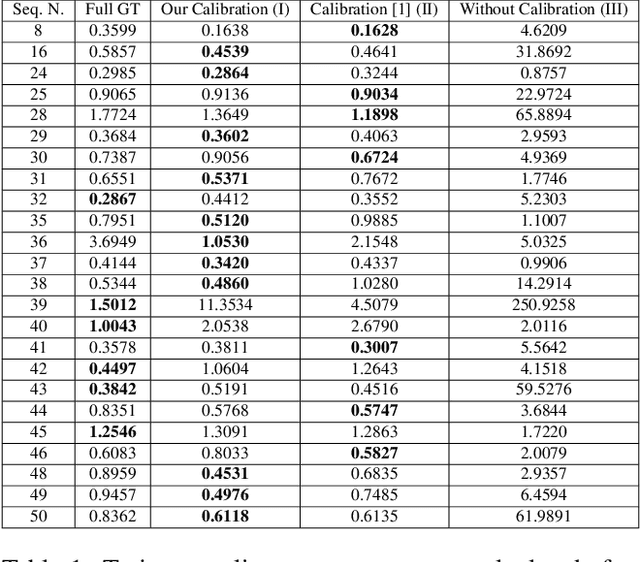
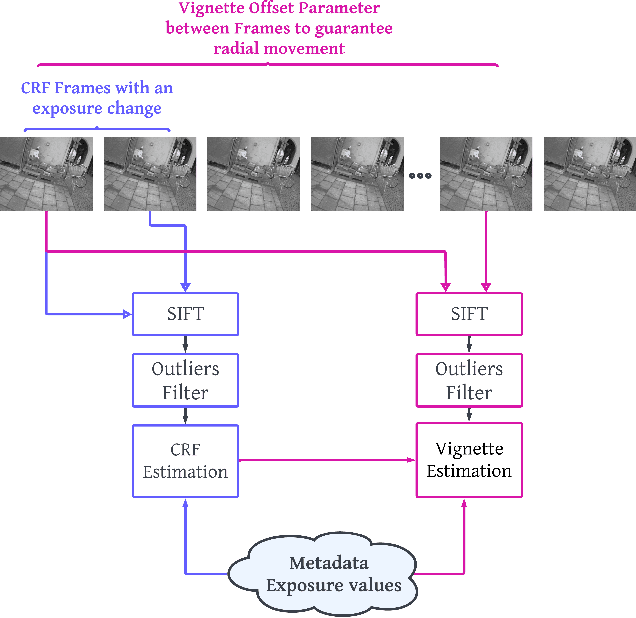
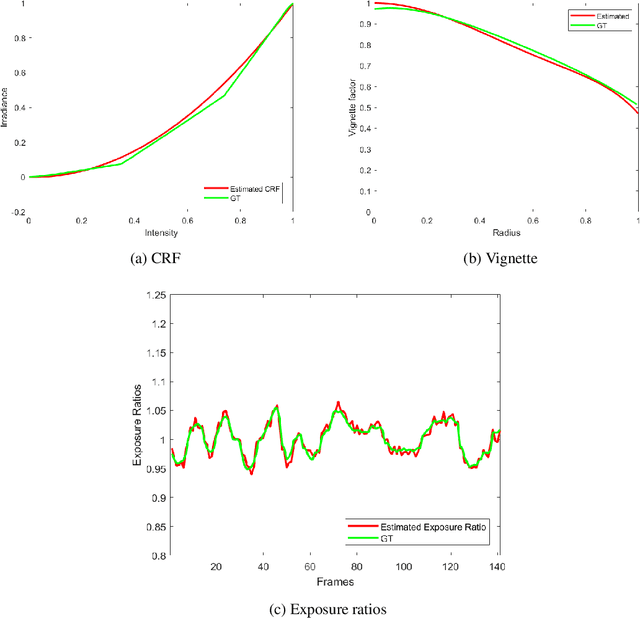
Abstract:Photometric calibration is essential to many computer vision applications. One of its key benefits is enhancing the performance of Visual SLAM, especially when it depends on a direct method for tracking, such as the standard KLT algorithm. Another advantage could be in retrieving the sensor irradiance values from measured intensities, as a pre-processing step for some vision algorithms, such as shape-from-shading. Current photometric calibration systems rely on a joint optimization problem and encounter an ambiguity in the estimates, which can only be resolved using ground truth information. We propose a novel method that solves for photometric parameters using a sequential estimation approach. Our proposed method achieves high accuracy in estimating all parameters; furthermore, the formulations are linear and convex, which makes the solution fast and suitable for online applications. Experiments on a Visual Odometry system validate the proposed method and demonstrate its advantages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge