Janis Keck
VIBE: Video-Input Brain Encoder for fMRI Response Modeling
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:We present VIBE, a two-stage Transformer that fuses multi-modal video, audio, and text features to predict fMRI activity. Representations from open-source models (Qwen2.5, BEATs, Whisper, SlowFast, V-JEPA) are merged by a modality-fusion transformer and temporally decoded by a prediction transformer with rotary embeddings. Trained on 65 hours of movie data from the CNeuroMod dataset and ensembled across 20 seeds, VIBE attains mean parcel-wise Pearson correlations of 32.25 on in-distribution Friends S07 and 21.25 on six out-of-distribution films. An earlier iteration of the same architecture obtained 0.3198 and 0.2096, respectively, winning Phase-1 and placing second overall in the Algonauts 2025 Challenge.
Merging Hazy Sets with m-Schemes: A Geometric Approach to Data Visualization
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Many machine learning algorithms try to visualize high dimensional metric data in 2D in such a way that the essential geometric and topological features of the data are highlighted. In this paper, we introduce a framework for aggregating dissimilarity functions that arise from locally adjusting a metric through density-aware normalization, as employed in the IsUMap method. We formalize these approaches as m-schemes, a class of methods closely related to t-norms and t-conorms in probabilistic metrics, as well as to composition laws in information theory. These m-schemes provide a flexible and theoretically grounded approach to refining distance-based embeddings.
IsUMap: Manifold Learning and Data Visualization leveraging Vietoris-Rips filtrations
Jul 25, 2024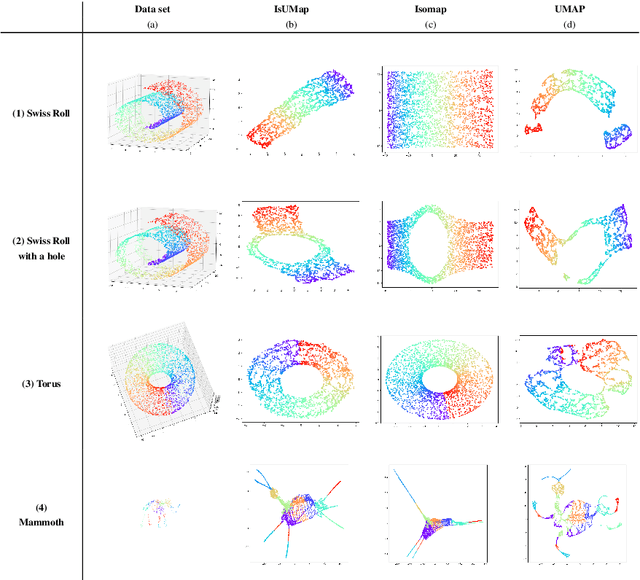
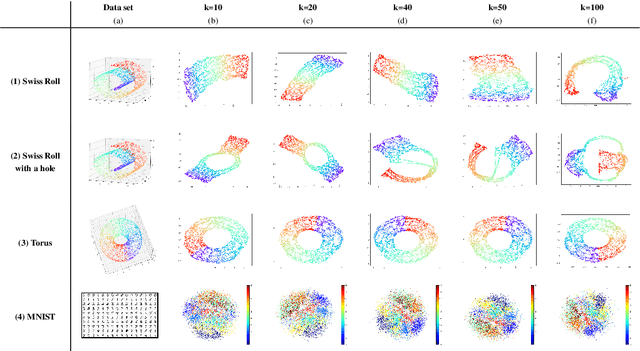
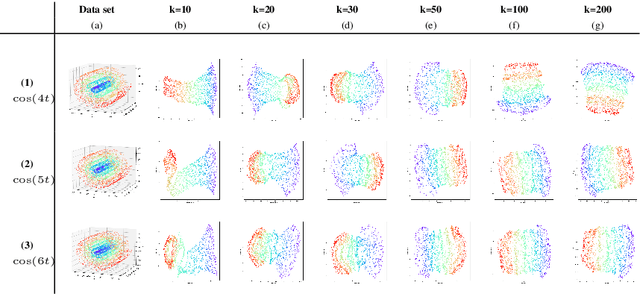
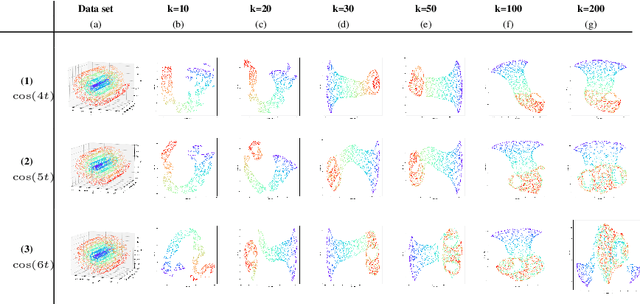
Abstract:This work introduces IsUMap, a novel manifold learning technique that enhances data representation by integrating aspects of UMAP and Isomap with Vietoris-Rips filtrations. We present a systematic and detailed construction of a metric representation for locally distorted metric spaces that captures complex data structures more accurately than the previous schemes. Our approach addresses limitations in existing methods by accommodating non-uniform data distributions and intricate local geometries. We validate its performance through extensive experiments on examples of various geometric objects and benchmark real-world datasets, demonstrating significant improvements in representation quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge