Janghyeok Yoon
Dynamic technology impact analysis: A multi-task learning approach to patent citation prediction
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning (ML) models are valuable tools for analyzing the impact of technology using patent citation information. However, existing ML-based methods often struggle to account for the dynamic nature of the technology impact over time and the interdependencies of these impacts across different periods. This study proposes a multi-task learning (MTL) approach to enhance the prediction of technology impact across various time frames by leveraging knowledge sharing and simultaneously monitoring the evolution of technology impact. First, we quantify the technology impacts and identify patterns through citation analysis over distinct time periods. Next, we develop MTL models to predict citation counts using multiple patent indicators over time. Finally, we examine the changes in key input indicators and their patterns over different periods using the SHapley Additive exPlanation method. We also offer guidelines for validating and interpreting the results by employing statistical methods and natural language processing techniques. A case study on battery technologies demonstrates that our approach not only deepens the understanding of technology impact, but also improves prediction accuracy, yielding valuable insights for both academia and industry.
Early screening of potential breakthrough technologies with enhanced interpretability: A patent-specific hierarchical attention network model
Jul 24, 2024



Abstract:Despite the usefulness of machine learning approaches for the early screening of potential breakthrough technologies, their practicality is often hindered by opaque models. To address this, we propose an interpretable machine learning approach to predicting future citation counts from patent texts using a patent-specific hierarchical attention network (PatentHAN) model. Central to this approach are (1) a patent-specific pre-trained language model, capturing the meanings of technical words in patent claims, (2) a hierarchical network structure, enabling detailed analysis at the claim level, and (3) a claim-wise self-attention mechanism, revealing pivotal claims during the screening process. A case study of 35,376 pharmaceutical patents demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach in early screening of potential breakthrough technologies while ensuring interpretability. Furthermore, we conduct additional analyses using different language models and claim types to examine the robustness of the approach. It is expected that the proposed approach will enhance expert-machine collaboration in identifying breakthrough technologies, providing new insight derived from text mining into technological value.
Design of reliable technology valuation model with calibrated machine learning of patent indicators
Jun 08, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning (ML) has revolutionized the digital transformation of technology valuation by predicting the value of patents with high accuracy. However, the lack of validation regarding the reliability of these models hinders experts from fully trusting the confidence of model predictions. To address this issue, we propose an analytical framework for reliable technology valuation using calibrated ML models, which provide robust confidence levels in model predictions. We extract quantitative patent indicators that represent various technology characteristics as input data, using the patent maintenance period as a proxy for technology values. Multiple ML models are developed to capture the nonlinear relationship between patent indicators and technology value. The reliability and accuracy of these models are evaluated, presenting a Pareto-front map where the expected calibration error, Matthews correlation coefficient and F1-scores are compared. After identifying the best-performing model, we apply SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) analysis to pinpoint the most significant input features by confidence bin. Through a case study, we confirmed that the proposed approach offers a practical guideline for developing reliable and accurate ML-based technology valuation models, with significant implications for both academia and industry.
Learning a Patent-Informed Biomedical Knowledge Graph Reveals Technological Potential of Drug Repositioning Candidates
Sep 04, 2023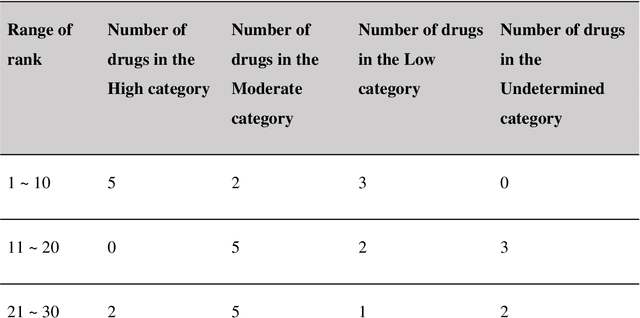
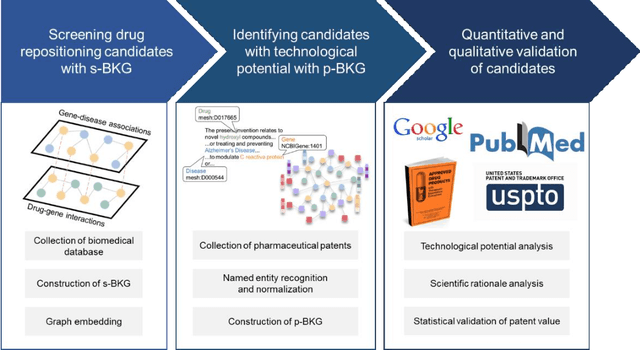
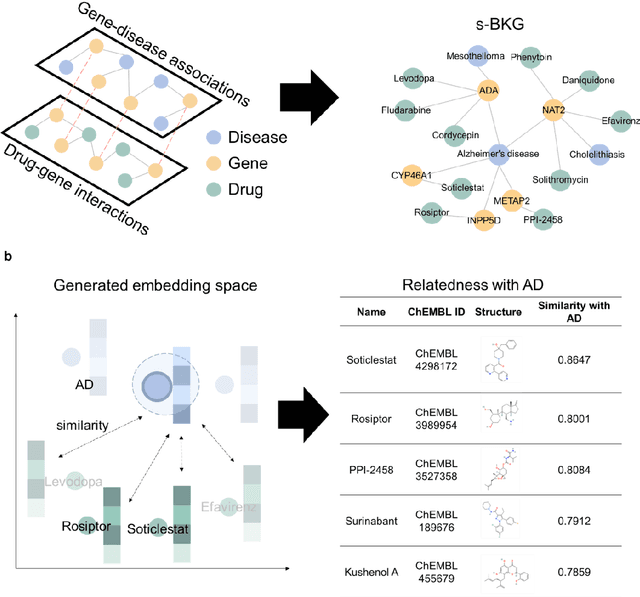
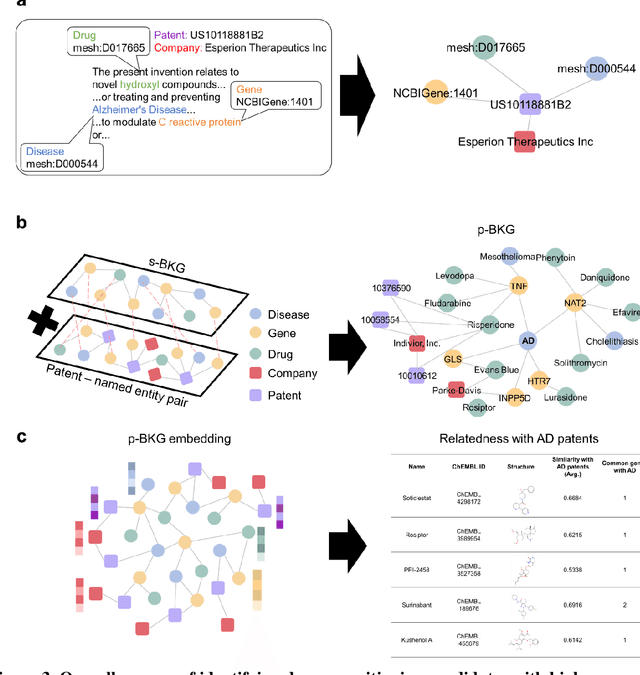
Abstract:Drug repositioning-a promising strategy for discovering new therapeutic uses for existing drugs-has been increasingly explored in the computational science literature using biomedical databases. However, the technological potential of drug repositioning candidates has often been overlooked. This study presents a novel protocol to comprehensively analyse various sources such as pharmaceutical patents and biomedical databases, and identify drug repositioning candidates with both technological potential and scientific evidence. To this end, first, we constructed a scientific biomedical knowledge graph (s-BKG) comprising relationships between drugs, diseases, and genes derived from biomedical databases. Our protocol involves identifying drugs that exhibit limited association with the target disease but are closely located in the s-BKG, as potential drug candidates. We constructed a patent-informed biomedical knowledge graph (p-BKG) by adding pharmaceutical patent information. Finally, we developed a graph embedding protocol to ascertain the structure of the p-BKG, thereby calculating the relevance scores of those candidates with target disease-related patents to evaluate their technological potential. Our case study on Alzheimer's disease demonstrates its efficacy and feasibility, while the quantitative outcomes and systematic methods are expected to bridge the gap between computational discoveries and successful market applications in drug repositioning research.
Time-aware topic identification in social media with pre-trained language models: A case study of electric vehicles
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Recent extensively competitive business environment makes companies to keep their eyes on social media, as there is a growing recognition over customer languages (e.g., needs, interests, and complaints) as source of future opportunities. This research avenue analysing social media data has received much attention in academia, but their utilities are limited as most of methods provide retrospective results. Moreover, the increasing number of customer-generated contents and rapidly varying topics have made the necessity of time-aware topic evolution analyses. Recently, several researchers have showed the applicability of pre-trained semantic language models to social media as an input feature, but leaving limitations in understanding evolving topics. In this study, we propose a time-aware topic identification approach with pre-trained language models. The proposed approach consists of two stages: the dynamics-focused function for tracking time-varying topics with language models and the emergence-scoring function to examine future promising topics. Here we apply the proposed approach to reddit data on electric vehicles, and our findings highlight the feasibility of capturing emerging customer topics from voluminous social media in a time-aware manner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge